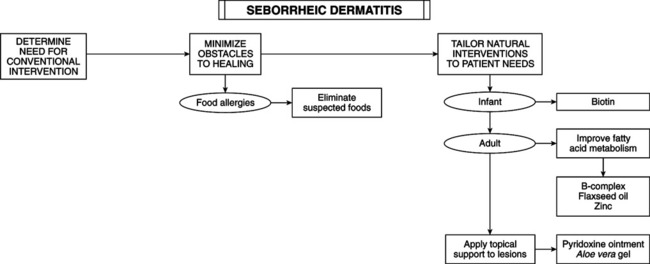
• Seborrheic dermatitis (SD) is a common papulosquamous condition with an appearance similar to eczema. It may be associated with excessive oiliness (seborrhea) and dandruff. Scale is yellowish and either dry or greasy. Erythematous, follicular, scaly papules may coalesce into large plaques or circinate patches. Flexural involvement often is complicated with Candida infection. • Occurs in infancy (between 2 and 12 weeks of age) and in the middle-aged and elderly. • Prognosis: lifelong recurrence. • Cause is unknown. Genetic predisposition, emotional stress, diet, hormones, and infection with yeastlike organisms are im-plicated. • Common manifestation of AIDS, affecting 83%; gives increased credence to the infection theory of SD.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
Basicmedical Key
Fastest Basicmedical Insight Engine