15 Extraction methods in pharmaceutical analysis
Solvent extraction methods
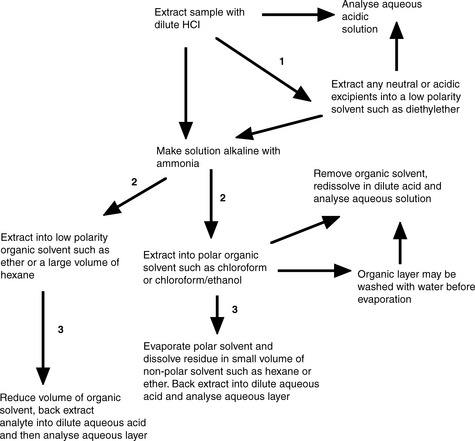
Extraction of organic bases and acids utilising their ionised and un-ionised forms
Salts of organic bases such as sulphates and hydrochlorides are often highly water soluble and the free bases are usually quite organosoluble, particularly in relatively polar solvents such as chloroform or mixtures of chloroform and ethanol. Similarly the sodium or potassium salts of organic acids are freely water soluble while the un-ionised acids are usually quite organosoluble. These properties can be used to advantage in designing an extraction procedure. A flow diagram for the extraction steps which can be used for the separation of an organic base from a formulation is shown in Figure 15.1.
Ion pair extraction
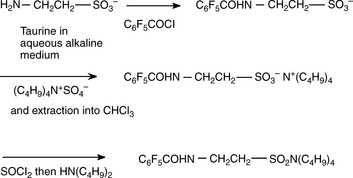
Ion pair extraction has also been used to extract polar analytes in bioanalytical procedures. Figure 15.2 exemplifies the determination of the amino acid taurine by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS); this figure also illustrates a useful property of amines (and phenols), which is that they will react more rapidly than water with an acylating reagent in an aqueous environment, thus improving their organosolubility. After acylation and ion pair extraction with tetrabutyl ammonium sulphate, the taurine is converted to an amide prior to analysis by GC–MS.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree