Varices, ascites if portal hypertension present
• Cutaneous, gastrointestinal, neuroophthalmic, musculoskeletal, renal, hematological manifestations also common
Top Differential Diagnoses
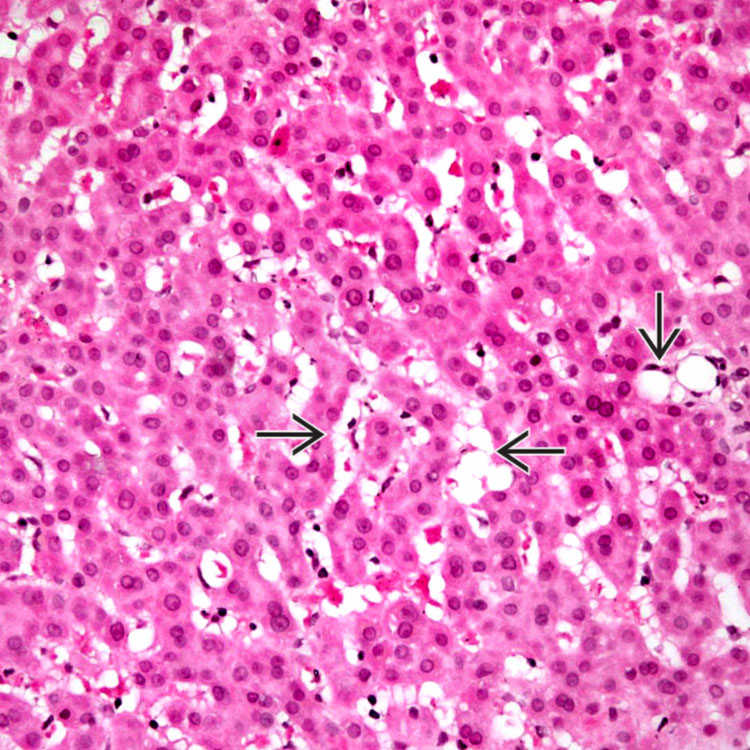
Low-power view of stellate cell hyperplasia in hypervitaminosis A illustrates bubbly, “multivacuolated” hepatic stellate cells in the sinusoids
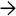 . Note the lack of inflammation or hepatocyte degeneration.
. Note the lack of inflammation or hepatocyte degeneration.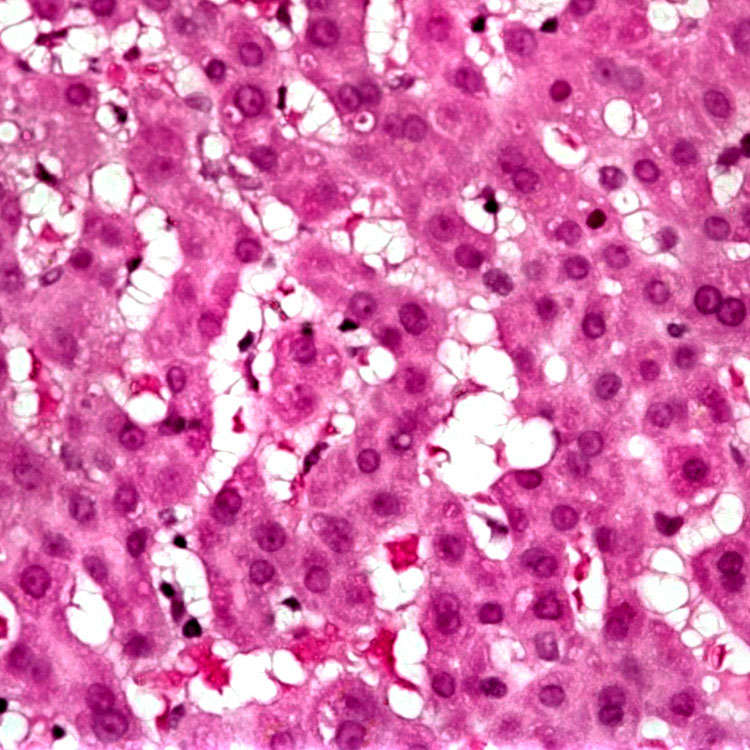
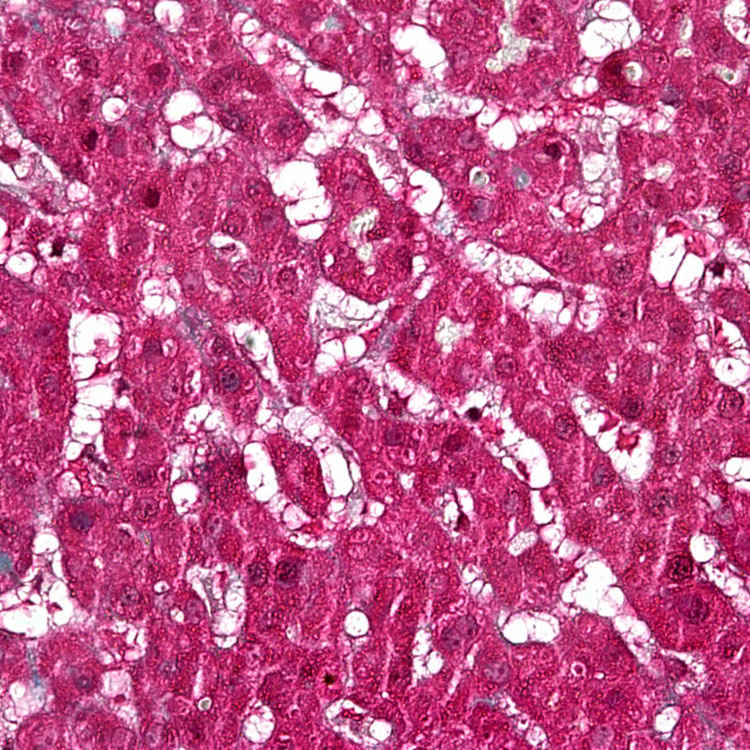
Hyperplastic, hypertrophic stellate cells are seen in the sinusoids of a patient who chronically overingested vitamin A supplements.
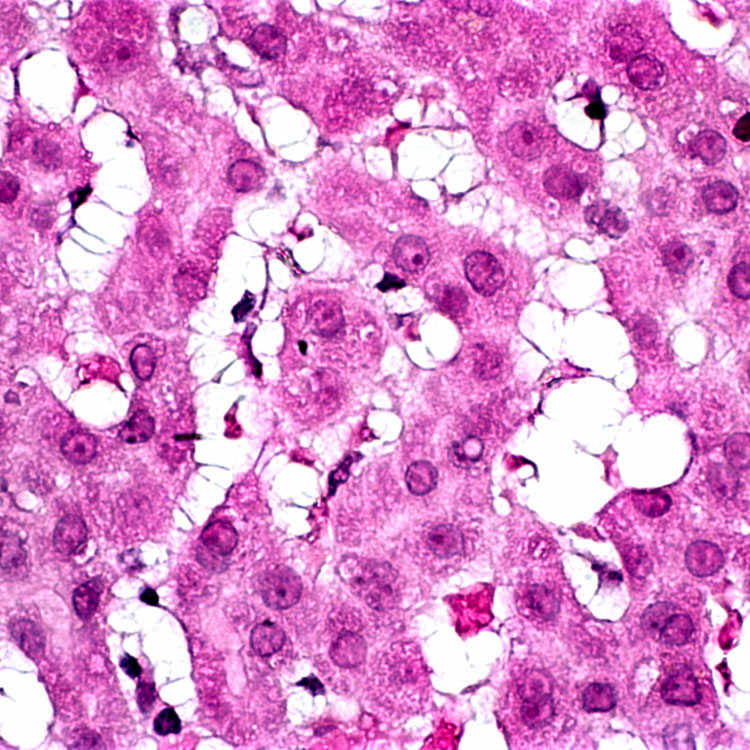
High magnification shows hyperplastic, hypertrophic stellate cells in the sinusoids with swollen, clear cytoplasm and delicate cytoplasmic processes.
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Definitions
• Stellate cells reside in space of Disse




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree