QUESTION 24.2
A. Bullous keratopathy
B. Chronic actinic keratopathy
C. Chronic herpes simplex keratitis
D. Fuchs endothelial dystrophy
E. Keratoconus
3. Which of the following types of corneal dystrophies is most frequently observed in corneal specimens submitted to the pathologist in the United States?
A. Fuchs endothelial dystrophy
B. Granular dystrophy
C. Lattice dystrophy
D. Macular dystrophy
E. Meesman juvenile epithelial dystrophy
4. A conjunctival biopsy is performed in a 50-year-old female with a history of chronic interstitial lung disease. The biopsy reveals nonnecrotizing granulomas, but stains and PCR analysis for microorganisms are negative. Which of the following is the most probable cause?
A. Cat scratch fever
B. Rheumatoid arthritis
C. Sarcoidosis
D. Treponema pallidum
E. Tularemia
5. Which of the following is the most common type of lymphoma affecting the conjunctiva and orbit?
A. Burkitt lymphoma
B. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
C. Follicular lymphoma
D. Hodgkin lymphoma
E. Marginal zone B-cell lymphoma
6. A 50-year-old woman undergoes excision of a yellowish nodule of the upper eyelid. The specimen is submitted for histologic evaluation with a clinical diagnosis of chalazion. This picture shows the microscopic appearance of the lesion. Which of the following is the correct diagnosis?
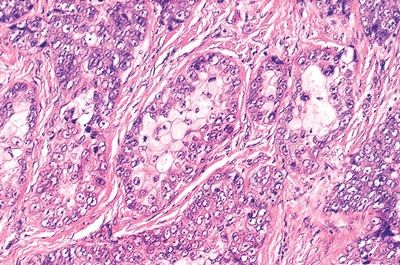
QUESTION 24.6
A. Chalazion
B. Hordeolum
C. Inverted follicular keratosis
D. Molluscum contagiosum
E. Sebaceous cell carcinoma
7. The microscopic appearance of an intraocular tumor is shown in this picture. Which of the following features is most significant in the prognosis of this neoplasm?
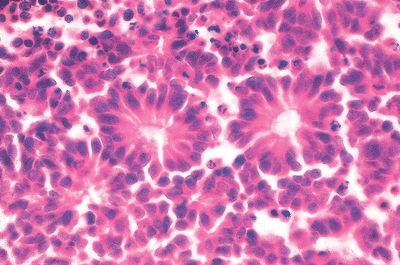
QUESTION 24.7
A. Extent of necrosis
B. Extent of optic nerve invasion
C. Immunohistochemical features
D. Mitotic activity
E. Presence of calcification
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


