Nipple Adenoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign proliferative lesion arising in major ducts of nipple
Clinical Issues
Patients present with nipple discharge (bloody or clear) &/or ill-defined indurated mass
Skin changes (crusting, erosion) can mimic Paget disease of nipple
Local excision is necessary for diagnosis and treatment
Occasional recurrences have been described after incomplete excision
Rare patients present with carcinomas involving NA
Microscopic Pathology
Diverse array of possible histologic patterns
Sclerosing papillomatosis pattern
Papillomatosis pattern
Adenosis pattern
Mixed patterns
Some features can be difficult to distinguish from malignancy
Florid hyperplasia
Focal necrosis
Sclerosing adenosis resembling invasive carcinoma
Skin erosion
Top Differential Diagnoses
Invasive ductal carcinoma
Papillary carcinoma
DCIS involving large ducts
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Nipple adenoma (NA)
Synonyms
Florid papillomatosis
Erosive adenomatosis
Superficial papillary adenomatosis
Subareolar duct papillomatosis
Nipple duct adenoma
Definitions
Benign lesion characterized by florid epithelial hyperplasia, arising from lactiferous ducts of nipple
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
˜ 1-2% of breasts
Age
Wide age range at presentation
Most often seen in 4th or 5th decade
Gender
Occurs in males and females
Presentation
Bloody nipple discharge
Unilateral and spontaneous
Skin changes
Crusting, nodularity, tenderness, swelling, erosion, and erythema
Can mimic Paget disease
Ill-defined palpable subcutaneous or protruding mass
Usually < 1 cm
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Local excision is necessary for diagnosis and treatment
Prognosis
Benign lesion but can recur locally if not completely excised
Association with carcinoma can occur but is rare
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Mammographic and ultrasound features may suggest carcinoma
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
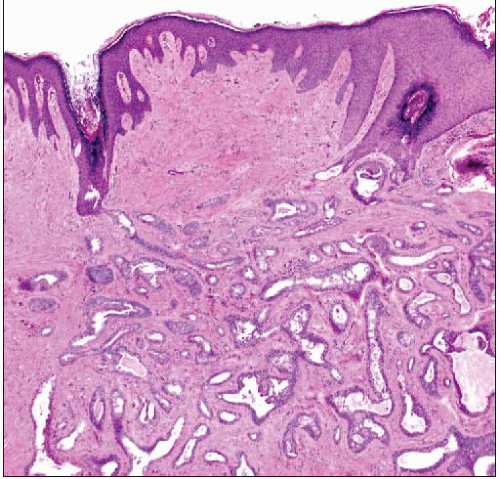
Firm mass under nipple epidermis with irregular borders
Macroscopic features similar to invasive carcinoma
Overlying epidermis may be scaly, eroded, or ulcerated
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
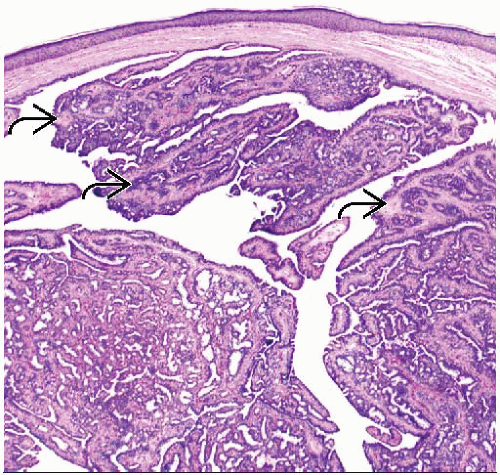
NA occurs just below skin of nipple and has multinodular pattern
Continuity with overlying squamous epithelium of skin may be seen
Histologic changes are quite diverse; grouped into 4 major categories by Rosen
Sclerosing papillomatosis pattern
Papillary growth within ducts
Prominent stromal proliferation: Typically collagenous bands, myxoid change, or elastosis
Overlying skin is intact but thickened
Squamous cysts are often present in duct orifices
Focal central necrosis can be present in areas of florid hyperplasia
Usually presents as mass with serous discharge
Papillomatosis pattern
Papillary growth within large ducts
Less prominent stromal proliferation
Epidermis replaced by glandular epithelium; creates clinical appearance of erythematous granular surface
Focal necrosis can be present
Usually presents with skin erosion and bloody discharge in an indurated area of nipple; may be mistaken for Paget disease clinically
Adenosis pattern
Proliferation of small glands similar to sclerosing adenosis
Entrapped ducts can have pseudoinfiltrative pattern; may closely mimic invasive carcinoma
Myoepithelial hyperplasia is present; IHC can be helpful to demonstrate presence in difficult cases
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree