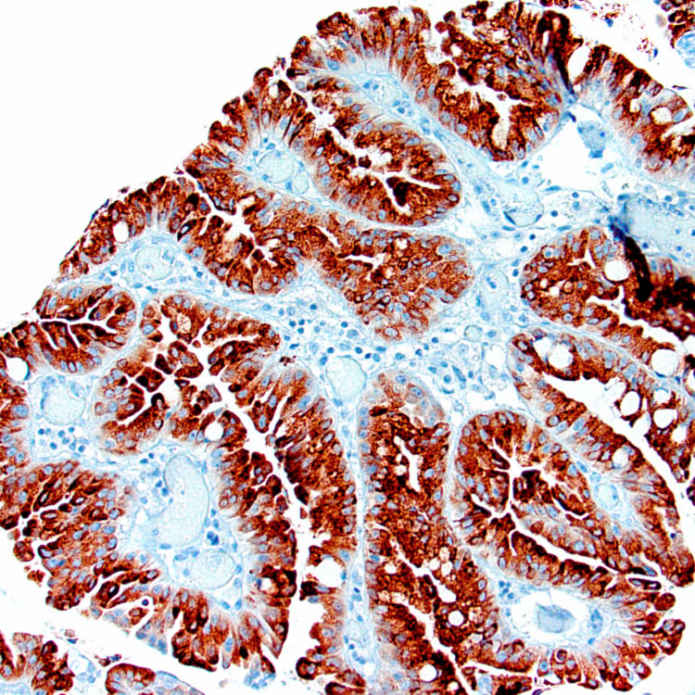
Often classified as having high-grade dysplasia given architectural complexity
• Neoplastic cells have abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm with large nuclei, prominent nucleoli
• Both intracytoplasmic and intercellular lumina found, many containing mucin, with scattered goblet cells
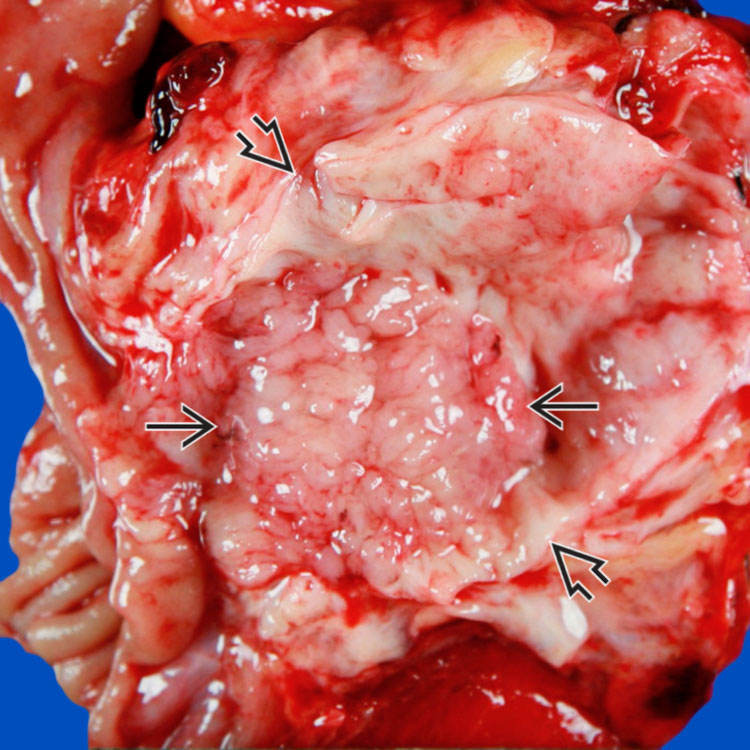
A tan-red luminal papillary mass
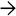 partially involves the dilated main pancreatic duct
partially involves the dilated main pancreatic duct 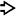 .
.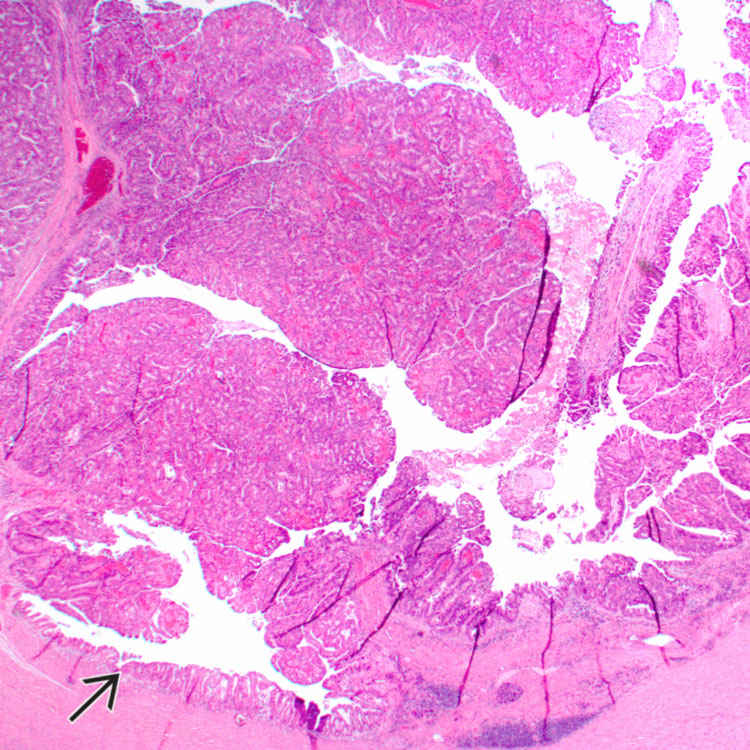
Intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasms (IOPNs) consist of architecturally complex, thick papillae, seen here growing in a dilated branch duct that is, in part, lined by relatively flat epithelium
 .
.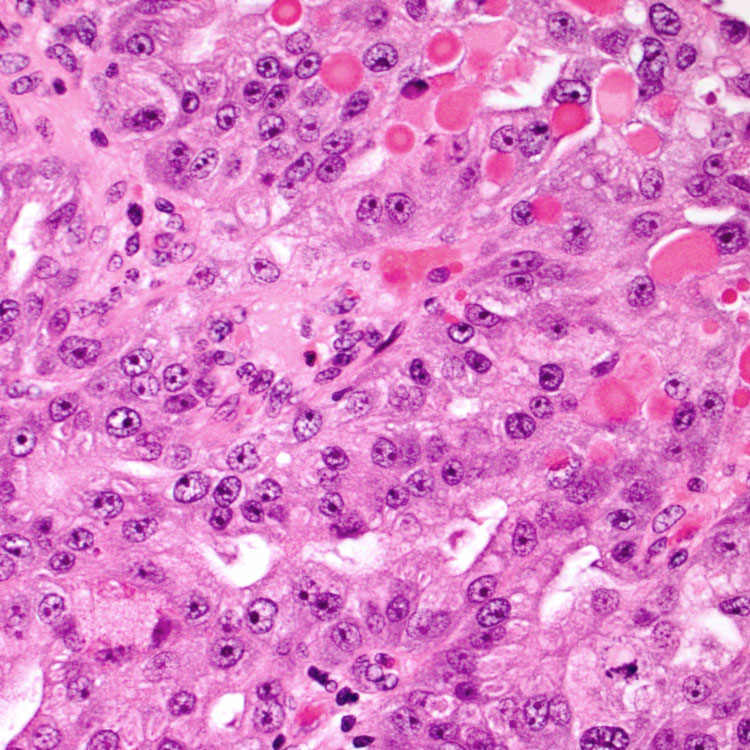
Higher magnification of IOPN exhibits architecturally complex growth with cribriforming &/or solid nests. The neoplastic epithelial cells have abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm and large nuclei with prominent nucleoli.