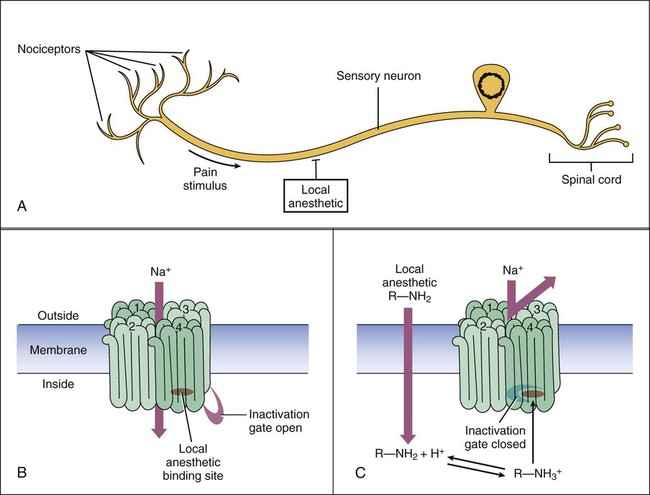
Based on their chemical structure, local anesthetics can be divided into ester-type drugs and amide-type drugs. Each local anesthetic has a lipophilic (hydrophobic) portion and a hydrophilic portion (Fig. 21-1). The hydrophilic portion, an amine that is a weak base, exists in both ionized and nonionized forms. The ionized, protonated form predominates at lower pH levels, and the nonionized, unprotonated form predominates at higher pH levels. Only the nonionized form can penetrate neuronal membranes to reach binding sites on the internal surface of sodium channels. Inflammation and acidosis decrease the pH of tissues, thereby increasing the ionization of local anesthetics. For this reason, local anesthetics are less effective in the presence of these conditions, necessitating larger doses. The duration of action of local anesthetics can be short, medium, or long (Table 21-1). Because local anesthetics act directly at the site of administration, their duration of action is determined primarily by the rate of diffusion and absorption away from the site of administration. Diffusion and absorption, in turn, depend on the chemical properties of the anesthetics and on such factors as local pH and blood flow. In some formulations, epinephrine is added to prolong a local anesthetic’s duration of action by producing vasoconstriction and slowing its rate of absorption. Because of the risk of ischemia and necrosis, however, local anesthetics with epinephrine are not used to anesthetize tissues with end arteries, such as tissues of the fingers, toes, ears, nose, and penis. TABLE 21-1 Properties of Selected Local Anesthetics *The duration varies with the dose and route of administration. Short, 0.25-1.5 hr; medium, >1.5-5 hr; and long, >5 hr. †Procaine is no longer available in the United States but is included here because it was used for many years and because of the popularity of its trade name (NOVOCAIN). Local anesthetics cause a reversible inhibition of action potential conduction by binding to the sodium channel and decreasing the nerve membrane permeability to sodium. The nonpolar, lipophilic form of the anesthetic molecule passes through the neuronal membrane and switches to the polar, hydrophilic form in the cytoplasm of the neuron. This cationic form of the anesthetic binds to the cytoplasmic side of the sodium channel protein and prolongs the inactivation state of the sodium channel (Fig. 21-2). With sodium channels blocked, action potentials cannot propagate along the neuronal fiber, and sensory input is lost. Cocaine, a naturally occurring plant alkaloid, was the first local anesthetic to be discovered. It has both local anesthetic and CNS stimulant properties, and it is the only local anesthetic that causes significant vasoconstriction as a result of its sympathomimetic effect. Because of its CNS effects and potential for abuse (see Chapter 25), cocaine is seldom used as a local anesthetic. It is occasionally used, however, to anesthetize the internal structures of the nose, where its vasoconstrictive action helps prevent bleeding after nasal surgery. A cocaine solution is applied to gauze and inserted into the nose for this purpose. Bupivacaine, mepivacaine, and ropivacaine have similar clinical uses but differ in their duration of action, as shown in Table 21-1. Bupivacaine has been the most widely used local anesthetic for obstetric anesthesia, but it causes cardiac depression more frequently than do many other local anesthetics. Bupivacaine is also available in a liposome-encapsulated formulation (EXPAREL) for long-acting analgesia in the treatment of postsurgical pain. Ropivacaine is a newer drug that may cause fewer cases of cardiac toxicity. Levobupivacaine is the isolated S(−)-stereoisomer of racemic bupivacaine, which is the active form of the chiral drug mixture. It is used in epidural anesthesia for labor and delivery.
Local and General Anesthetics
Local Anesthetics
Drug Properties
Chemistry and Pharmacokinetics
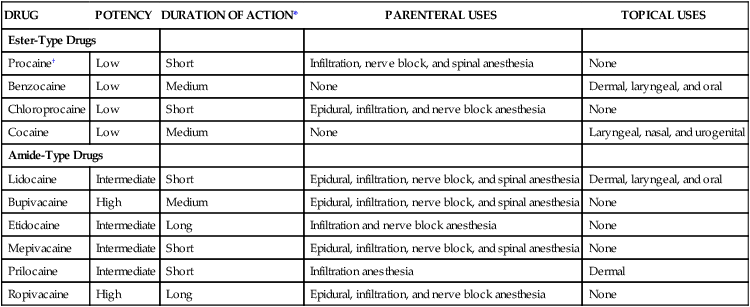
DRUG
POTENCY
DURATION OF ACTION*
PARENTERAL USES
TOPICAL USES
Ester-Type Drugs
Procaine†
Low
Short
Infiltration, nerve block, and spinal anesthesia
None
Benzocaine
Low
Medium
None
Dermal, laryngeal, and oral
Chloroprocaine
Low
Short
Epidural, infiltration, and nerve block anesthesia
None
Cocaine
Low
Medium
None
Laryngeal, nasal, and urogenital
Amide-Type Drugs
Lidocaine
Intermediate
Short
Epidural, infiltration, nerve block, and spinal anesthesia
Dermal, laryngeal, and oral
Bupivacaine
High
Medium
Epidural, infiltration, nerve block, and spinal anesthesia
None
Etidocaine
Intermediate
Long
Infiltration and nerve block anesthesia
None
Mepivacaine
Intermediate
Short
Epidural, infiltration, nerve block, and spinal anesthesia
None
Prilocaine
Intermediate
Short
Infiltration anesthesia
Dermal
Ropivacaine
High
Long
Epidural, infiltration, and nerve block anesthesia
None
Mechanism of Action
Specific Agents
Ester-Type Local Anesthetics
Amide-Type Local Anesthetics
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree