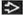Papillary Carcinoma
Antonio L. Cubilla, MD
Alcides Chaux, MD
Elsa F. Velazquez, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Represents 5-15% of all penile SCC
Accounts for 27-53% of all verruciform tumors
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Evidence of HPV infection found in minority of cases
Clinical Issues
Inguinal metastases are found in 0-12% of patients
Cancer-specific mortality rate of 0-6%
Less aggressive than usual SCC
Macroscopic Features
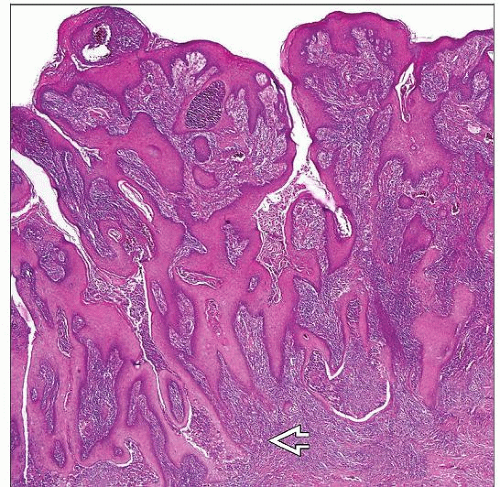
Exophytic verruciform pattern of growth
Glans is most frequently affected compartment
Extension to multiple compartments
Microscopic Pathology
Papillae are architecturally complex
Tips of papillae can be blunt or spiky
Well- to moderately well-differentiated
High-grade areas unusual; absent koilocytotic atypia
Tumoral base irregular and jagged
Squamous hyperplasia, differentiated PeIN, and lichen sclerosus are frequently found
Top Differential Diagnoses
Warty (condylomatous) carcinoma
Verrucous carcinoma
Carcinoma cuniculatum
Mixed usual-verrucous carcinoma
Giant condyloma
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
Synonyms
Papillary carcinoma, NOS
Definitions
Low-grade malignant epithelial tumor with typical exophytic pattern of growth
Diagnosis is made only after exclusion of other verruciform tumors
Represents 5-15% of all penile SCC
Accounts for 27-53% of all verruciform tumors
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiologic Factors
Etiology unknown but frequently associated with lichen sclerosus
Evidence of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection found in minority of cases
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Average age is 63 years (range from 43-85 years)
Presentation
Granular and firm cauliflower-like exophytic tumor
Treatment
Partial penectomy as primary treatment
Inguinal lymphadenectomy according to risk group stratification
Prognosis
Less aggressive than usual SCC
Recurrence rate of about 1/10, usually due to insufficient surgery
Inguinal metastases are found in about 1/10 of patients
Cancer-specific mortality rate very low
Similar to other verruciform tumors in biological behavior
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Tumors present exophytic verruciform pattern of growth
Glans is most frequently affected anatomical compartment
Foreskin exclusively affected in minority of cases
Extension to multiple anatomical compartments in up to 50% of cases
Average size = 4.5-5.8 cm
Cut surface depicts serrated tumoral base
Poorly defined tumor-stroma interface
Invasion of penile erectile tissues is common
Anatomical Extension
Most tumors (65%) invade up to corpus spongiosum or dartos
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree