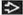Locally Recurrent Carcinoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Subsequent carcinoma in breast (after breast-conserving therapy) or in chest wall (after mastectomy) following prior diagnosis of breast carcinoma
True recurrent carcinoma is due to failure of initial treatment to eradicate carcinoma
New primary carcinomas are not clonally related to 1st carcinoma
Etiology/Pathogenesis
After breast-conserving therapy
True recurrences are most common in 1st 5 years
Prognosis is generally poor, as carcinoma is resistant to treatment, and majority of patients develop distant metastases
New primaries are more common 10 years and beyond after initial diagnosis
Prognosis is generally favorable because carcinoma may be sensitive to therapy
After mastectomy
Majority of cases are true recurrences of original invasive carcinoma present in chest wall or skin
Prognosis is generally poor because majority of patients eventually develop distant metastases
In rare cases, new carcinomas may arise from residual normal breast tissue remaining after surgery
Ancillary Tests
DNA-based assays are more accurate in determining whether cancer is true recurrence or new primary cancer
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Subsequent carcinoma in breast after breast-conserving therapy or in chest wall after mastectomy, following prior diagnosis of breast carcinoma
True recurrences (TR) due to failure to eradicate carcinoma by initial treatment
New primary cancers (NP) not clonally related to first carcinoma
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Types of Recurrent Carcinoma
After breast-conserving therapy
May be DCIS or invasive carcinoma
Approximately 1/3 of cases will be NP
Location, histologic type, and tumor markers can help determine if cancer is TR or NP
Recurrent DCIS has favorable prognosis
About 1/2 of recurrent cases after diagnosis of DCIS will again be DCIS and 1/2 invasive carcinoma
Recurrent invasive carcinoma after initial diagnosis of invasive carcinoma has less favorable prognosis
If TR, then carcinoma is resistant to therapy given to patient and prognosis is generally poor
If NP, prognosis is more favorable as carcinoma may be sensitive to treatment
If patient has developed new invasive carcinoma due to residual DCIS, effect on prognosis is less clear
This finding suggests original DCIS was resistant to treatment
After mastectomy
Majority of cases are due to TR and occur in chest wall or skin
Prognosis generally poor because majority of patients eventually develop distant metastases
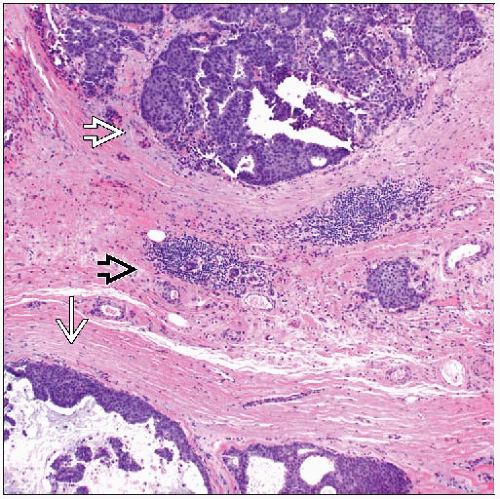
Recurrent carcinoma likely arose from foci of lymph-vascular invasion
In rare cases, NP may occur due to residual normal breast tissue remaining after surgery
Impossible to remove all breast tissue in all patients because breast tissue can be present in subcutaneous tissue over anterior chest wall and can extend into axilla
Important to evaluate “chest wall” excisions for residual normal breast tissue &/or DCIS
NP occurring in residual breast tissue likely has better prognosis than TR
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree