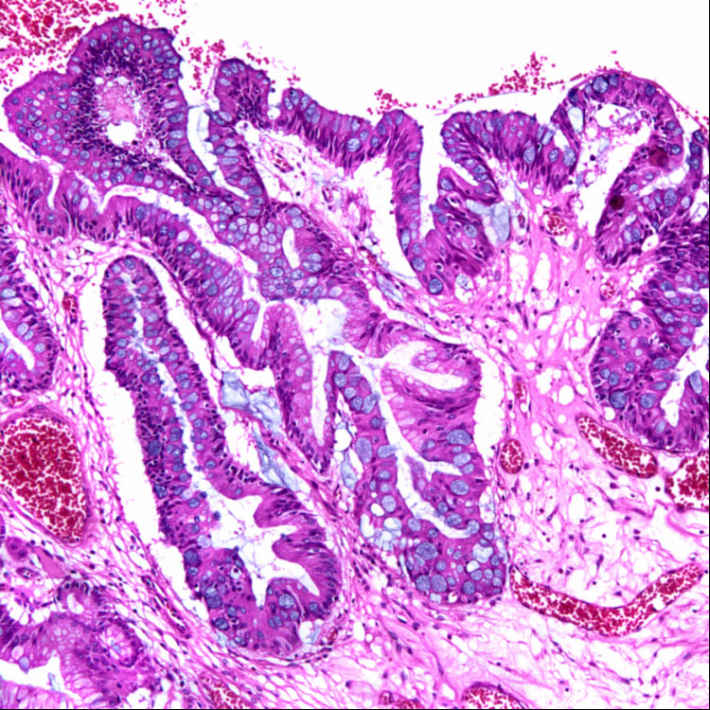
Usually in context of inflammatory process
• Historically, a.k.a. metaplastic polyp, mucosal hyperplasia, inflammatory polyp, or localized papillary hyperplasia
Microscopic
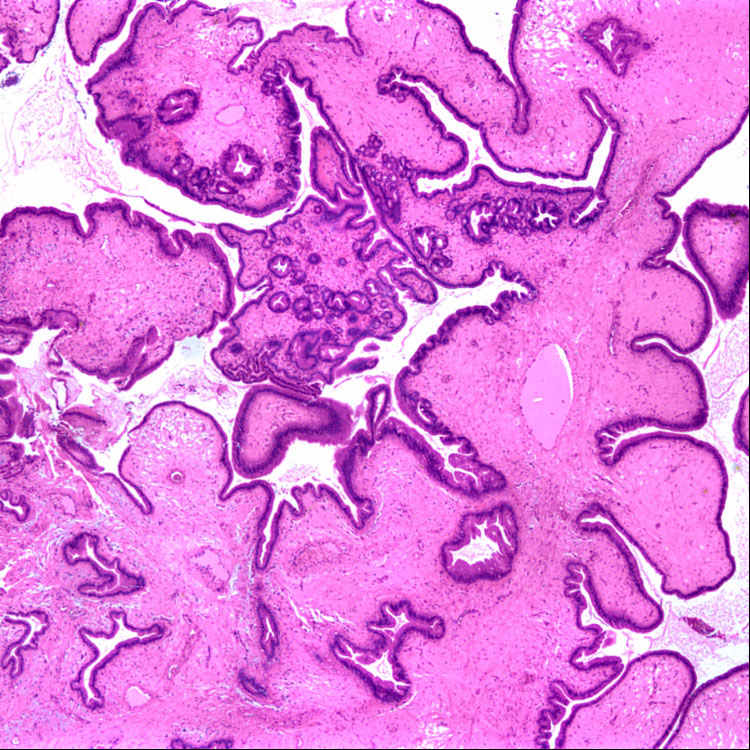
Low-power view of a hyperplastic polyp of the gallbladder illustrates the prominent mucosal folds and papillae with abundant intervening stroma.
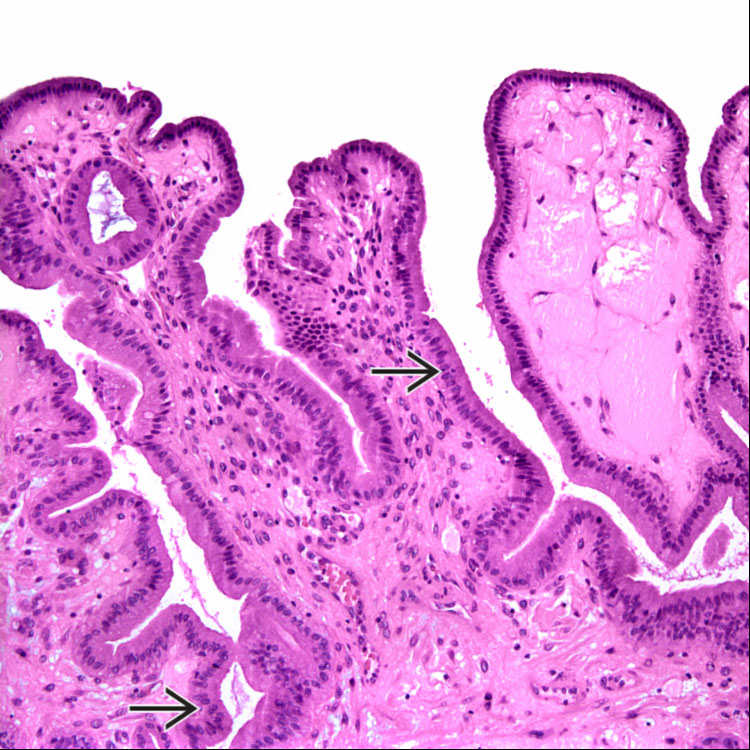
H&E of a hyperplastic polyp at high power shows that the polyp surface is lined by normal-appearing gallbladder mucosa
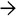 .
.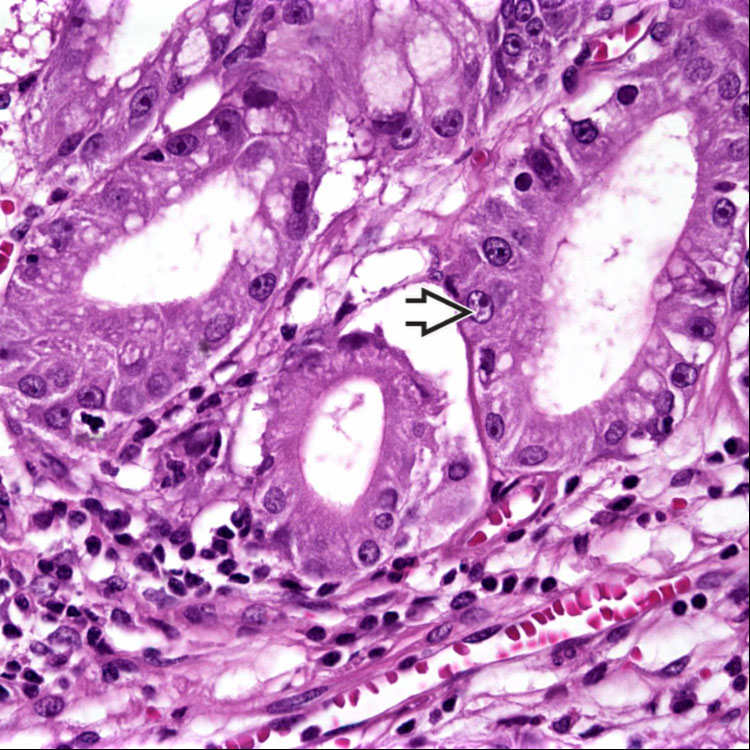
Reactive epithelial changes in a hyperplastic polyp include vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli
 associated with inflammation.
associated with inflammation.TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Synonyms
• Metaplastic polyp, mucosal hyperplasia, inflammatory polyp, localized papillary hyperplasia




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree