Duct Ectasia
Key Facts
Terminology
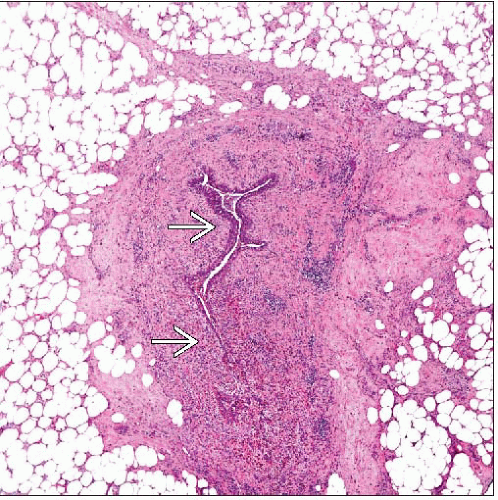
Large subareolar ducts dilate due to loss of elastic fibers with age (“duct ectasia”)
If ducts rupture, secretions spill into surrounding tissues resulting in chronic inflammation and fibrosis
Clinical Issues
Patients present with palpable irregular subareolar mass
Mass can be tethered to skin and nipple
Thick nipple discharge may be present
Mammography may show irregular mass, dilated ducts, &&/or calcifications
Top Differential Diagnoses
Squamous metaplasia of lactiferous ducts (SMOLD)
Plasma cell mastitis
Invasive carcinoma
Lymphoma
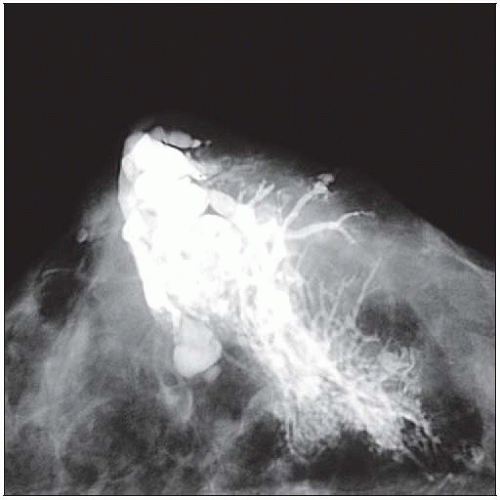 With age, the supporting tissue of large ducts below the nipple may weaken. The ducts can fill with inspissated secretions and become markedly dilated, as seen in this nipple duct injection. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Duct ectasia (DE)
Definitions
Benign condition characterized by ectasia (dilation) of large subareolar ducts with associated periductal inflammation and fibrosis
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Walls of large ducts weaken with age
Elastic fibers thin and become attenuated
Dilated ducts fill with secretory debris
Inspissated secretions can result in thick white nipple discharge
If rupture occurs, an intense chronic inflammatory response results in response to extravasated lipids
Periductal fibrosis forms an irregular mass
Fibrosis can involve overlying skin causing retraction