QUESTION 6.2
A. Alcohol abuse
B. Diabetes mellitus
C. Spinal cord injury
D. Syphilis
E. Syringomyelia
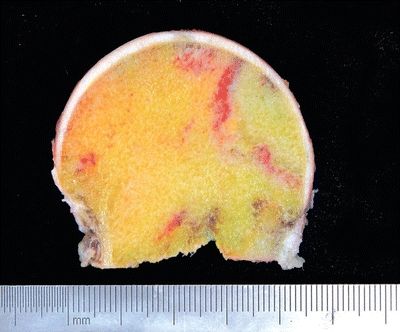
3. This photomicrograph shows a section of the femoral head removed from an elderly woman with acute hip pain. The lesion seen here is most consistent with:
QUESTION 6.3
A. Degenerative joint disease
B. Insufficiency fracture
C. Osteolytic metastasis
D. Osteonecrosis
E. None of the above
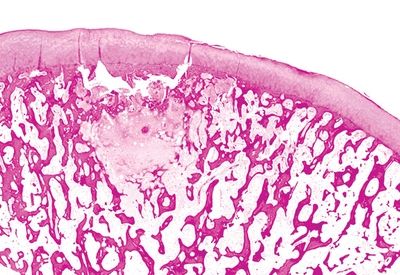
A. Degenerative joint disease
B. Insufficiency fracture
C. Intraosseous lipoma
D. Osteoblastic metastasis
E. Osteonecrosis
5. The florid inflammatory process in joints affected by rheumatoid arthritis tends to regress following destruction of which of the following components?
A. Articular cartilage
B. Joint capsule
C. Menisci
D. Subchondral bone
E. Synovial membrane
6. A biopsy of a destructive lesion in the foot of a patient with a history of gout is submitted for pathologic examination. Which of the following is the most appropriate manner to handle this specimen?
A. Fixation in alcohol
B. Fixation in formalin
C. Fixation in glutaraldehyde
D. Formalin fixation followed by 3% potassium chromate
E. Microscopic examination of unstained frozen tissue
7. A 48-year-old patient develops acute swelling and pain of the knee. A synovial aspirate from the affected joint leads to identification of crystals, which are blue when parallel and yellow when perpendicular to the axis of a red compensator. These crystals are composed of:
A. Calcium oxalate
B. Calcium pyrophosphate
C. Homogentisic acid
D. Hydroxyapatite
E. Monosodium urate
8. Finding at least five neutrophils per high-power field in five high-power fields is a histologic criterion for assessing the presence of infection in which of the following situations?
A. Acute gout attack
B. Bone fracture
C. Hemorrhage
D. Reactive arthritis
E. Revision arthroplasty
9. In Hoffa disease, the most characteristic pathologic alteration is:
A. Accumulation of metallic particles in the capsular tissue
B. Degeneration of the cartilage matrix
C. Detachment of a piece of bone with overlying cartilage
D. Enlargement of the infrapatellar fat pad
E. Formation of pannus over the articular surface
10. A 25-year-old woman presents with swelling and mild pain in the volar aspect of the right wrist. A portion of the synovium is excised. Its macroscopic features are shown in this photograph. Histologically, it consists of sheets of polygonal and occasionally multinucleated cells. Papillary fronds arise from the adjacent synovial lining. Foamy histiocytes, hemosiderin-laden macrophages, and multinucleated giant cells are abundant at the periphery. These features are most consistent with:
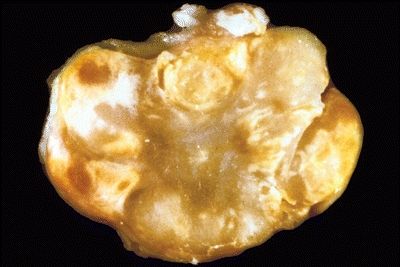
QUESTION 6.10
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree