Biochemical evidence of cholestasis
• Variable prognosis, ranging from benign clinical course to progressive disease requiring liver transplantation
Diagnostic Checklist
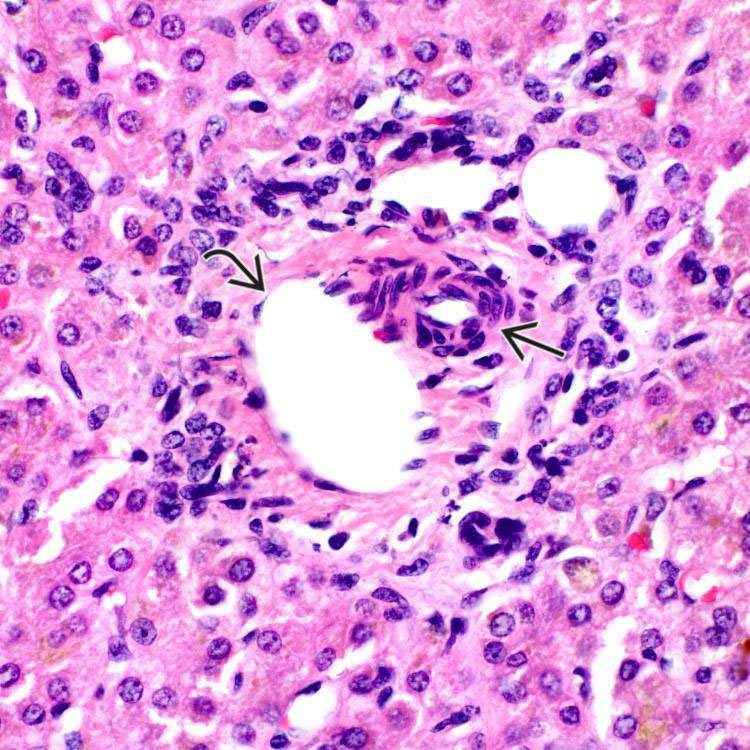
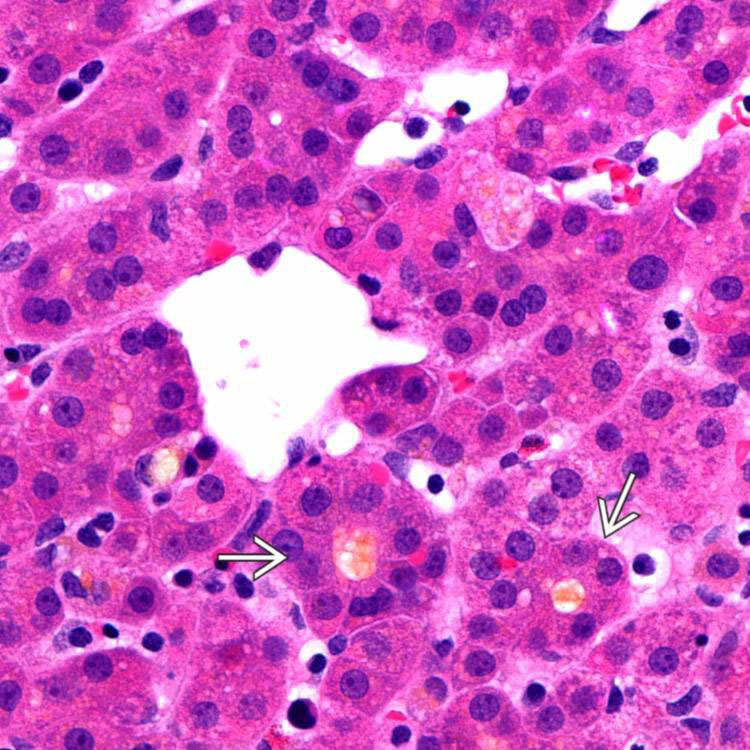
This liver biopsy from a young man with persistent elevation of serum alkaline phosphatase levels and hyperbilirubinemia with no identifiable cause shows the presence of the hepatic artery
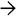 and portal vein
and portal vein 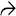 but no bile duct in the majority of portal tracts. Note the presence of minimal portal inflammation.
but no bile duct in the majority of portal tracts. Note the presence of minimal portal inflammation.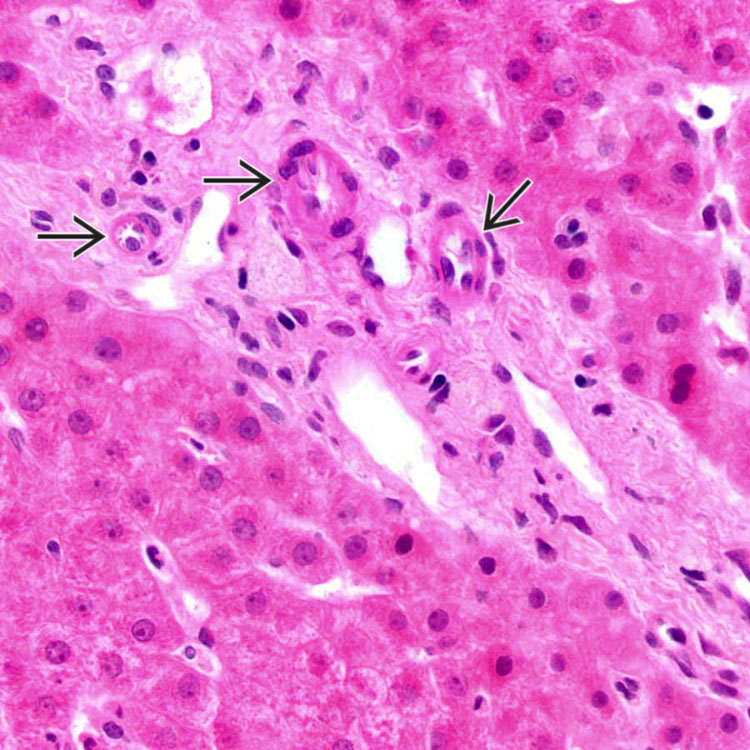
Another case of idiopathic adulthood ductopenia shows hepatic artery branches
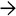 in a portal tract, unaccompanied by bile ducts. Ductular reaction is not evident in this portal tract.
in a portal tract, unaccompanied by bile ducts. Ductular reaction is not evident in this portal tract.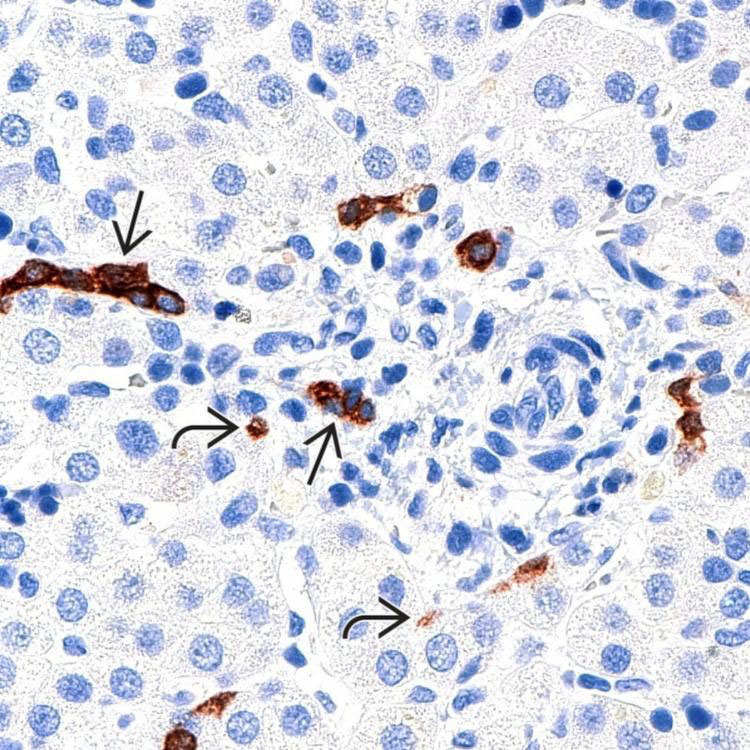
This case of idiopathic adulthood ductopenia shows the absence of bile duct as confirmed by CK7 immunostaining. The positively stained cells represent bile ductules
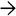 or canals of Hering
or canals of Hering 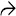 .
.



 indicating a chronic cholestatic process.
indicating a chronic cholestatic process.


