Mucocele-like Lesions
Key Facts
Terminology
Mucocele-like lesion (MLL)
Uncommon lesion involving breast, composed of mucin-containing cysts that may rupture
Analogous to mucocele of minor salivary glands
Clinical Issues
MLL is usually asymptomatic
Screening mammograms may show mass or calcifications
Less commonly, MLL is detected as palpable mass
MLL without associated carcinoma is benign lesion
Microscopic Pathology
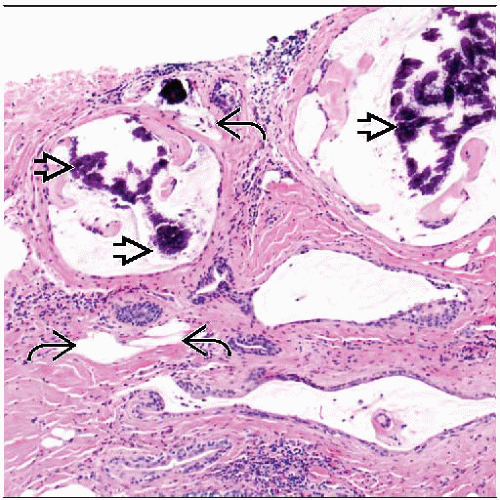
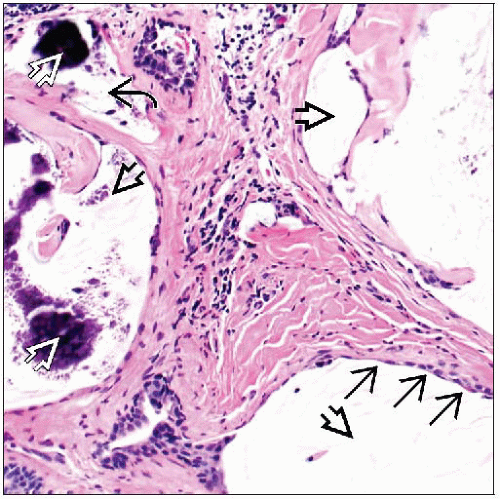
Cystically dilated ducts contain luminal mucin
Spaces lined by cuboidal to attenuated epithelium
Epithelium may show spectrum of proliferative changes including hyperplasia, ADH, or DCIS
May include associated ruptured ducts with extravasated mucin within surrounding stroma
Histocytes and inflammatory cells may be present
Strips or clusters of epithelial cells may become detached from wall, floating free in mucin
Multiple H&E levels may be necessary to exclude invasive mucinous carcinoma
Top Differential Diagnoses
MLL with ADH/DCIS
ADH is reported in 50% of cases
Mucinous carcinoma
Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
Nodular mucinosis
Cystic hypersecretory breast lesions
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Mucocele-like lesion (MLL)
Synonyms
Mucocele-like tumor
Definitions
Uncommon breast lesion, composed of mucin-containing cysts that may rupture
Analogous to mucocele of minor salivary glands
MLL of breast was initially described as benign lesion
However, MLL may be associated with atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH), ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), &/or invasive carcinoma
Associated DCIS and invasive carcinoma are usually mucin producing
MLL may represent spectrum of lesions ranging from benign to neoplastic
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Relationship with Mucinous Carcinoma
Several lines of evidence suggest that at least some MLLs may be related to mucinous carcinoma
ADH reported in up to 50% of patients with MLL
Some may later develop mucinous carcinoma
Some MLLs contain areas of DCIS and invasive mucinous carcinoma at initial diagnosis
Mucin found in MLL is identical to that found in mucinous carcinoma
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Wide range at presentation
27-79 years (mean: 48 years)
Presentation
MLL is usually asymptomatic
Screening mammograms may show mass or calcifications
Less commonly, MLL is detected as palpable mass
Treatment
Diagnosis of MLL on needle core biopsy warrants excision for further evaluation
Careful evaluation of excised tissue sample for atypia or carcinoma is required
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree