Mastectomies
INTRODUCTION
Surgical Procedure
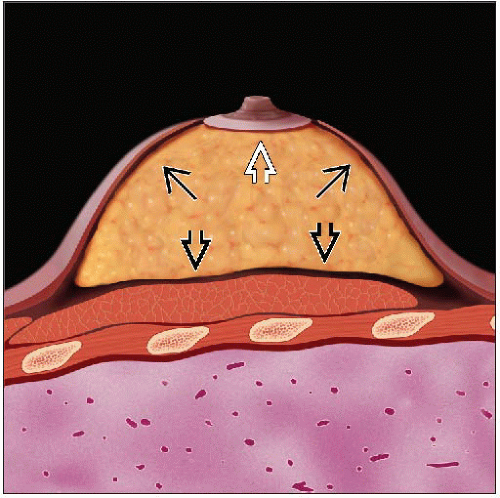
Mastectomy is intended removal of all breast tissue
In some women, breast epithelium is present in subcutaneous tissue or axillary tissue beyond the typical extent of the breast
Therefore, all breast epithelial cells may not be removed by mastectomy
Prophylactic mastectomies reduce risk of breast cancer by 90%
Rarely, breast cancers arise in residual breast tissue
Indications
Majority of women can be successfully treated with breast-conserving therapy (BCT) and radiation therapy
Rate of local recurrence is higher with BCT, but survival is similar
Women with potentially surgically curable disease (DCIS, small node-negative invasive carcinomas) may have a greater benefit from mastectomy as cancer may recur at a higher stage
Mastectomy may be preferred procedure in some cases
Extensive carcinoma or multiple carcinomas that cannot be removed with cosmetically acceptable results
Centrally located carcinomas
Skin or chest wall involvement; many patients will be treated 1st with neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Patients with high risk of subsequent carcinoma (e.g., BRCA germline mutation carriers)
Patients not eligible for radiation due to previous treatment or collagen vascular disease
Patient choice
Types of Mastectomy
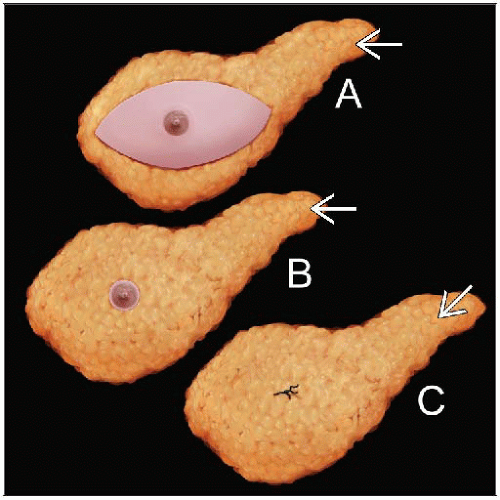
Simple
Removes breast tissue and skin ellipse including nipple
Small amount of muscle may be removed if carcinoma is close to deep margin
Axillary dissection is not performed
However, some lower lymph nodes may be present; lateral tissue should always be examined for nodes
Radical
Removes breast tissue, skin ellipse (including nipple, pectoralis major, and minor muscles), and axillary lymph nodes
Currently performed rarely except for carcinomas that invade into chest wall
Modified radical mastectomy is a simple mastectomy (without removal of muscle) and axillary dissection
Skin-sparing
Removes breast tissue and nipple with small amount of surrounding skin
Nipple-sparing
Removes breast tissue
Does not remove nipple or skin
May be appropriate for carcinomas at least 2 cm from nipple with limited amounts of DCIS
Base of nipple is a margin that must be sampled separately and submitted by the surgeon
Subcutaneous
Removes 85-90% of breast tissue
Does not remove nipple or skin; flaps are usually thick
Similar to nipple-sparing mastectomy but removes less breast tissue
Most common indication is gynecomastia in men
Prophylactic
Removes breast tissue and skin ellipse including nipple
Performed for risk reduction; no known carcinoma is present in the breast at time of surgery
Occult invasive carcinomas are found in 3-15% of cases; generally < 1 cm
Lymph Node Sampling with Mastectomy
Sentinel node biopsy
Sentinel nodes are identified by dye or radioactive tracer
Average number of nodes is 2, but more may be identified in some patients
Metastases are most often found at the pole of the node stained with blue dye
Axillary dissection
Extent of dissection may include levels I, II, or III
Surgeon should indicate extent of dissection
Ideally, at least 10 nodes should be found
If fewer nodes are present, additional examination of specimen &/or submission of tissue should be considered
Intramammary nodes
Nodes may be present within the breast and are usually located in upper outer quadrant
Typically not the sentinel node
SPECIMEN PROCESSING
Requisition Form
In addition to information germane to all types of breast specimens, additional information is required for mastectomies
Number and type of lesions (masses, calcifications, clips, etc.) present
Often multiple, thus requiring mastectomy for removal
Known or suspected involvement of skin or muscle
Distance between lesions and distance from nipple
Presence and extent of axillary dissection
Specimens should always be examined for lymph nodes even if axillary dissection was not performed
Amount of additional gross examination and tissue sampling if lymph nodes are not found is influenced by the number of nodes expected in specimen
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree