Top Differential Diagnoses
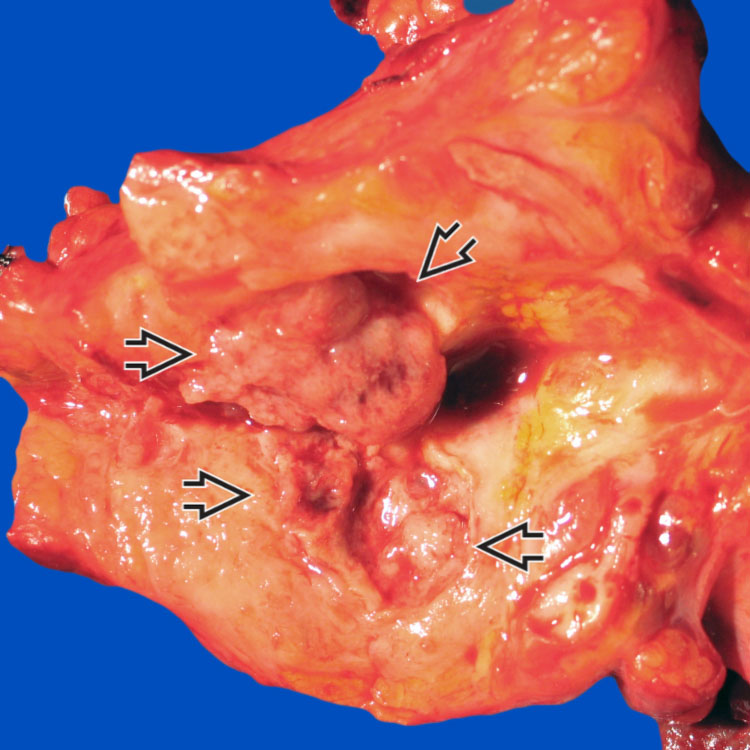
This intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm (ITPN) is forming solid nodules
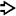 that obstruct the dilated pancreatic duct. There is no grossly visible mucin.
that obstruct the dilated pancreatic duct. There is no grossly visible mucin.
This low-power view shows an ITPN with stromal invasion. Note the solid masses with focal necrosis
 within a dilated duct. A focus of invasion is also seen
within a dilated duct. A focus of invasion is also seen 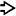 .
.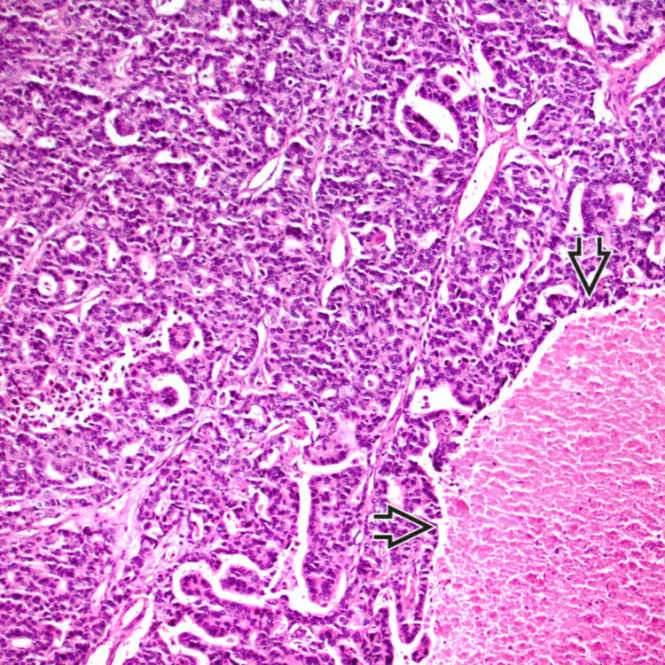
ITPN typically exhibits a cellular, tubulopapillary growth pattern with high-grade cytologic atypia and easily identifiable necrosis
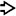 .
.






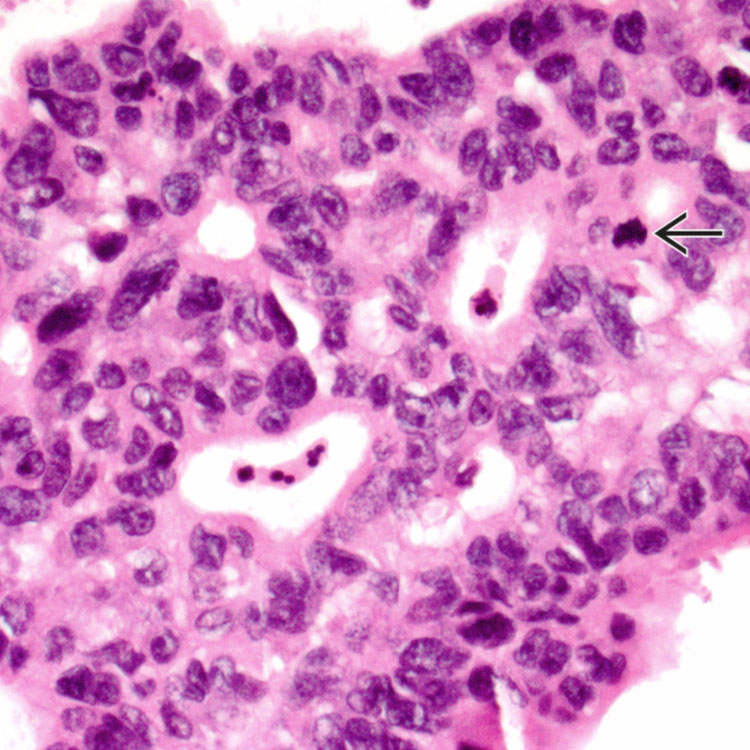
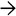 . There is no mucinous epithelium.
. There is no mucinous epithelium.


