• Prodrome of anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, flulike symptoms 2 weeks to 1 month before liver involvement depending on incubation period of virus. • Symptoms may occur abruptly or insidiously. • Fever, headaches, abdominal discomfort, light stools, diarrhea, myalgia, arthralgia, drowsiness, enlarged and tender liver, jaundice, itching. • Normal to low white blood cell count, markedly elevated aminotransaminases, elevated bilirubin. • Hepatitis A: caused by virus from Picornaviridiae family. It occurs sporadically or in epidemics and is transmitted primarily by fecal contamination from poor hygiene and sanitation. • Hepatitis B: linked to 50% of viral cases in the United States; transmitted by infected blood or blood products or sexual contact (virus shed in saliva, semen, vaginal secretions). • Hepatitis C (hepatitis non-A, non-B): linked to hepacivirus and a member of Flaviviridae family. Transmitted by blood contamination and responsible for 90% of all cases of hepatitis through blood transfusions (10% of people receiving blood transfusions in the past developed hepatitis C). However, only 4% of cases of hepatitis C result from transfusions. Most cases are attributable to intravenous drug use; in other cases the source is unclear. The mortality rate (1%-12%) is much higher than for other forms. • Other viral causes: hepatitis viruses D, E, and G; herpes simplex; cytomegalovirus; and Epstein-Barr virus. • Acute viral hepatitis: extremely debilitating form requiring bed rest and 2-16 weeks of recovery. Most patients completely recover (9 weeks for type A and 16 weeks for B, C, D, and G). One in 100 will die. Ten percent of hepatitis B and 10%-40% of hepatitis C cases become chronic. Hepatitis C contracted by blood transfusion has a 70%-80% rate of chronicity. • Symptoms of chronic hepatitis: vary from nonexistent to chronic fatigue, serious liver damage, and even death. Hepatitis B Serologic Patterns and Interpretations
Hepatitis
DIAGNOSTIC SUMMARY
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
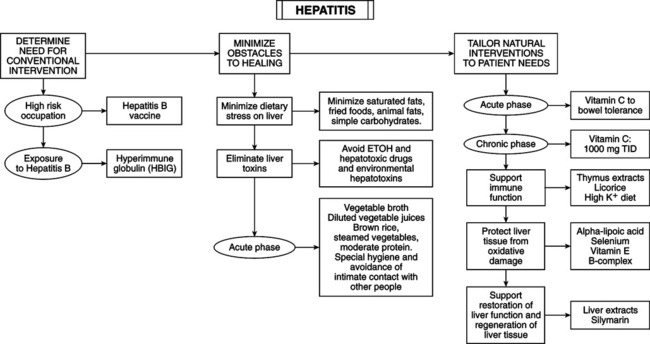
DIAGNOSTIC CONSIDERATIONS
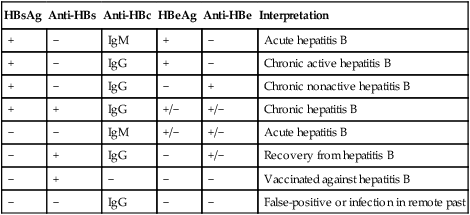
HBsAg
Anti-HBs
Anti-HBc
HBeAg
Anti-HBe
Interpretation
+
−
IgM
+
−
Acute hepatitis B
+
−
IgG
+
−
Chronic active hepatitis B
+
−
IgG
−
+
Chronic nonactive hepatitis B
+
+
IgG
+/−
+/−
Chronic hepatitis B
−
−
IgM
+/−
+/−
Acute hepatitis B
−
+
IgG
−
+/−
Recovery from hepatitis B
−
+
−
−
−
Vaccinated against hepatitis B
−
−
IgG
−
−
False-positive or infection in remote past
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Basicmedical Key
Fastest Basicmedical Insight Engine
