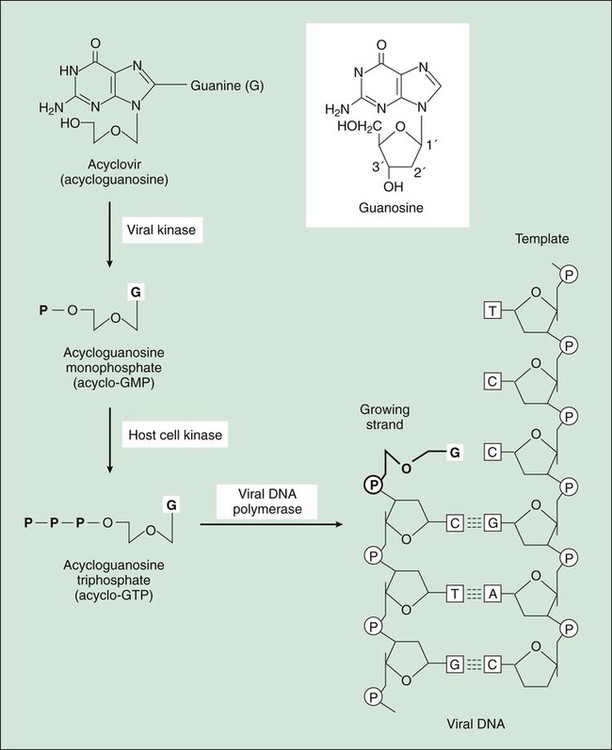
The nucleoside analogues are prodrugs that are phosphorylated by viral and host cell kinases to form active triphosphate metabolites (Fig. 43-1). In this process, the nucleoside analogues are initially converted to monophosphate metabolites by a virus-encoded thymidine kinase. The conversion occurs only in infected host cells, thereby contributing to the selective toxicity of the analogues. Host cell kinases subsequently convert the monophosphates to active triphosphate metabolites. The active metabolites then compete with endogenous nucleoside triphosphates and competitively inhibit viral DNA polymerase, which in turn prevents the synthesis of viral DNA. Some nucleoside analogues (e.g., acyclovir) are incorporated into nascent viral DNA and cause DNA chain termination because they lack the 3′-hydroxyl group required for attachment of the next nucleoside (see Fig. 43-1). Other analogues (e.g., ganciclovir and penciclovir) inhibit viral DNA polymerase but do not cause DNA chain termination. The properties and clinical uses of individual drugs for herpesvirus infections are compared in Tables 43-1 and 43-2. TABLE 43-1 Pharmacokinetic Properties of Antiviral Drugs* *Values shown are the mean of values reported in the literature. TABLE 43-2 Use of Drugs for Treating Herpesvirus Infections *Can be used for prophylaxis but not for treatment. †For treating patients with intolerance of or resistance to other drugs. Acyclovir, famciclovir, and valacyclovir are nucleoside analogues that are effective in the treatment of various HSV and VZV infections (see Table 43-2). These drugs are not sufficiently active against CMV to be effective in treating CMV infections, but acyclovir and valacyclovir can be used for prophylaxis of CMV infections, such as in bone marrow and organ transplant recipients and in persons with HIV infection. All three drugs are available for oral use. In addition, acyclovir is available for intravenous and topical use.
Antiviral Drugs
Drugs for Herpesvirus Infections
Nucleoside Analogues
Drug Properties
Chemistry and Mechanisms.
Pharmacokinetics and Indications.
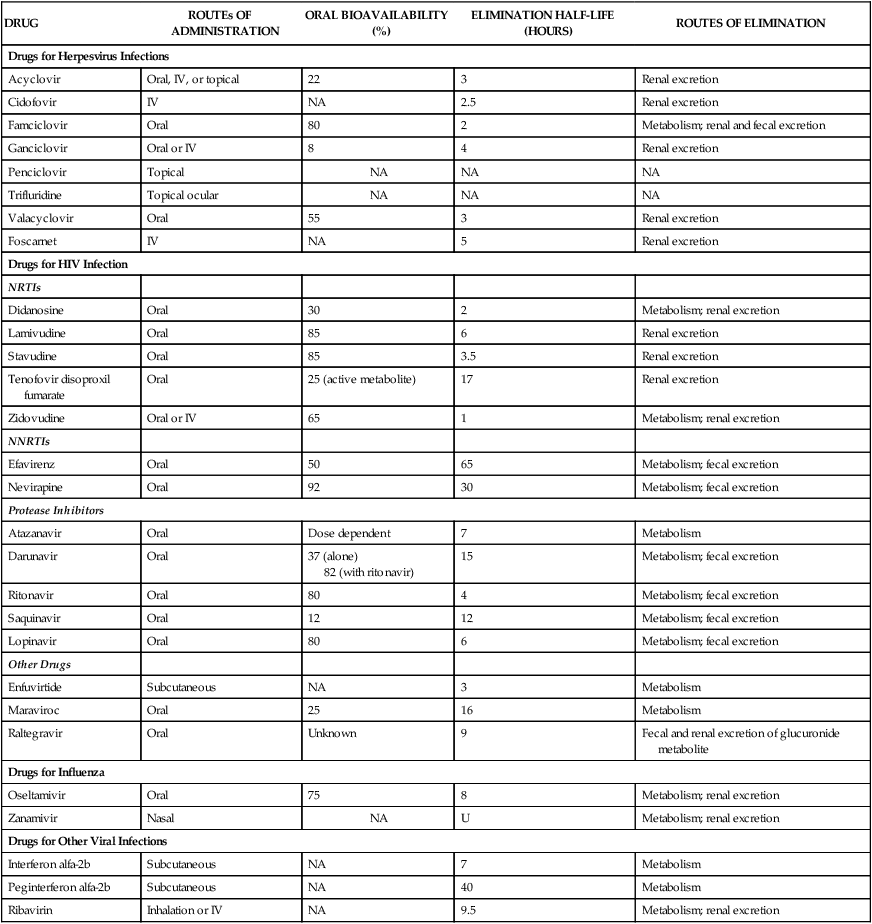
DRUG
ROUTEs OF ADMINISTRATION
ORAL BIOAVAILABILITY (%)
ELIMINATION HALF-LIFE (HOURS)
ROUTES OF ELIMINATION
Drugs for Herpesvirus Infections
Acyclovir
Oral, IV, or topical
22
3
Renal excretion
Cidofovir
IV
NA
2.5
Renal excretion
Famciclovir
Oral
80
2
Metabolism; renal and fecal excretion
Ganciclovir
Oral or IV
8
4
Renal excretion
Penciclovir
Topical
NA
NA
NA
Trifluridine
Topical ocular
NA
NA
NA
Valacyclovir
Oral
55
3
Renal excretion
Foscarnet
IV
NA
5
Renal excretion
Drugs for HIV Infection
NRTIs
Didanosine
Oral
30
2
Metabolism; renal excretion
Lamivudine
Oral
85
6
Renal excretion
Stavudine
Oral
85
3.5
Renal excretion
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate
Oral
25 (active metabolite)
17
Renal excretion
Zidovudine
Oral or IV
65
1
Metabolism; renal excretion
NNRTIs
Efavirenz
Oral
50
65
Metabolism; fecal excretion
Nevirapine
Oral
92
30
Metabolism; fecal excretion
Protease Inhibitors
Atazanavir
Oral
Dose dependent
7
Metabolism
Darunavir
Oral
37 (alone)
82 (with ritonavir)
15
Metabolism; fecal excretion
Ritonavir
Oral
80
4
Metabolism; fecal excretion
Saquinavir
Oral
12
12
Metabolism; fecal excretion
Lopinavir
Oral
80
6
Metabolism; fecal excretion
Other Drugs
Enfuvirtide
Subcutaneous
NA
3
Metabolism
Maraviroc
Oral
25
16
Metabolism
Raltegravir
Oral
Unknown
9
Fecal and renal excretion of glucuronide metabolite
Drugs for Influenza
Oseltamivir
Oral
75
8
Metabolism; renal excretion
Zanamivir
Nasal
NA
U
Metabolism; renal excretion
Drugs for Other Viral Infections
Interferon alfa-2b
Subcutaneous
NA
7
Metabolism
Peginterferon alfa-2b
Subcutaneous
NA
40
Metabolism
Ribavirin
Inhalation or IV
NA
9.5
Metabolism; renal excretion
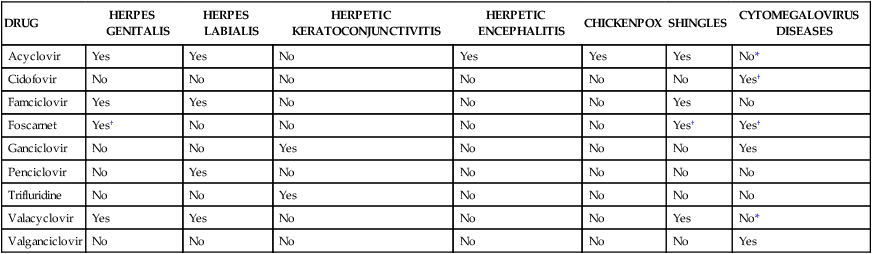
DRUG
HERPES GENITALIS
HERPES LABIALIS
HERPETIC KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS
HERPETIC ENCEPHALITIS
CHICKENPOX
SHINGLES
CYTOMEGALOVIRUS DISEASES
Acyclovir
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
No*
Cidofovir
No
No
No
No
No
No
Yes†
Famciclovir
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
Yes
No
Foscarnet
Yes†
No
No
No
No
Yes†
Yes†
Ganciclovir
No
No
Yes
No
No
No
Yes
Penciclovir
No
Yes
No
No
No
No
No
Trifluridine
No
No
Yes
No
No
No
No
Valacyclovir
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
Yes
No*
Valganciclovir
No
No
No
No
No
No
Yes
Acyclovir, Famciclovir, and Valacyclovir
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Antiviral Drugs
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue