H&E at high power shows lipofuscin pigment 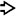 in centrizonal hepatocytes.
in centrizonal hepatocytes.
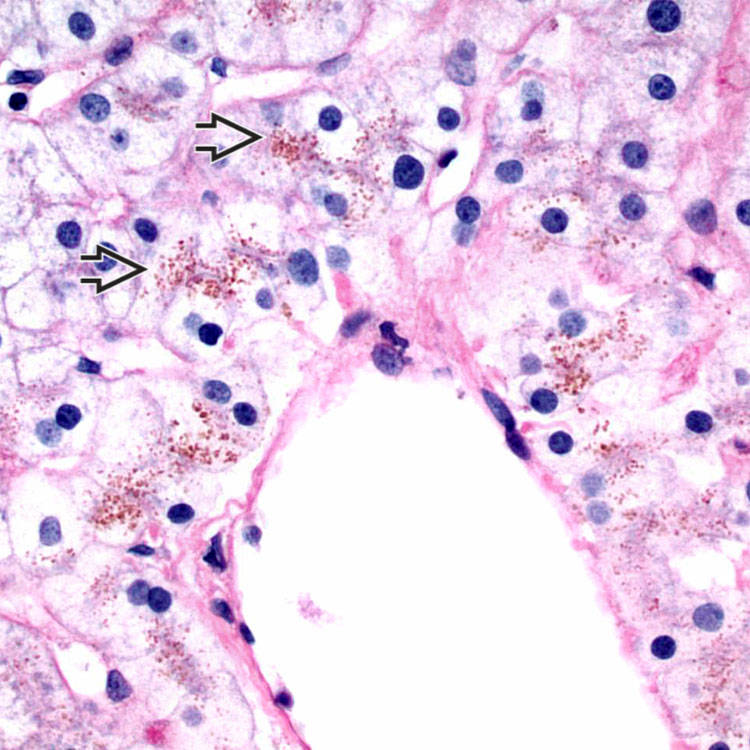
Periodic acid-Schiff with diastase digestion accentuates the granular pigment in centrizonal hepatocytes
 , even though the pigment is not PAS-D positive.
, even though the pigment is not PAS-D positive.
Fontana-Masson stain highlights the increased lipofuscin marked by black staining in the centrizonal hepatocytes.
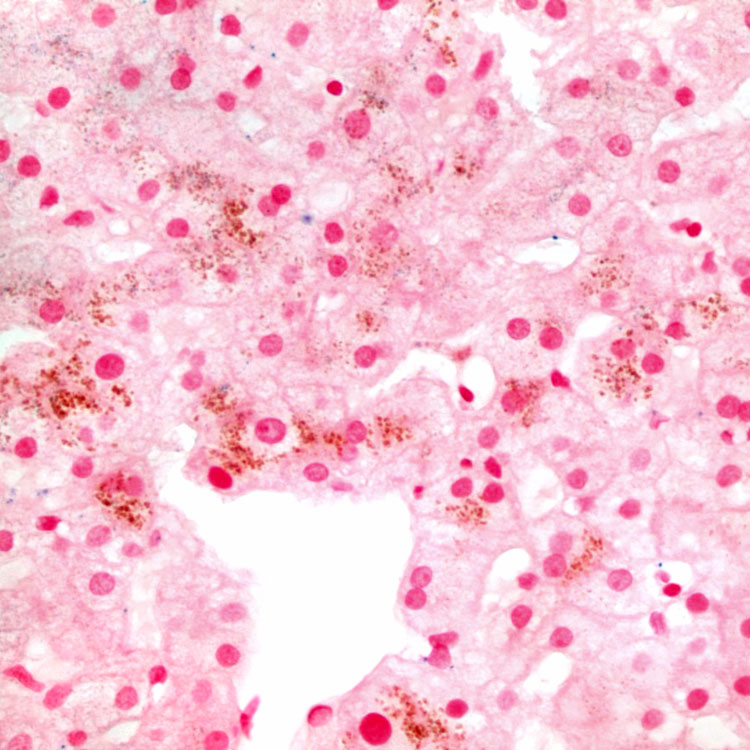
Prussian blue stain for iron is negative and helps to confirm that the cytoplasmic pigment is not hemosiderin.
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
• Age
 Often diagnosed at puberty, possibly related to increased hemoglobin turnover and inhibition of bilirubin glucuronidation by endogenous steroid hormones
Often diagnosed at puberty, possibly related to increased hemoglobin turnover and inhibition of bilirubin glucuronidation by endogenous steroid hormones




 Often diagnosed at puberty, possibly related to increased hemoglobin turnover and inhibition of bilirubin glucuronidation by endogenous steroid hormones
Often diagnosed at puberty, possibly related to increased hemoglobin turnover and inhibition of bilirubin glucuronidation by endogenous steroid hormonesStay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





