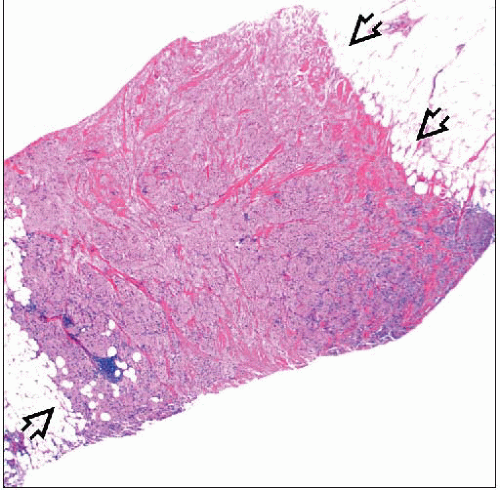
Granular Cell Tumor
Key Facts
Terminology
Previously termed “granular cell myoblastoma”
Tumor thought to arise from Schwann cells, consisting of granular cells (cells with abundant eosinophilic bubbly cytoplasm)
Clinical Issues
Rare; only 1 case per 100-200 cases of carcinoma
Presents as firm to hard palpable mass or as a density on screening mammography
Some tumors can retract skin or be adherent to chest wall
Majority of tumors are benign and cured by surgical excision
Rare reports of local recurrence
Very rare reports of malignant tumors with metastases to lymph nodes or lung
Image Findings
Most common in upper inner breast (carcinomas are most common in upper outer breast)
Ancillary Tests
Immunohistochemical studies are useful to distinguish granular cells from other types of cells
Granules seen by light microscopy correspond to numerous lysosomes by electron microscopy
Myelin figures are also present, supporting neural origin
Top Differential Diagnoses
Benign inflammatory lesions containing histiocytes
Invasive carcinoma (histiocytoid, secretory)
Metastatic tumors (renal cell carcinoma, melanoma)
Alveolar soft part sarcoma
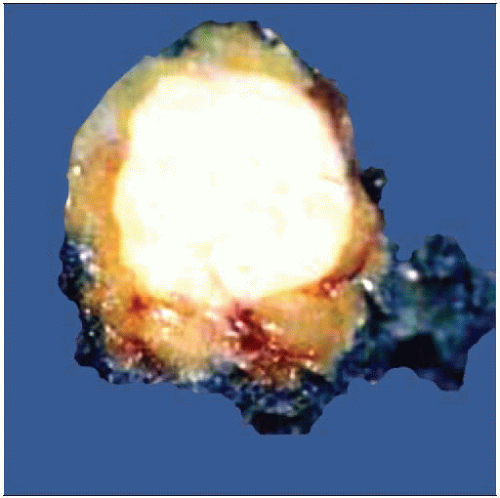 Granular cell tumors form solid firm masses that can be circumscribed or irregular. This tumor has a homogeneous white surface and pushing border in contrast to the surrounding yellow adipose tissue. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Granular cell tumor (GCT)
Synonyms
Granular cell myoblastoma
Definitions
Tumor thought to arise from Schwann cells, consisting of granular cells (cells with abundant eosinophilic bubbly cytoplasm)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare breast lesion: Only 1 GCT occurs for every 100-200 cases of carcinoma
Age
Occurs most commonly during childbearing years (range: 17-74 years of age)
Gender
Similar to other breast lesions, majority occur in women with only 10% in men
Ethnicity
African-American women are affected more commonly than Caucasian women
Presentation
Majority of patients present with solitary palpable mass that may be firm or hard
Most common in upper inner breast (carcinomas are most common in upper outer breast)
Rarely, multiple masses are present (5-10%)
Mass may retract skin or be adherent to chest wall
Smaller tumors may be detected as a density on mammographic screening
Natural History
Benign and slow growing
Rare reports of local recurrence
Very rare reports of malignant GCT with metastases to lymph nodes or lung
Treatment
Most tumors are completely excised by surgery
IMAGE FINDINGS
Mammographic Findings
Mass with irregular, circumscribed, or lobulated borders
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree