Secretory Carcinoma
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Very rare type of invasive breast carcinoma (< 0.2% of breast carcinomas)
Occurs over wide age range: < 5 years to > 80 years (median: 25 years)
Majority of patients have been treated surgically with excision of breast tumor and lymph nodes
Microscopic Pathology
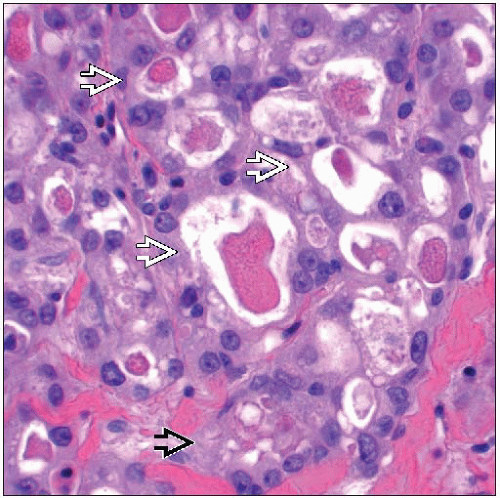
Characterized by proliferation of tubules containing characteristic eosinophilic secretory material
Cells have typical bubbly or granular cytoplasm and are strongly positive for S100
These carcinomas have characteristic balanced translocation, t(12;15)(p13;q25), resulting in ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion product
Same translocation occurs in pediatric mesenchymal cancers (congenital fibrosarcoma and congenital cellular mesoblastic nephroma) and adult acute myeloid leukemia
Majority of secretory carcinomas are negative for ER, PR, and HER2
Although secretory carcinomas have immunohistochemical similarities to basal-like carcinomas, genetic/molecular relationship with this group is unclear
Top Differential Diagnoses
Invasive ductal carcinoma of other types
Lactational changes in normal breast tissue
Granular cell tumor
Microglandular adenosis (MGA)
Cystic hypersecretory carcinoma (CHC)
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Juvenile breast carcinoma (this name is discouraged as majority of cases occur in older patients)
Definitions
Very rare type of breast cancer characterized by specific translocation and occurring over wide age range from children to adults
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Very rare type of invasive breast carcinoma (< 0.2% of breast carcinomas)
Age
Occurs over wide range: < 5 years to > 80 years (median: 25 years)
Presentation
In young women and men, carcinoma is generally in subareolar location due to presence of breast tissue at this site
Not associated with pregnancy or lactation, although histologic appearance mimics lactating breast tissue
Treatment
Majority of patients have been treated surgically with excision of breast and lymph nodes
Too few patients to determine benefit of chemotherapy and radiation
Rare patients with metastatic secretory carcinoma who received chemotherapy progressed during treatment
Prognosis
Majority of patients remain free of disease after surgical excision
About 30% of patients have axillary lymph node metastases
Local recurrences can occur in residual breast tissue or in chest wall many years after initial surgery
In rare cases, systemic metastases have resulted in death of patient
Only 5 cases with distant metastases have been reported
IMAGE FINDINGS
Mammographic Findings
May appear as circumscribed or irregular densities
Calcifications may be present
No specific imaging features
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Gross tumors are firm and lobulated or circumscribed
No gross features that are specific for secretory carcinoma
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
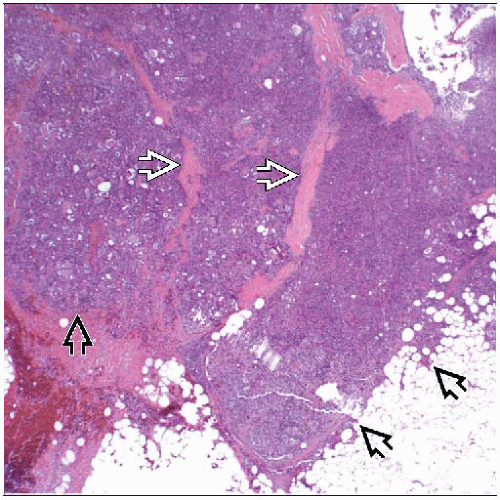
Generally grows as nests of cells
Separated by thick fibrous bands giving lobulated appearance
Less frequently, carcinoma has irregular invasive pattern into adjacent stroma
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree