Once known etiologies are excluded, then considered idiopathic
• By mid-2000s, idiopathic neonatal hepatitis (INH) comprised only 15-30% of neonatal cholestasis due to increased ability to detect and diagnose metabolic and genetic disorders previously considered idiopathic
Top Differential Diagnoses
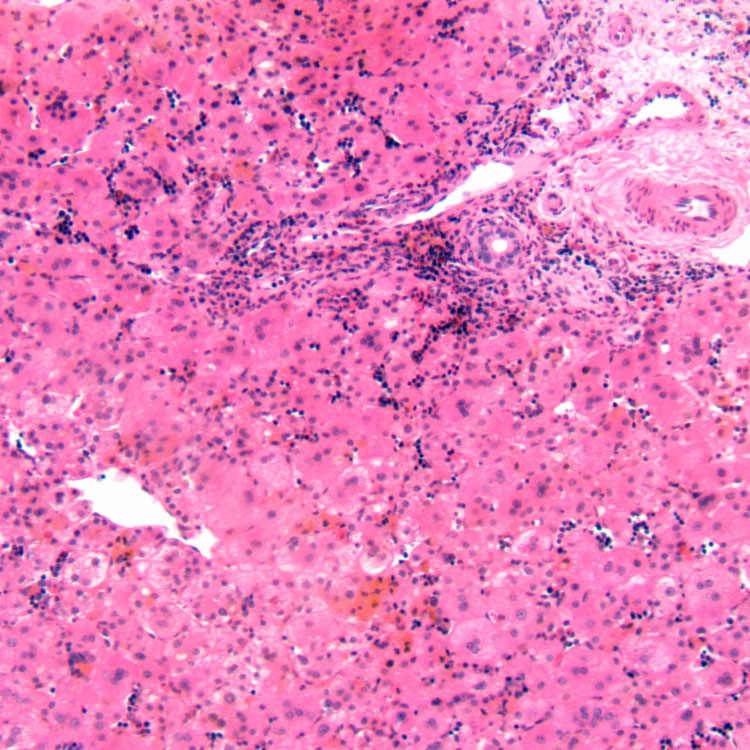
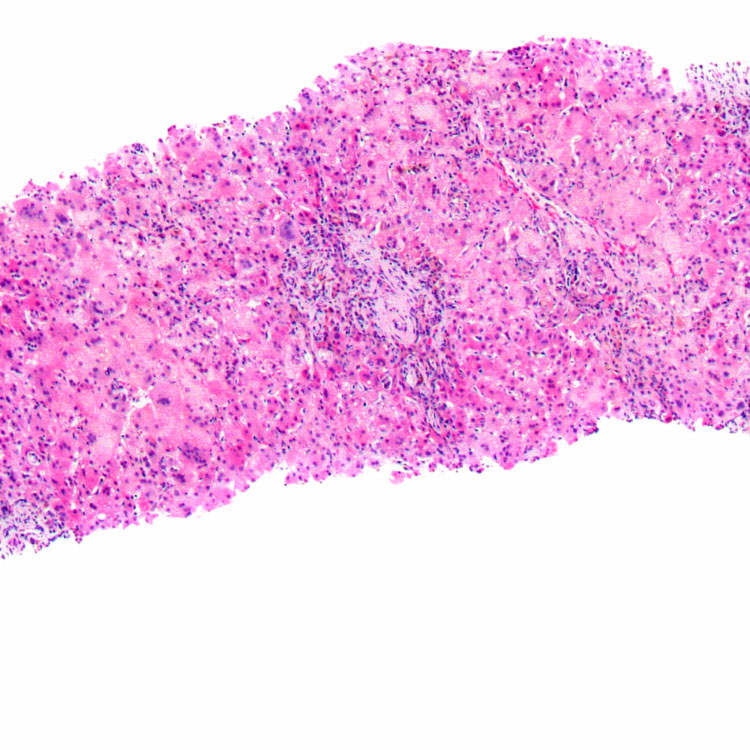
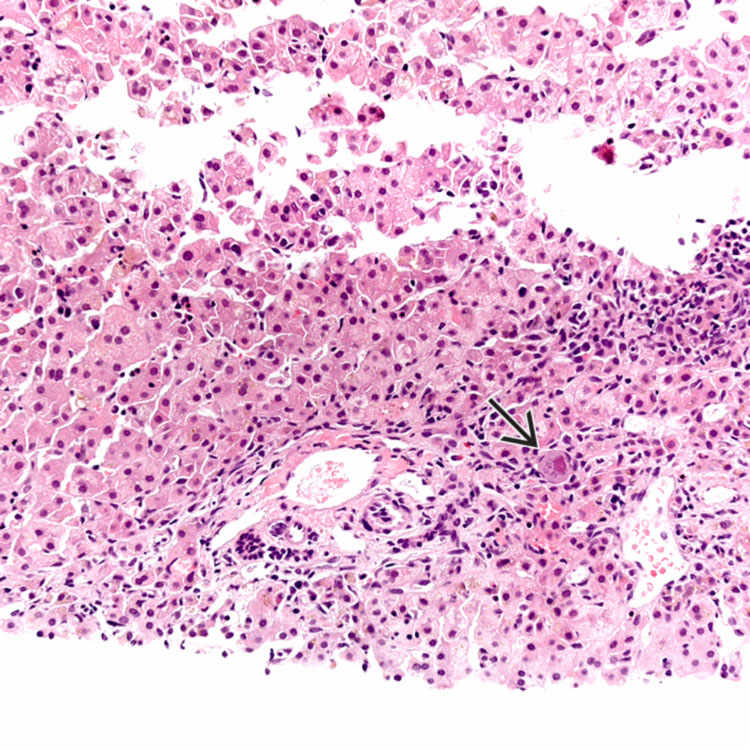
The characteristic features of idiopathic neonatal hepatitis include lobular giant cell transformation and prominent extramedullary hematopoiesis. Portal changes are minimal, and ductular reaction is absent.
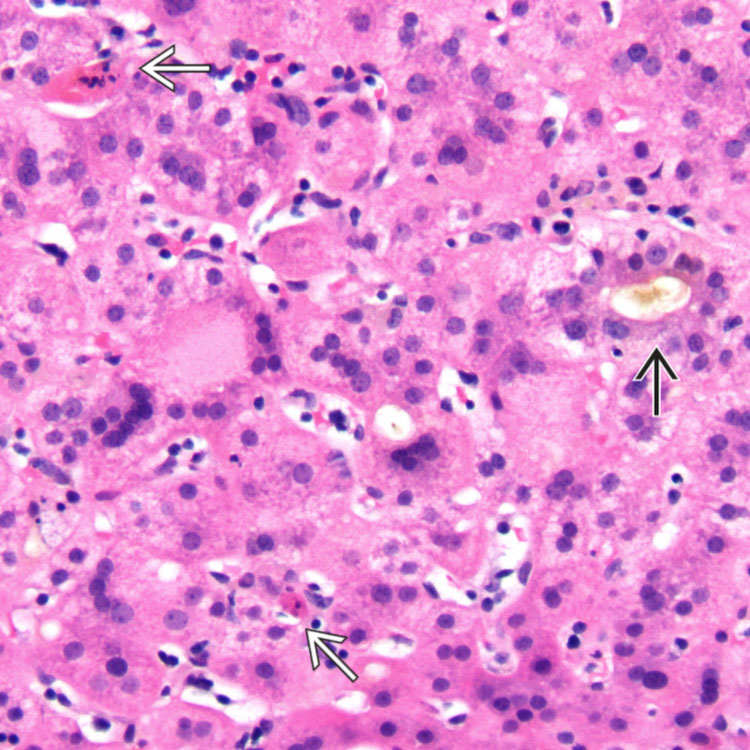
The lobular hepatocytes show giant cell change and scattered apoptotic hepatocytes
 , along with canalicular cholestasis and a cholestatic rosette
, along with canalicular cholestasis and a cholestatic rosette 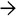 .
.
This case of neonatal hepatitis due to CMV shows a few giant cell hepatocytes along with extramedullary hematopoiesis. A single CMV inclusion
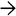 was identified.
was identified.TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Definitions
• General term for clinical condition manifested by prolonged jaundice in neonates with variable but definable histologic picture




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree