Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Invasive carcinoma composed of 2 cell populations: Luminal-like cells and myoepithelial-like cells
Rare; only 0.1% of breast cancers
Clinical Issues
Excellent prognosis: 90-100% survival at 10 years
Most frequently presents as palpable circumscribed or lobulated mass
These carcinomas will score as having poor prognosis using either 21 gene recurrence score or 70 gene prognosis profile
Therefore, histologic type is more important than gene expression profiling in predicting outcome for adenoid cystic carcinomas
Microscopic Pathology
3 histologic patterns
Cribriform: Most common pattern
Reticular-tubular: Tumor cells are surrounded by predominant component of stroma
Solid: Myoepithelial cells predominate with few luminal-type cells
Grading has been suggested but does not correlate well with clinical outcome
Top Differential Diagnoses
Invasive cribriform carcinoma
Adenomyoepithelial carcinoma
Ductal carcinoma in situ, cribriform type
Collagenous spherulosis
Cylindroma
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC)
Definitions
Invasive carcinoma composed of 2 cell populations: Luminal-like cells and myoepithelial-like cells
Rare; only 0.1% of breast cancers
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Most frequently presents as palpable circumscribed or lobulated mass below the nipple
Some carcinomas are tender
Rarely presents as mammographic mass; may be lobulated or irregular
Most patients are women; rare cases are reported in men
Average age: 50-65 years
Prognosis
Excellent prognosis
90-100% survival at 10 years
Local recurrence: 6% of patients
Axillary lymph node metastasis: 3% of patients
Distant metastasis and death: 3% of patients
Most common site is lung; also reported to bone, liver, brain, and kidney
These carcinomas will score as having a poor prognosis using either 21 gene recurrence score or 70 gene prognosis profile
Therefore, histologic type is more important than gene expression profiling in predicting outcome for ACC
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Firm, white, circumscribed or ill-defined mass
Microscopic extent of tumor may be greater than appreciated grossly due to minimal stromal response associated with peripheral infiltrating tumor nests
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
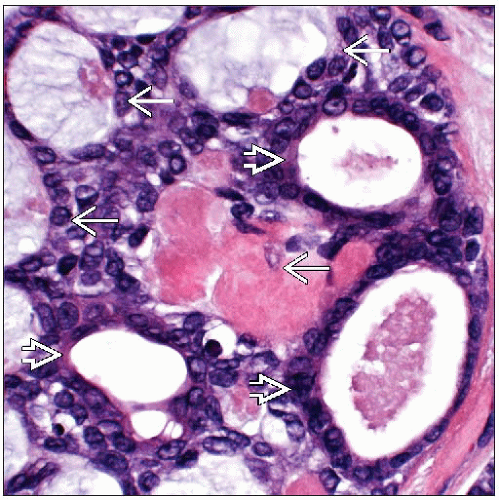
3 histologic patterns
Cribriform: Most common pattern
Reticular-tubular: Tumor cells are surrounded by predominant component of stroma
Solid: Myoepithelial cells predominate with few luminal-type cells
Large cribriform spaces are lined by myoepithelial-type cells
Spaces are filled with basement membrane-type material that can be collagenous, myxoid, or mucinous
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree