Most often gram-negative infection
• Mechanisms uncertain but probably involve decreased activity and expression of canalicular and sinusoidal transporters
Diagnostic Checklist
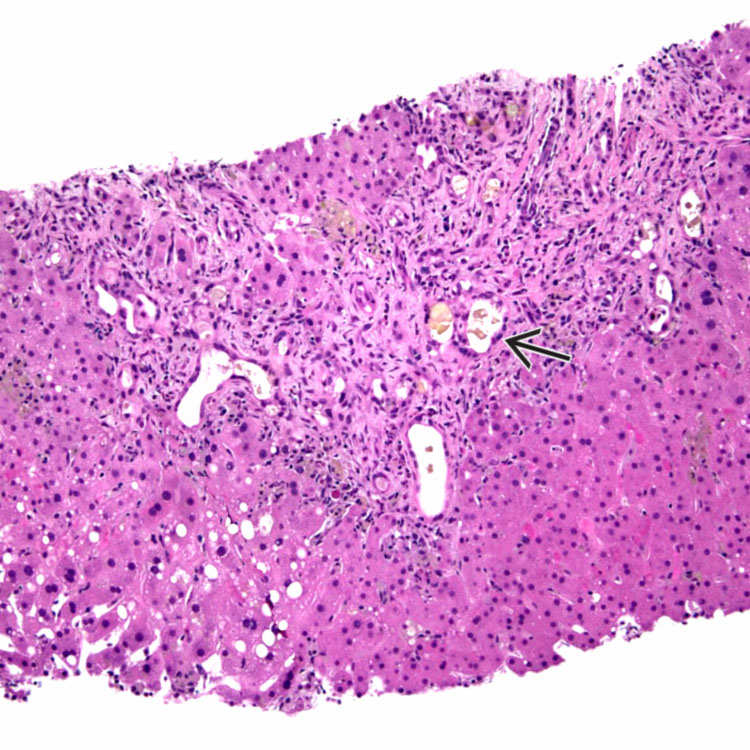
A low-power photograph of a liver biopsy specimen in a septic patient shows expanded portal tracts with ductular reaction. Many of the ductules are dilated and contain inspissated bile
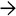 . The lobule shows reactive changes.
. The lobule shows reactive changes.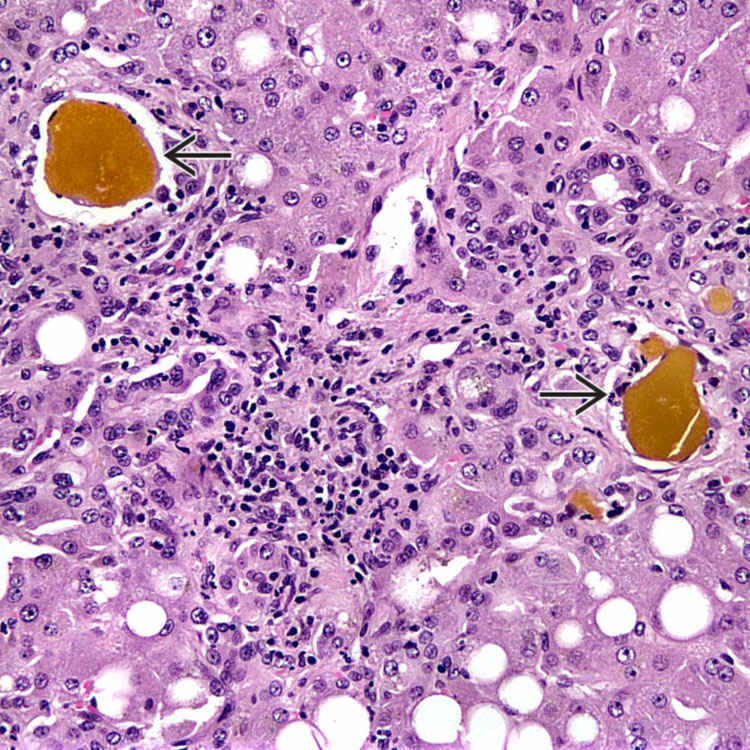
This portal tract has ductular reaction at the periphery. The ductules contain dense, inspissated bile
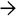 (ductular cholestasis). Neutrophils may be variably present.
(ductular cholestasis). Neutrophils may be variably present.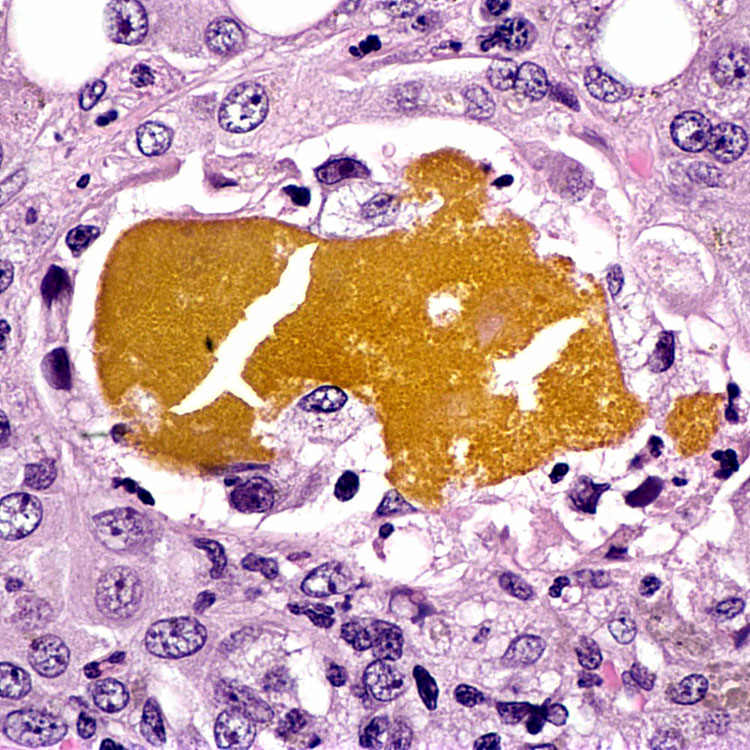
This high-power view of a bile ductule illustrates the flattened, atrophic epithelium and dense, inspissated bile that are typical of ductular cholestasis.
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
• Systemic infection, usually gram-negative sepsis




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





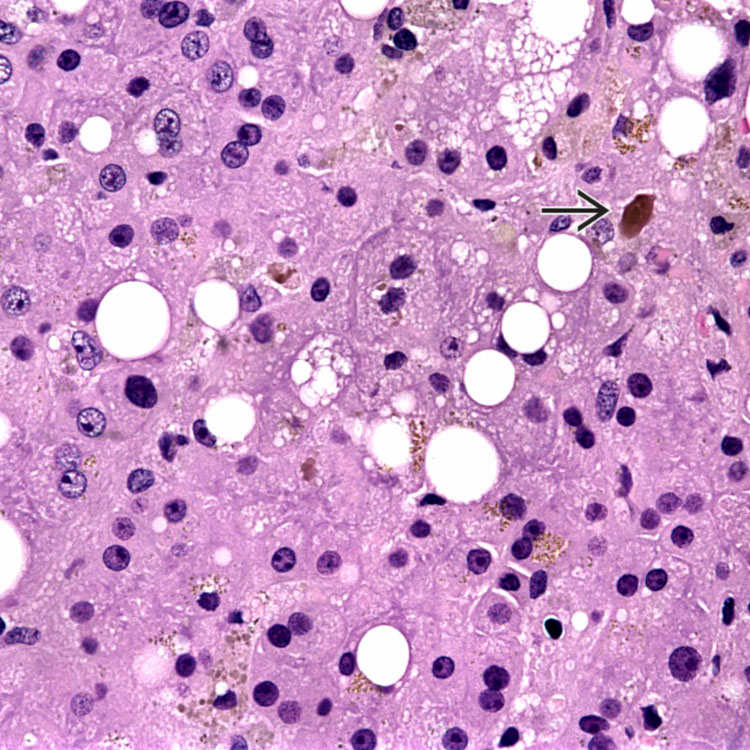
 without significant accompanying inflammation, or “pure” cholestasis, is common in patients with sepsis/systemic infection, particularly infants and children.
without significant accompanying inflammation, or “pure” cholestasis, is common in patients with sepsis/systemic infection, particularly infants and children.
