Commonly implicated drugs: Anabolic steroids, oral contraceptives, prochlorperazine, thiabendazole, warfarin
• Sclerosing duct injury: Fibrosis affecting large bile ducts similar to primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
Top Differential Diagnoses
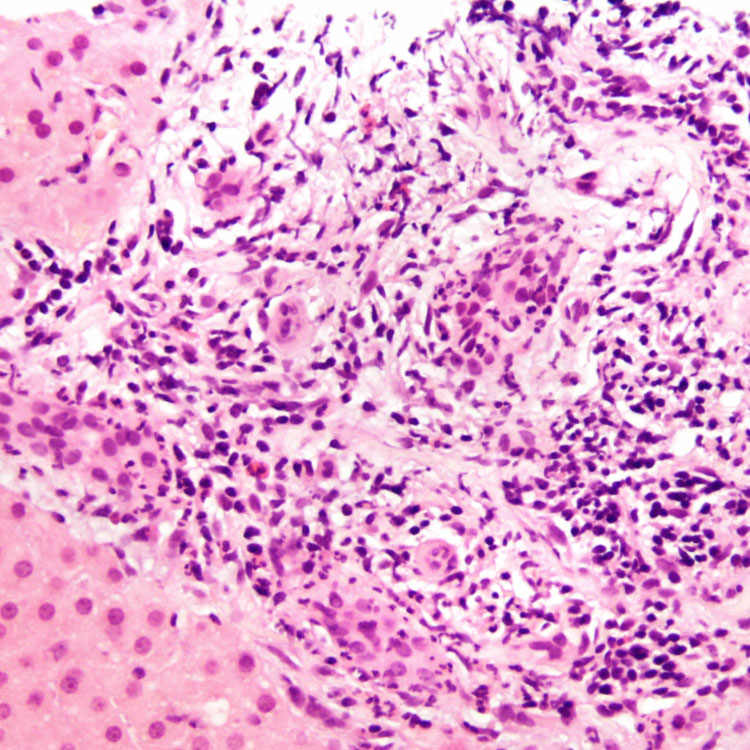
Portal edema, inflammation, and bile ductular reaction in drug-induced liver injury (DILI) may be indistinguishable from obstructive biliary disease on histologic grounds.
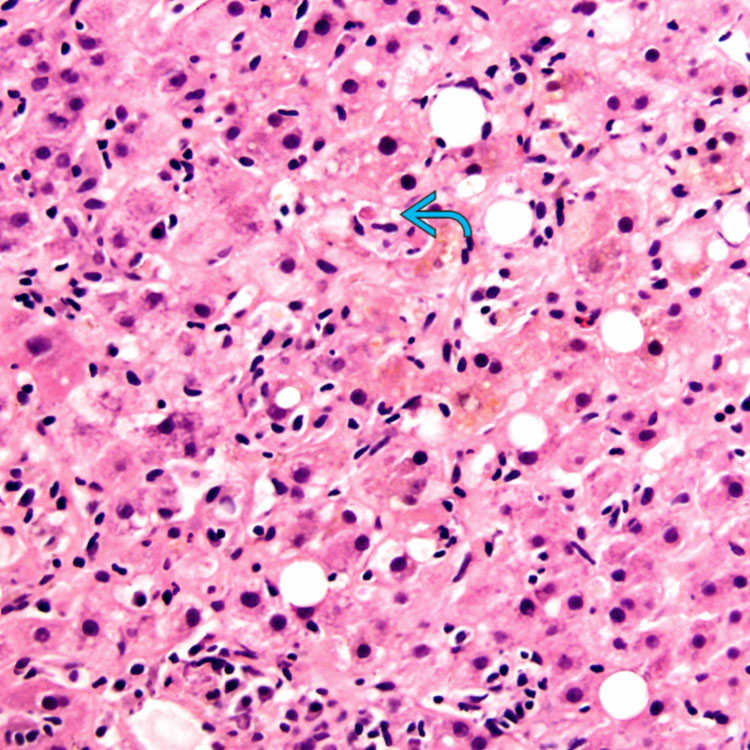
Cholestasis is accompanied by hepatitic features evidenced by lobular inflammation and hepatocellular dropout
 . This is the most common histologic pattern observed in DILI.
. This is the most common histologic pattern observed in DILI.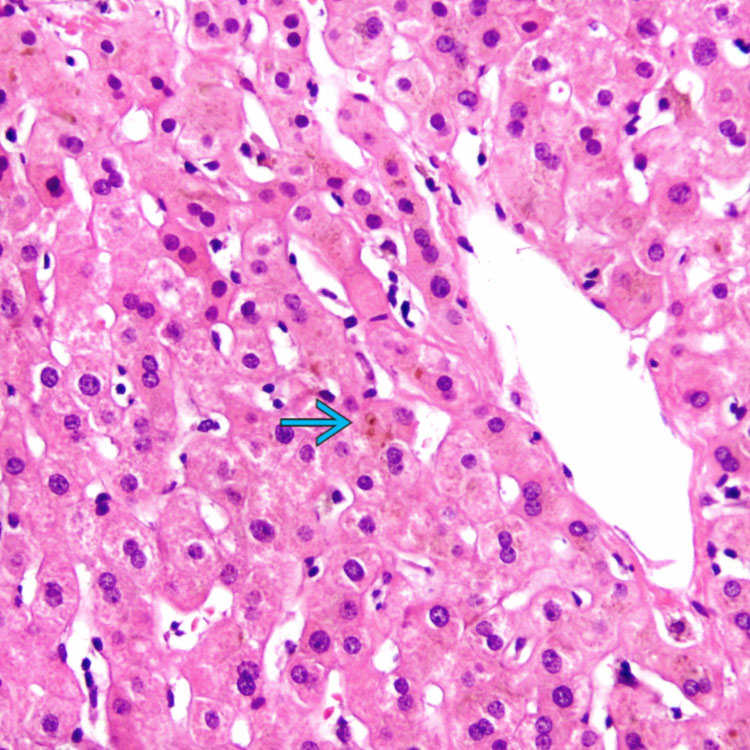
This pattern, also known as bland cholestasis, is characterized by bile in hepatocytes and canaliculi
 with no significant hepatocellular injury or inflammation. The portal tracts and interlobular bile ducts are normal and ductular reaction is not present in this pattern.
with no significant hepatocellular injury or inflammation. The portal tracts and interlobular bile ducts are normal and ductular reaction is not present in this pattern.ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
4 General Categories
Pure Cholestasis
• Commonly implicated drugs: Anabolic steroids, oral contraceptives, prochlorperazine, thiabendazole, warfarin
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





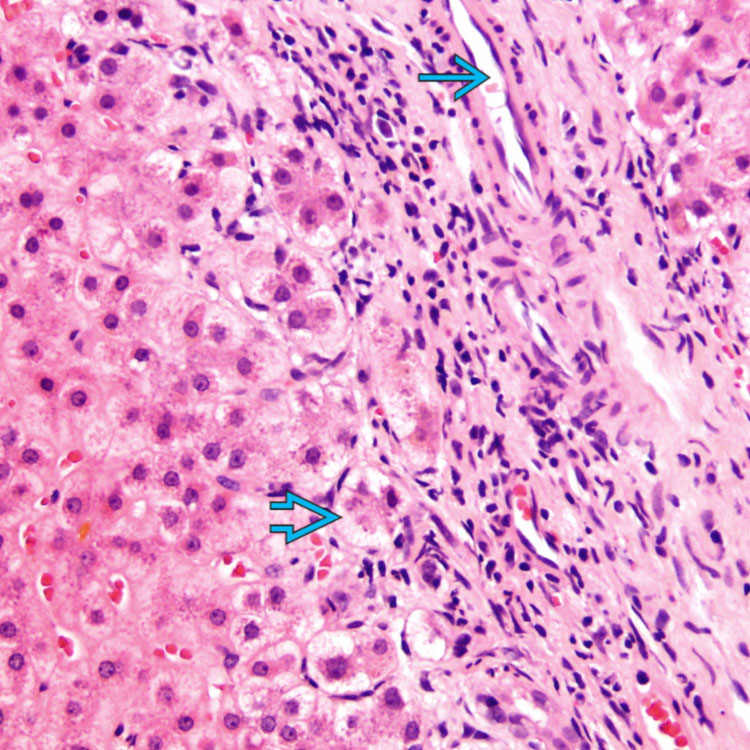
 . Swelling of periportal hepatocytes is present
. Swelling of periportal hepatocytes is present  (cholate stasis), a feature of prolonged cholestasis.
(cholate stasis), a feature of prolonged cholestasis.