Gonadoblastoma
Steven S. Shen, MD, PhD
Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Tumor composed of mixture of seminomatous cells and immature sex cord tumor resembling Sertoli or granulosa cell tumors
Clinical Issues
Extremely rare
Occurs usually in patients with abnormal, dysgenetic gonads
Microscopic Pathology
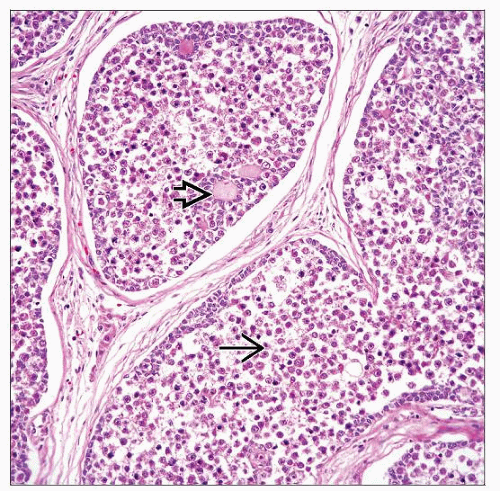
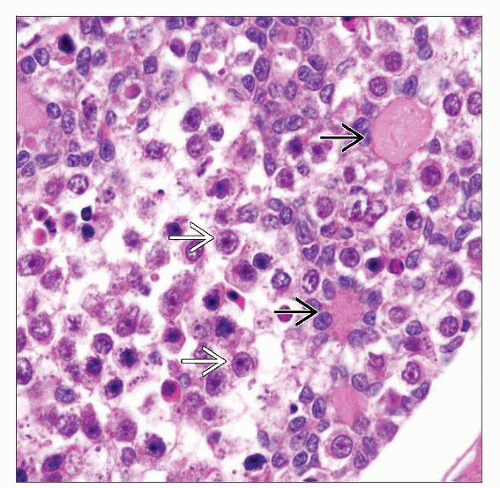
Nests of tumor cells composed of mixture of 2 types of cells (seminomatous germ cells and sex cord stromal cells)
Germ cells are large and round with vacuolated or clear cytoplasm, fine chromatin, and inconspicuous nucleoli
Sex cord stromal cells are usually immature Sertoli cells or granulosa cells, but rarely cells resembling Leydig cells or lutein-like cells
Small round to oval sex cord derivative forming Call-Exner bodies with central eosinophilic hyaline material
Marked hyalinization or calcification present within nests or stroma
Adjacent seminiferous tubules with intratubular germ cell neoplasia may be seen
Overgrowth of malignant germ cell tumor (usually seminoma) may obliterate gonadoblastomatous foci
Ancillary Tests
Germ cells (+) for PLAP, Podoplanin, Oct3/4, CD117
Stromal cells (+) for inhibin, calretinin, vimentin, and may be positive for cytokeratin
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Mixed germ cell and sex cord stromal cell tumor
Definitions
Tumor composed of mixture of seminomatous germ cells and immature sex cord tumor elements resembling Sertoli or granulosa cell tumors
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Extremely rare
Occurs usually in patients with abnormal, dysgenetic gonads
Age
Younger than 20 years old
Gender
20% phenotypically male, 80% phenotypically female (during early embryonic development, immature bi-potential gonads fail to differentiate along male pathway)
XY gonadal dysgenesis or X0-XY mosaicism may be seen
Presentation
Cryptorchidism, hypospadias or other ambiguous genitalia, and gynecomastia
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Bilateral gonadectomy is recommended and curative
Prognosis
Excellent if no associated invasive germ cell or malignant sex cord stromal tumor components
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Gray to yellow-brown mass with a soft, fleshy or firm and gritty cut surface
Streak gonads with incidental findings in very smallsized tumors
Invasive malignant germ cell tumor component, usually seminoma, results in larger tumors
Size
Range: Microscopic focus to 8 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Nests of tumor cells composed of mixture of 2 types of cells (seminomatous germ cells and sex cord stromal cells)
Germ cells are large and round with vacuolated or clear cytoplasm, central nuclei with fine chromatin and prominent nucleoli
Sex cord stromal cells are usually immature Sertoli cells or granulosa cells, but rarely cells resemble Leydig cells or luteinizing theca-like cells
Sex cord stromal cells are located at periphery of nests
Small round to oval sex cord derivative cells form Call-Exner bodies with central eosinophilic hyaline material
Marked hyalinization or calcification present within nests or stroma
Adjacent seminiferous tubules with intratubular germ cell neoplasia may be seen
Overgrowth of malignant germ cell tumor (usually seminoma) may obliterate gonadoblastomatous foci
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Neoplastic; nests of tumor cells with germ cells and sex cord stromal tumor
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Mixed germ cells and sex cord stromal cells
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
Germ cells positive for PLAP, Podoplanin(D2-40), Oct3/4, SALL4, CD117
Gonadal stromal cells positive for inhibin, calretinin, Melan-A(MART-1), vimentin; may be positive for cytokeratin
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Unclassified Mixed Germ Cell and Sex Cord Stromal Tumors
Occurs in patients with normal gonads and without cytogenetic abnormalities (normal XY chromosomes)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree