Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Usual Type
Antonio L. Cubilla, MD
Alcides Chaux, MD
Elsa F. Velazquez, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
HPV infection in about 1/4 of cases
Macroscopic Features
Glans frequently affected
Superficial pattern of growth in most cases
Gross features are nondistinctive
Microscopic Pathology
Most common histological subtype of penile SCC
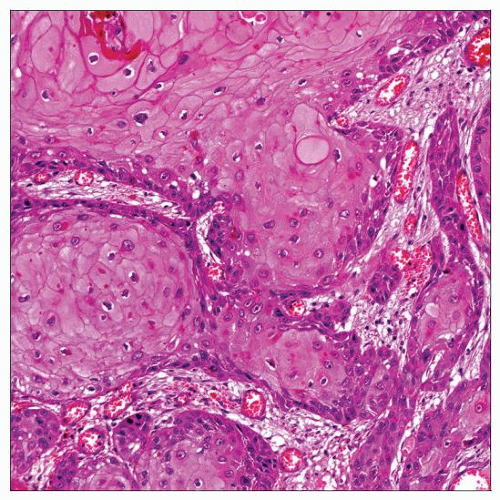
Keratinization evident in most cases
Mostly well-to-moderately differentiated
Pure grade 1 or 3 is very rare
Heterogeneous tumors in about 1/2 of all cases
Focal presence of anaplastic cells is enough for grade 3
Frequent invasion of penile erectile tissues
Frequent extension to multiple compartments
SH and differentiated PeIN commonly found
Most important prognostic factors
Histologic grade
Anatomical level of infiltration
Vascular invasion
Perineural invasion
Inguinal nodal metastases in 1/3 of patients
Top Differential Diagnoses
Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia
Pseudohyperplastic carcinoma
Urothelial carcinoma of distal urethra
High-grade SCC
Mixed SCC
Metastatic SCC to penis
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
Synonyms
Conventional/typical SCC
Epidermoid carcinoma
SCC, not otherwise specified (NOS)
Definitions
Invasive carcinoma with features of keratinization (intracellular keratin pearls and intracellular bridges)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection in about 1/4 of cases
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Most common histologic subtype of penile SCC (60-65%)
Age
Average: 58 years
Presentation
Solid tumoral mass usually affecting glans
Ulceration, pain, bleeding, or erythema may be seen
Treatment
Primary treatment is surgical
Penile-preserving therapy in low-grade superficial tumors
Radiotherapy as adjuvant or neoadjuvant therapy
Chemotherapy for advanced cases (irresectable primary tumor &/or regional involvement)
Inguinal lymphadenectomy according to risk group
Prognosis
Most important prognostic factors include
Histologic grade
Anatomic level of infiltration (pathologic stage)
Vascular, lymphatic, and perineural invasion
Recurrences in 1/4 of cases
Inguinal nodal metastases in 1/3 of patients
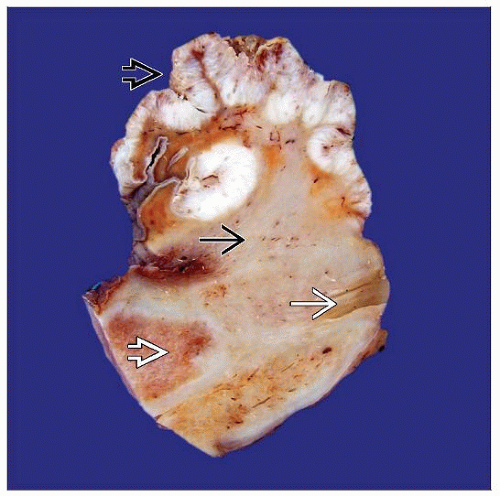
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Most tumors affect glans
Tumors exclusive of foreskin are less common
Superficial spreading is predominant pattern of growth
Gross features are nondistinctive
Average size is 2-4.8 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Evident squamous differentiation (keratinization)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree