Depending on severity of portal hypertension, biliary infection, and renal disease
Top Differential Diagnoses
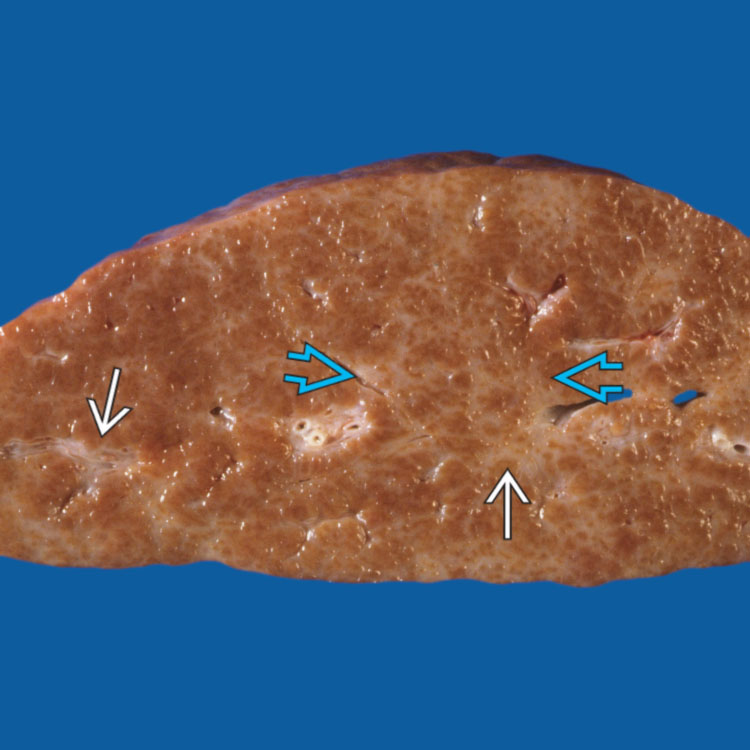
A gross photograph of congenital hepatic fibrosis shows white fibrous bands
 that divide the liver parenchyma in a reticular pattern
that divide the liver parenchyma in a reticular pattern  . There is no definite nodularity, as opposed to cirrhosis.
. There is no definite nodularity, as opposed to cirrhosis.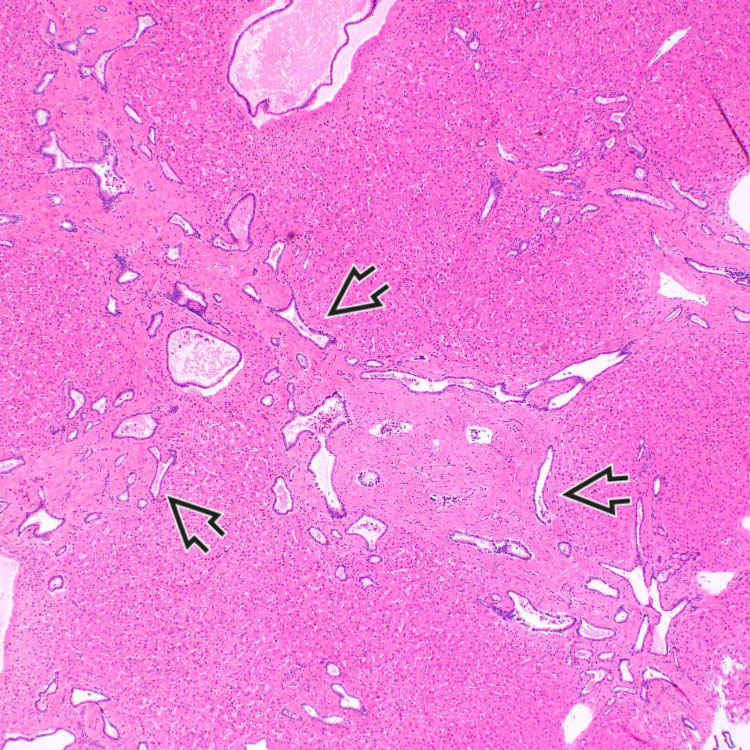
Marked fibrous portal expansion with bridging fibrosis and numerous ectatic and irregularly shaped bile ducts are present, some of which are characteristically located at the interface with liver parenchyma
 . Note that there is no significant inflammation in this case.
. Note that there is no significant inflammation in this case.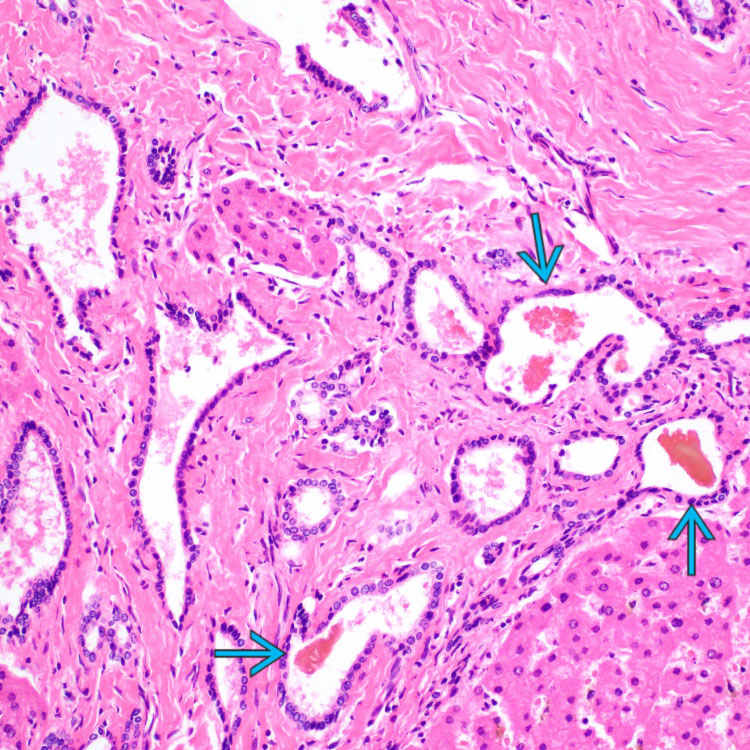
The aberrantly formed bile ducts are lined by cuboidal biliary epithelium, and some contain inspissated bile
 . There is no significant inflammation.
. There is no significant inflammation.ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Disease Associations
• Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






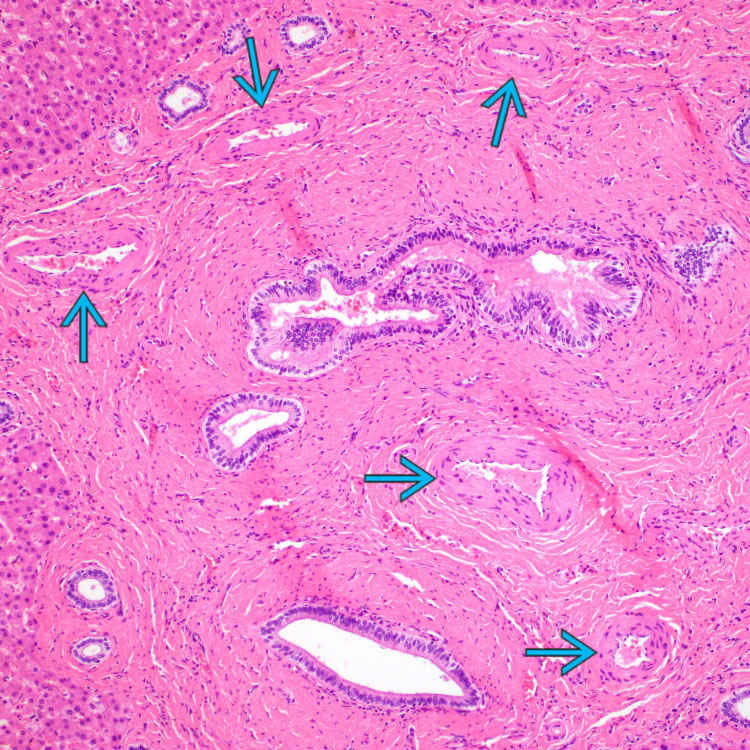
 , but portal veins are not recognizable.
, but portal veins are not recognizable.

