Bowenoid Papulosis
Elsa F. Velazquez, MD
Antonio L. Cubilla, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Most often related to HPV 16
Clinical Issues
Often multifocal
Benign-looking papules
Usually affecting skin of shaft of young adults
May also affect glans and coronal sulcus
Microscopic Pathology
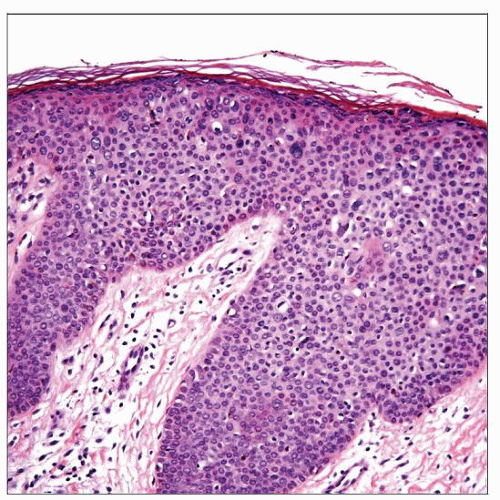
Proliferation of atypical basaloid and koilocytic cells as scattered single units or involving full thickness of epithelium
Most cases are indistinguishable from SCCIS
Top Differential Diagnoses
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCCIS)
Treated condyloma
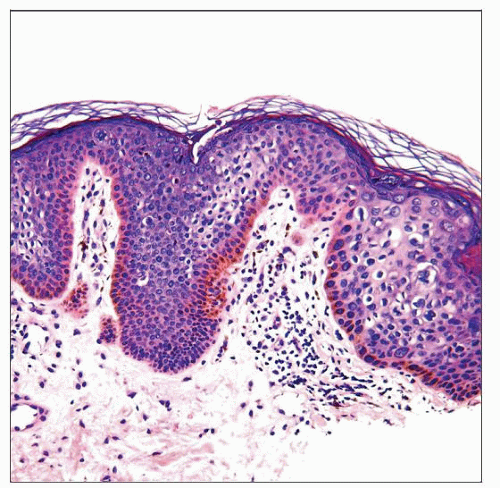 Patchy foci of atypia are present throughout the epidermis. Atypical cells vary from small basaloid to larger and more pleomorphic cells with koilocytic-like changes. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Bowenoid papulosis (BP)
Definitions
Multifocal HPV-related papular condition affecting anogenital region in young adults
Lesions exhibit spectrum of changes from dysplasia to in situ carcinoma; usually associated with favorable prognosis
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Related to high-risk types of HPV, especially type 16
Other types of HPV (18, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 39, 42, 48, 51, 52, 53, and 54) have also been implicated
Usually transmitted via sexual contact
Pathogenesis
Oncogenic HPV elaborate proteins that interfere with normal cellular homeostasis
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Unknown and probably underestimated
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree