•
Defect in hepatocellular secretion of conjugated bilirubin
•
Autosomal recessive
•
Mutations in
ABCC2 (
CMOAT /
MRP2) gene, which codes for ATP-dependent organic anion transport localized to canalicular membrane
Results in impaired biliary canalicular transport of organic anions including conjugated bilirubin
Impaired glutathione excretion reduces bile salt-independent bile flow
•
Incidence
Rare
•
Age
Develop jaundice in teenage years
•
Sex
M = F
•
Ethnicity
Prevalence highest among Moroccan and Iranian Jews (1:1,300)
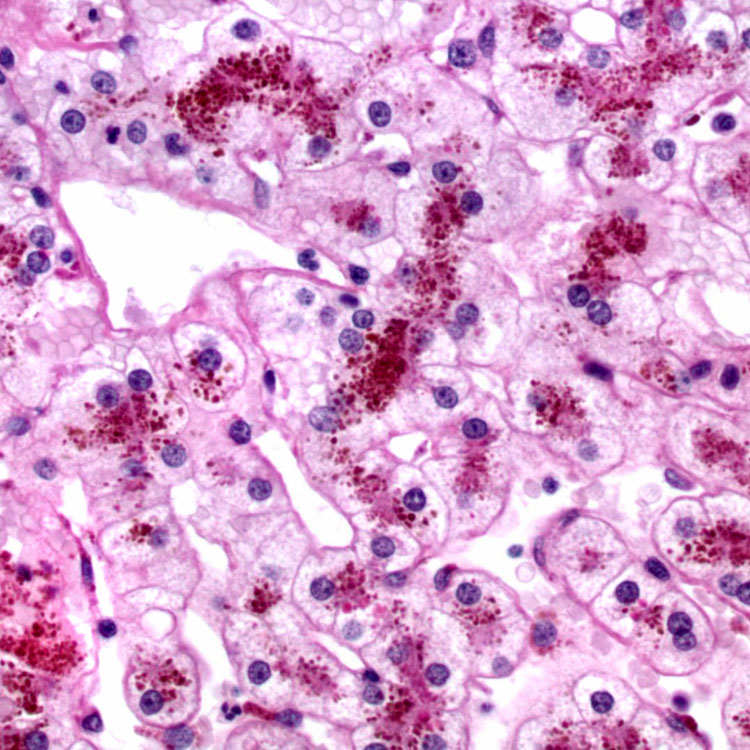
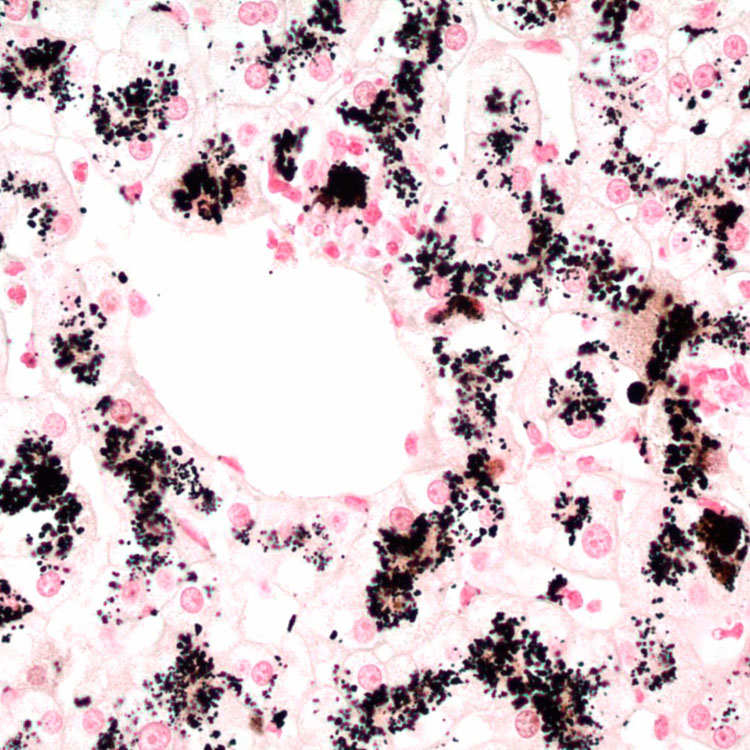
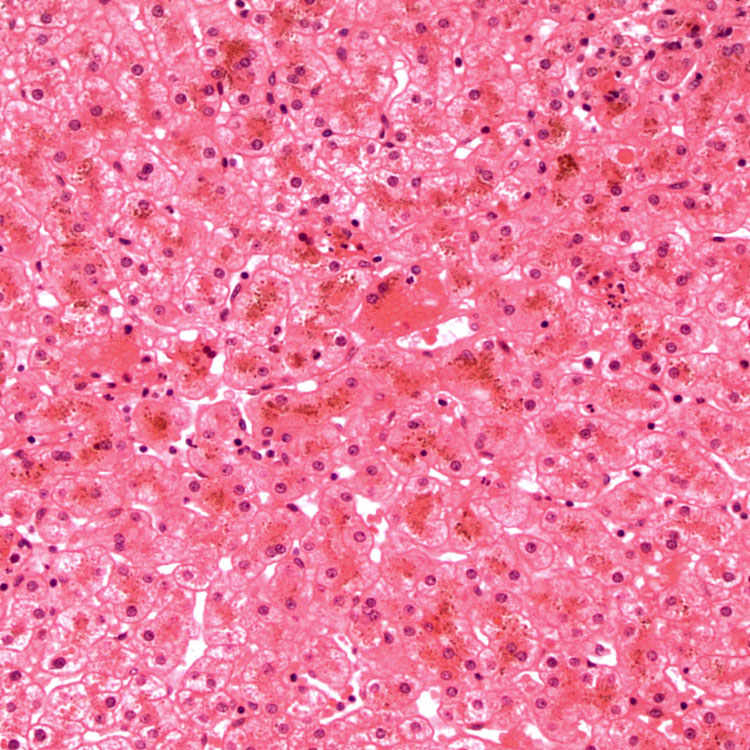
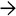 corresponding to the pigment within centrizonal hepatocytes.
corresponding to the pigment within centrizonal hepatocytes.