(G-bands) characteristic of each of the 22 pairs of autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes. Darkly staining (positive) G-bands are rich in adenine (A) and thymine (T) residues and have relatively few genes, in contrast with lightly staining G-bands, which are rich in guanine (G) and cytosine (C) residues and are relatively gene rich.
TABLE 3.1 CYTOGENETIC METHODS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
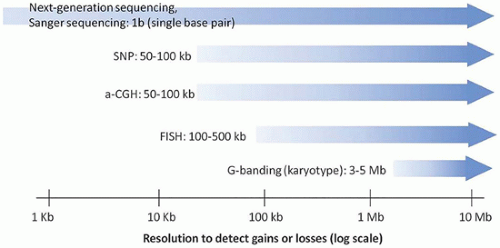 FIGURE 3-1 • Maximum resolution of cytogenetic and molecular laboratory methods. Ranges are approximate, and different laboratories may have different limits of detection and reportable ranges. |
TABLE 3.2 ONLINE RESOURCES FOR CYTOGENETICS AND MOLECULAR GENETICS | |
|---|---|
|
first-line test (9,10). Unlike G-banding and FISH, which use metaphase and interphase cells as the substrate, microarrays evaluate DNA that has been extracted from the specimen. These assays can detect copy number gains or losses with a markedly increased resolution (typically <100 kb, depending on the array configuration). Like FISH, arrays evaluate specimen DNA with fluorescent labeled probes. However, unlike FISH, in which a single probe set is applied to patient DNA affixed to a slide, in array-based testing, the patient DNA is applied to a slide to which thousands of oligonucleotide probes are affixed. The level of resolution of these arrays is dependent on the number of these probes in the array, the distance between probes on a chromosome, and the degree to which certain chromosomal regions are “targeted” (i.e., sampled by a larger number of probes than other regions).
TABLE 3.3 INDICATIONS FOR PRENATAL GENOMIC TESTING | |
|---|---|
|
TABLE 3.4 TISSUE SAMPLING FOR CYTOGENETIC STUDIES: TECHNICAL CONSIDERATIONS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
TABLE 3-5 GLOSSARY OF TERMS USED FREQUENTLY IN CYTOGENETICS | |
|---|---|
|
TABLE 3-6 INCIDENCE OF ANEUPLOIDY DURING DEVELOPMENT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TABLE 3-7 CHROMOSOMAL ANOMALIES IN SPONTANEOUS ABORTIONS | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||
development, leading to abnormalities of development. This is supported by the presence of common features between trisomies and segmental chromosomal duplications, including craniofacial abnormalities, structural cardiac abnormalities, and cognitive impairment. The “gene dosage effect” hypothesis asserts that a small set of genes, expressed at 1.5-fold greater than normal levels, is responsible for many of the phenotypic findings. Based on phenotypic mapping studies of individuals with duplications of part of chromosome 21 and clinical features of Down syndrome, a 1.6 to 5 Mb region of the long arm of chromosome 21 has been proposed to be the “Down syndrome critical region,” three copies of which are thought to account for many of the features of Down syndrome (7,65). In mice, duplication of part of chromosome 16 (homologous to human chromosome 21) results in phenotypic features similar to those in Down syndrome, including craniofacial alterations, changes in cerebellar architecture, and impaired learning and memory. Similar critical regions have been proposed for trisomy 13 (14) and trisomy 18 (66). Selective overexpression of smaller regions or single candidate genes in these homologous regions in the mouse may provide an experimental basis for understanding how trisomies influence development.
TABLE 3-8 MALFORMATIONS AND POSTNATAL DISORDERS ASSOCIATED WITH TRISOMY 21/DOWN SYNDROME (DS) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
is currently the most sensitive noninvasive screening method for detecting trisomy 21, with a detection rate of 98% to 100% and a false-positive rate of 0% to 0.3% (80,81). cfDNA testing is also in clinical use to detect trisomies 13 and 18; the sensitivity for detection of these aneuploidies ranges from 78% to 100%, with greater sensitivity for trisomy 18 than for trisomy 13 (80). Because cfDNA is mostly derived from placental trophoblast cells, one potential source of false-positive and false-negative results is confined placental or fetal mosaicism, estimated to affect 1 in 1000 to 1 in 4000 pregnancies (82). Therefore, despite the high specificity, confirmatory invasive diagnostic testing (by chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis) is required
before a decision is made to terminate the pregnancy (83). Another current testing option is an “integrated test” that includes quantitative measurement of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A, alpha-fetoprotein, unconjugated estriol, free β-human chorionic gonadotropin, and/or inhibin A in maternal serum, early second-trimester ultrasound evaluation of nuchal translucency, and maternal age (Table 3-11). This approach affords an 80% to 85% detection rate of trisomy 21, with a false-positive rate of 1% to 5% (84,85). Similar sensitivity and specificity have been reported for trisomy 18 based on a two-stage screening approach using maternal serum markers.
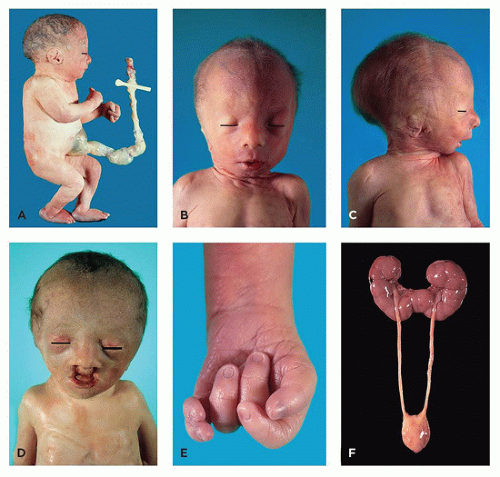
TABLE 3-9 MALFORMATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH TRISOMY 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TABLE 3-10 MALFORMATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH TRISOMY 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
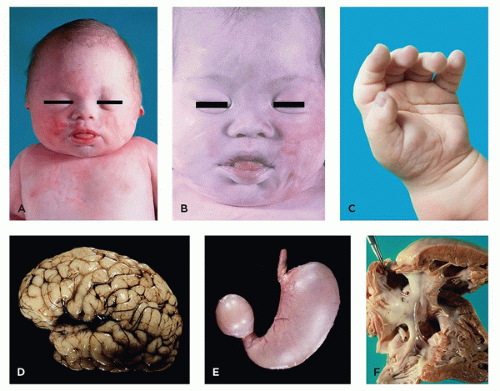
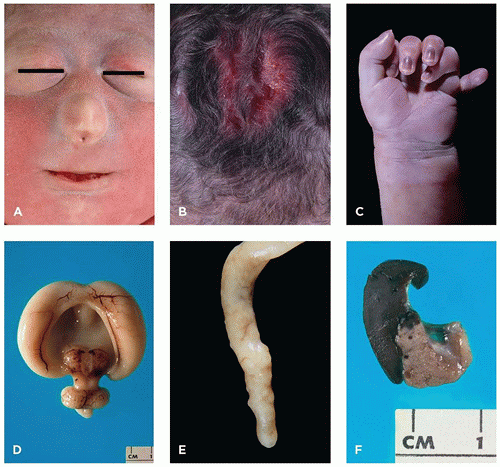 FIGURE 3-4 • Trisomy 13. A: Infant with cebocephaly (ocular hypotelorism and single nostril nose), one of the facial changes associated with holoprosencephaly. B: Aplasia cutis of the scalp. C: Postaxial polydactyly. D: Alobar holoprosencephaly. E: Appendiceal diverticula (“dinosaur tail”) are pathognomonic for trisomy 13, although not present in every case. F: Fusion of spleen (left) and tail of pancreas (note tiny splenic islands within the pancreas).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|