Nonproliferative Changes
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign breast disease (BBD) with nonproliferative changes includes a commonly encountered constellation of pathologic findings
Stromal fibrosis
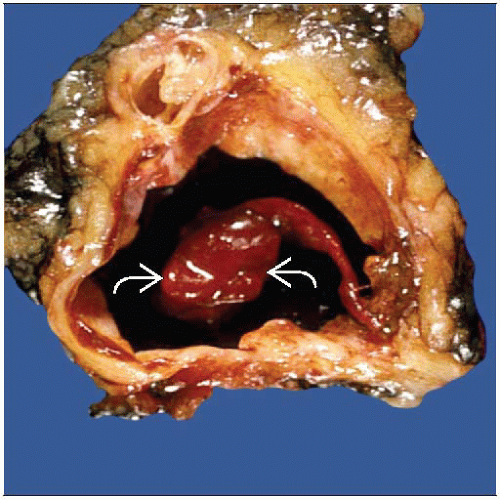
Cysts
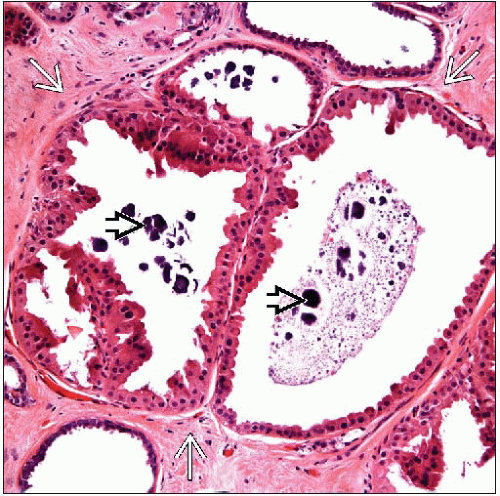
Apocrine metaplasia
Calcifications
Adenosis
Clinical Issues
Frequent findings: Evident in up to 50-60% of women of reproductive age
Nonproliferative changes do not increase risk of breast cancer
Often presents as palpable masses (cysts) or mammographic lesions (densities or calcifications)
Top Differential Diagnoses
BBD with proliferative changes &/or atypia
These changes increase subsequent risk of developing breast carcinoma
Reporting Considerations
“Fibrocystic changes” or “fibrocystic disease” can include a number of different pathologic processes
Can be useful descriptive terms but not as diagnostic terms for pathologic diagnosis
Clinically more relevant to list specific types of benign lesions present including
Lesion conferring highest risk of subsequent carcinoma (if present)
Lesion that correlates with symptom or radiologic finding that prompted biopsy
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Benign breast disease (BBD) with nonproliferative changes
Synonyms
Fibrocystic breast disease
Fibrocystic changes
Definitions
Commonly encountered constellation of benign breast changes including cysts, apocrine metaplasia, stromal fibrosis, and adenosis
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Hormonal Effects
Responsiveness of breast tissues to monthly changes of estrogen and progesterone levels plays an important role in pathogenesis of BBD
May be related to excess hormonal stimulation &/or hypersensitivity of breast tissue
Clinical factors associated with increased risk of BBD
Late age at menopause, estrogen replacement therapy, nulliparity, low body mass index, and family history of breast cancer
Clinical factors associated with decreased risk of BBD
High parity, oral contraceptives, physical activity
Tamoxifen, when used for breast cancer prevention, is associated with 28% reduction in prevalence of BBD (relative risk 0.72)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Very common
Some elements of BBD are evident in up to 50-60% of women of reproductive age
Increased incidence of BBD seen in postmenopausal women receiving estrogens ± progestins for > 8 years (relative risk increased by 1.70)
Presentation
Mammographic screening
May present with densities or calcifications
Palpable lumps
Diffuse symmetrical lumpiness is commonly found on physical examination
Size and symptoms may fluctuate over course of menstrual cycle
Cyclic breast pain may occur during late luteal phase of menstrual cycle
Natural History
BBD with nonproliferative changes does not increase risk of breast cancer