Minority of cases progress to chronic hepatitis and rarely cirrhosis

Jaundice, high AST levels, and preexisting chronic liver disease are adverse prognostic factors
Microscopic
•
Most medications produce inflammation-predominant pattern
•
Most toxins & a few medications like acetaminophen produce necrosis-predominant pattern
•
Concomitant bile duct injury, eosinophils, granulomas, perivenular necrosis, and cholestasis out of proportion to hepatocellular injury suggest DILI, but none of these are specific
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
•
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
2 Chief Mechanisms
•
Intrinsic hepatotoxicity

Predictable, dose-dependent hepatocellular damage
–
Industrial, household, or environmental toxins

Typically shows necrosis with negligible inflammation
•
Idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity

Majority of adverse drug reactions fall in this category

Metabolic and immunological categories
–
Metabolic: Drug is metabolized into toxic metabolite in predisposed individuals
–
Immunological: Drug allergy or hypersensitivity following sensitization to drug

Typically shows inflammation-predominant liver injury
Herbals/Botanicals
•
Important but often overlooked cause of hepatotoxicity
•
Not regulated by Food and Drug Administration and hence not subject to rigorous testing
•
Nearly 20% of American adults have used herbal remedies, and > 5 billion dollars are spent on these annually
•
Heavy metal contaminants in these agents (arsenic, cadmium, lead, mercury) can also lead to liver toxicity
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
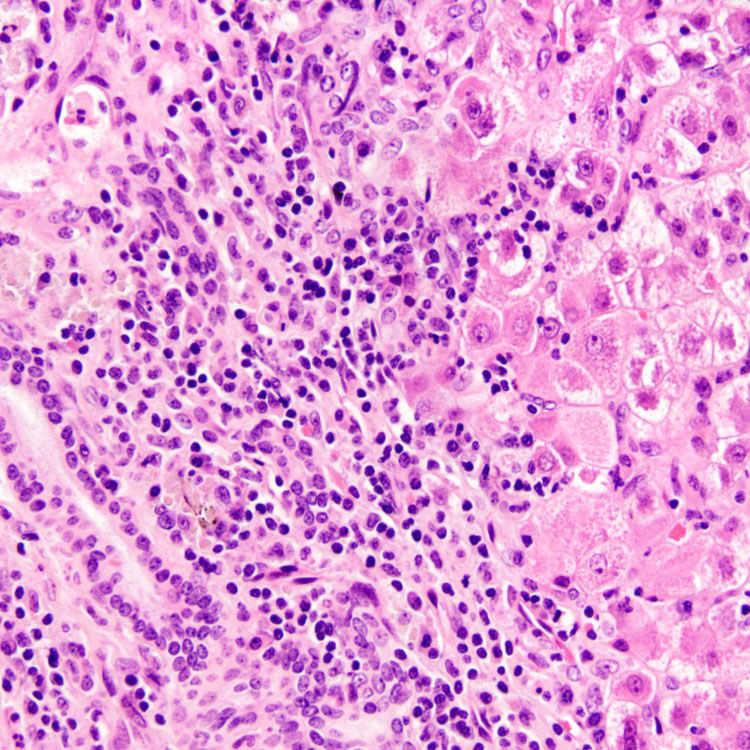
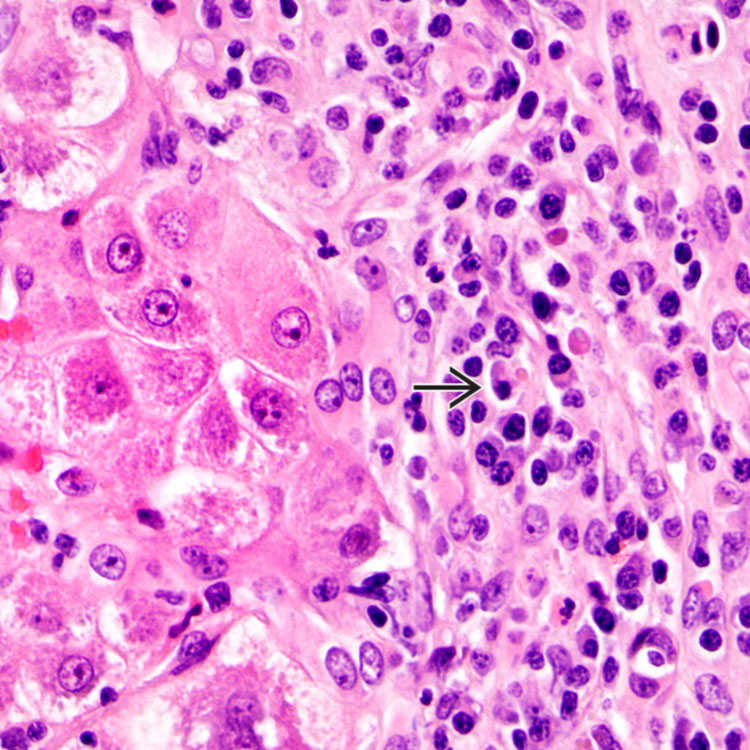
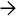 can be seen in drug-induced liver injury and do not necessarily indicate autoimmune hepatitis.
can be seen in drug-induced liver injury and do not necessarily indicate autoimmune hepatitis.
 , while the periportal area with ductular reaction shows light staining
, while the periportal area with ductular reaction shows light staining 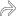 . The latter indicates confluent necrosis rather than fibrosis.
. The latter indicates confluent necrosis rather than fibrosis.



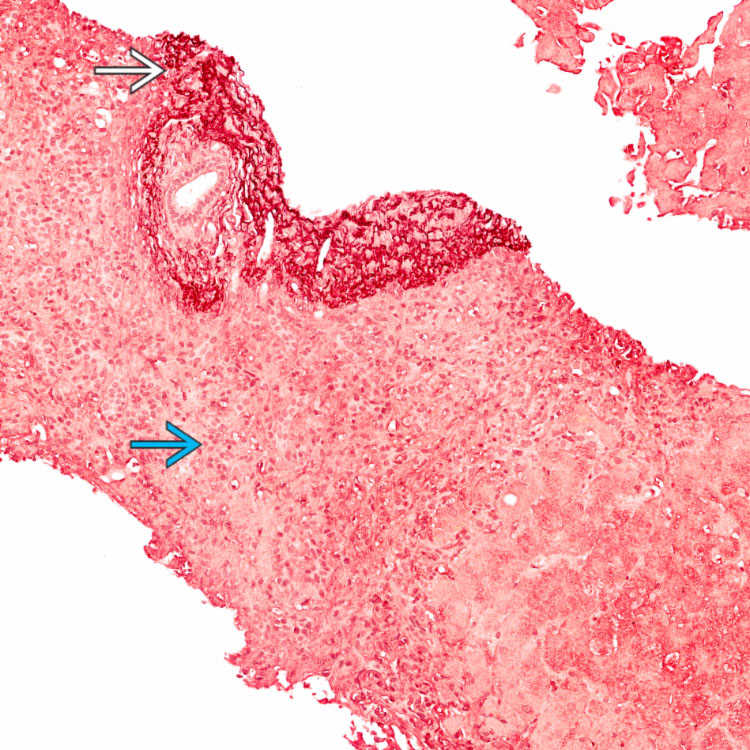
 , while the area of confluent necrosis is negative
, while the area of confluent necrosis is negative  . The combination of trichrome and elastic stains help in distinguishing confluent necrosis (acute hepatitis) from fibrosis (chronic hepatitis).
. The combination of trichrome and elastic stains help in distinguishing confluent necrosis (acute hepatitis) from fibrosis (chronic hepatitis).







