Chapter 39 Adrenocorticosteroids
| Abbreviations | |
|---|---|
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| AVP | Arginine vasopressin |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CRH | Corticotropin-releasing hormone |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| GR | Glucocorticoid receptor |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| HPA | Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal |
| MR | Mineralocorticoid receptor |
| MSH | Melanocyte-stimulating hormone |
| POMC | Proopiomelanocorticotropin |
| StAR | Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein |
| t1/2 | half-life |
Therapeutic Overview
| Therapeutic Overview |
|---|
| Glucocorticoids |
| Replacement therapy in adrenal insufficiencies |
| Antiinflammatory and immunosuppressive action |
| Myeloproliferative diseases |
| Mineralocorticoids |
| Replacement therapy in primary adrenal insufficiencies |
| Hypoaldosteronism |
| Steroid Synthesis Inhibitors |
| Adrenocortical hyperfunction |
| Steroid Receptor Blockers |
| Glucocorticoid excess |
| Mineralocorticoid excess |
glucocorticoids, a withdrawal plan must be instituted, or serious morbidity and even mortality may occur. Safe removal from dependence on exogenous glucocorticoids requires systematic and gradual lowering of the administered dosage, which may require up to a year for the natural secretion of cortisol to recover. Also, during periods of emotional or physiological stress, such patients may require glucocorticoid supplementation.
Mechanisms of Action
The biosynthetic pathways and structures for cortisol and aldosterone are shown in Figures 38-1 and 38-2.
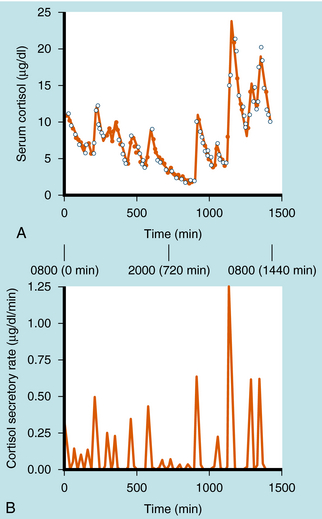
Cortisol synthesis and secretion are regulated physiologically by ACTH synthesized in the anterior pituitary. ACTH is synthesized in the corticotrope cells of the anterior pituitary as part of the large precursor molecule proopiomelanocorticotropin (POMC), which is proteolytically cleaved to form ACTH, β-endorphin, and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). β-Endorphin has opioid effects that reduce pain perception (see Chapter 36), whereas MSH acts on the melanocytes that confer skin pigmentation. The hyperpigmentation that is associated with overproduction of ACTH is thought to be associated with overproduction of MSH. The POMC gene is also transcribed in the posterior pituitary, where the POMC precursor is differentially cleaved into endorphins and MSH, but not ACTH. ACTH is secreted episodically from the anterior pituitary, and these pulses can contribute to the larger ACTH fluctuations regulated by circadian rhythms. Generally, the ACTH pulses exhibit greater frequency and magnitude in the early morning compared with the early afternoon. There is a close correlation of ACTH and cortisol secretion, which is characterized by a sharp rise in plasma concentrations followed by a slower decline, with approximately 8 to 10 major bursts of cortisol secretion occurring daily (Fig. 39-1).
The rate-limiting enzyme in steroid synthesis converts cholesterol to pregnenolone by the P450 cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme (see Fig. 38-1), desmolase, located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. ACTH-stimulated increases in cAMP accelerate transcription rates of the gene coding for this enzyme and most other enzymes in the cortisol biosynthetic pathway.
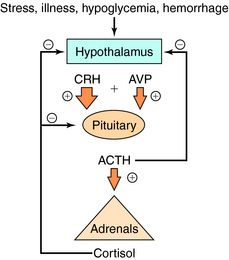
Serum concentrations of ACTH are modulated by integrated stimulatory signals from hypothalamic releasing peptides and by inhibitory feedback from circulating cortisol (Fig. 39-2). Physiologically, serum ACTH concentrations are increased in response to metabolic stresses such as severe trauma, illness, burns, hypoglycemia, hemorrhage, fever, exercise, and psychological stresses such as anxiety and depression. These stresses are believed to induce physiological changes by altering the release of hypothalamic factors. Two hypothalamic peptides, corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and to a lesser extent arginine vasopressin (AVP or antidiuretic hormone), both act to stimulate ACTH release. These peptides bind to distinct membrane receptors on the corticotrope. CRH exerts its effect primarily via cAMP-dependent pathways, whereas AVP stimulates phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis and activates protein kinase C. CRH is the most important physiological stimulating factor and can be used pharmacologically to screen for appropriate corticotrope function. CRH may also increase POMC gene transcription and processing, thus increasing available peptide stores for subsequent release.
All natural and synthetic glucocorticoids act by binding to specific receptors that are members of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Glucocorticoids bind to both glucocorticoid receptors (GR, also known as NR3C1) and mineralocorticoid receptors (MR, also known as NR3C2). These receptors are closely related in their overall DNA sequence but differ considerably in the N-terminal antigenic region of the ligand-binding domains. Both receptors have similar binding affinities for glucocorticoids and are expressed in many cell types including liver, muscle, adipose tissue, bone, lymphocytes, and pituitary. The receptors are proteins consisting of approximately 800 amino acids, which can be divided into functional domains similar to those for other steroid receptors (see Chapter 1). The structure of the steroid receptor is characterized by zinc finger domains formed by stabilization of protein folds by zinc interaction with cysteine residues. In the cytoplasm the inactive steroid receptor exists as a heteromer associated with cytoplasmic proteins (e.g., heat shock protein 90). The interaction of this complex with a steroid leads to dissociation of the accessory protein-receptor complex. This sequence of events is generally called glucocorticoid receptor activation. Phosphorylation of the receptor stabilizes a configuration, the nuclear location signal that interacts with importin at nuclear pores and initiates translocation of the hormone-receptor complex across the nuclear membrane. Once inside the nuclear membrane, the steroid-receptor complex interacts at specific palindromic sites on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), termed glucocorticoid-responsive elements. The binding to DNA is stabilized by the interaction of the zinc finger structures with the major groove of DNA, and specificity is partially conferred by the sequence of the palindromic sites. Specificity among different steroids appears to be conferred by the structure of the steroid-occupied receptor, amino acid sequence of the DNA binding region of the receptor protein, especially the Zn fingers, nucleotide sequence of the DNA binding motif and space between half sites, and chromatin architecture of the gene promoter at sites of interaction of bound receptor protein and DNA. The presence of the specific glucocorticoid response elements in the promoter region of specific genes allows steroids to alter transcription (see Chapter 1).
Aldosterone is the major mineralocorticoid produced by the adrenal cortex and acts primarily at the distal portion of the convoluted renal tubule to promote reabsorption of Na+ and the excretion of K+ (see Chapter 21). Adrenal secretion of aldosterone is controlled by the renin-angiotensin system and the circulating concentration of K+. ACTH stimulates aldosterone formation but plays a secondary role in the regulation of aldosterone secretion.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree