Warty Carcinoma
Elsa F. Velazquez, MD
Antonio L. Cubilla, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Condylomatous carcinoma
Etiology/Pathogenesis
HPV-related tumor
Clinical Issues
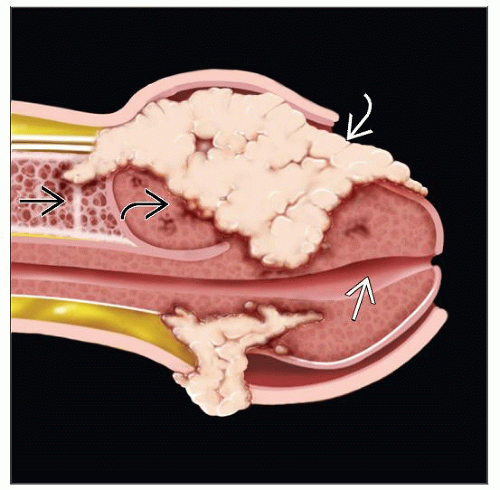
Papillomatous tumor with cobblestone appearance usually affecting glans
Macroscopic Features
Usually large, cauliflower-like tumor
Exo- to endophytic neoplasm
Papillomatous surface
Variable (pushing or infiltrative) deep border
Usually infiltrates corpus spongiosum
Microscopic Pathology
Low-power view shows classical clear and dark pattern
Arborescent papillae
Pleomorphic tumor
Numerous mitoses
Koilocytosis throughout neoplasm
Variable (bulbous or infiltrative) deep borders
Clear cell changes may be prominent
Top Differential Diagnoses
Condyloma acuminatum (including giant condyloma)
Verrucous carcinoma
Papillary carcinoma
Adnexal carcinomas
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
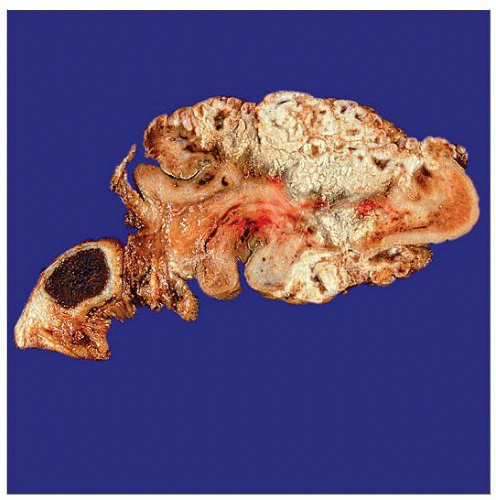 Cut section of a partial penectomy specimen shows a cauliflower, complex, papillomatous neoplasm deeply invading into corpus spongiosum, a warty (condylomatous) carcinoma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Warty carcinoma (WC)
Synonyms
Condylomatous carcinoma
Definitions
Tumor related to human papilloma virus (HPV)
Shares some gross and microscopic characteristics with condyloma
Definitive malignant histology and metastatic potential
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
HPV-related in majority of cases (most cases associated with HPV-16)
Pathogenesis
HPV oncoproteins E6 and E7 appear crucial in process of carcinogenesis
E6 interferes with p53 pathway, causing suppression of p53 normal inhibitory function of cell cycle
E7 targets retinoblastoma protein (pRB) interfering with p16/cyclin-D1/rb pathway
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology