Large areas of fat necrosis along with variable parenchymal necrosis
Top Differential Diagnoses
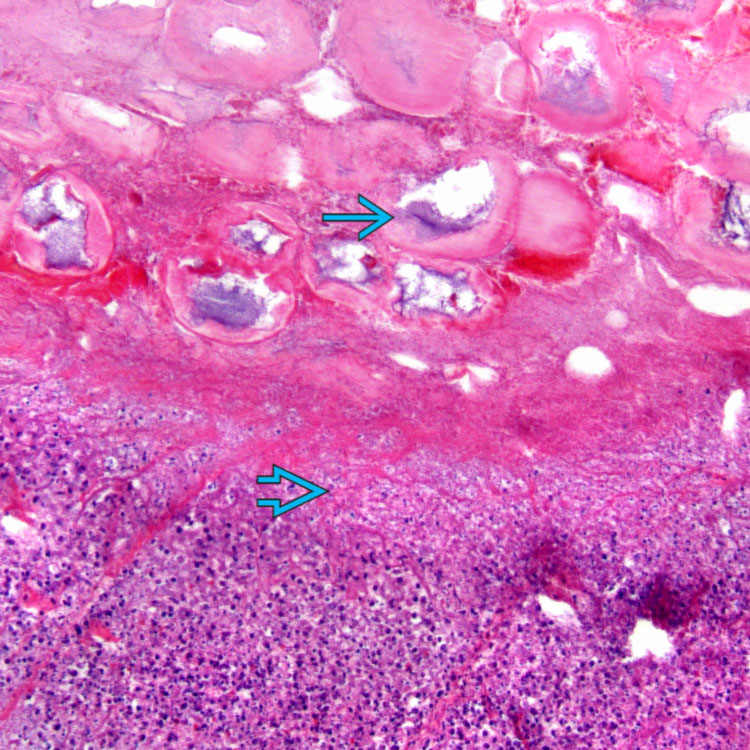
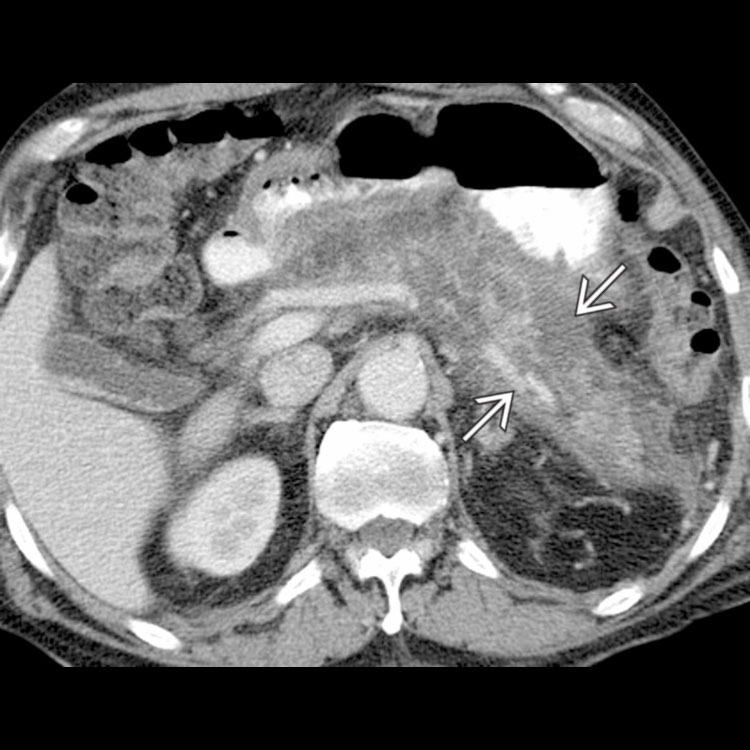
Pancreatic necrosis
 and saponification of peripancreatic fat with calcification
and saponification of peripancreatic fat with calcification  are shown in a patient with acute pancreatitis.
are shown in a patient with acute pancreatitis.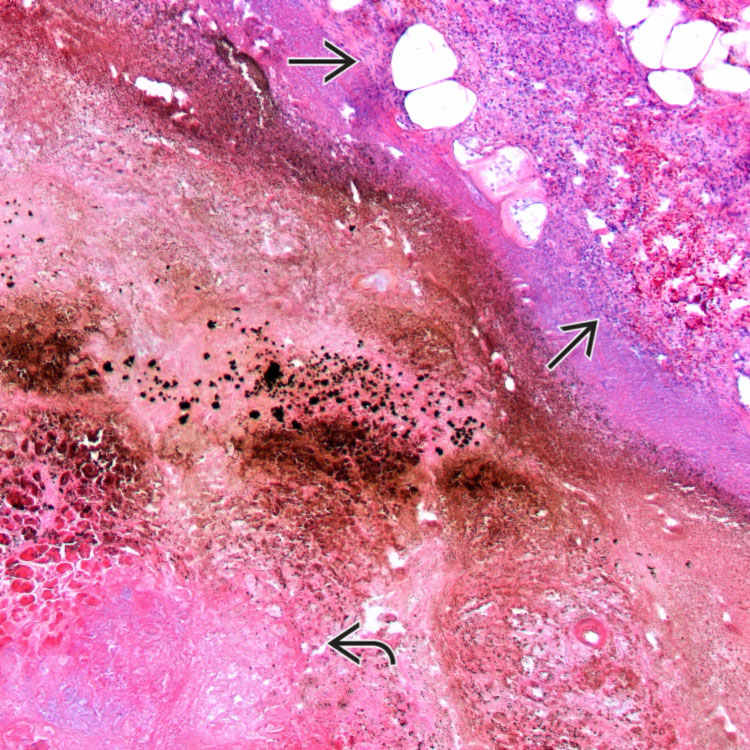
Trypsinogen activation is a key step in the development of acute pancreatitis. The release of digestive enzymes results in fat necrosis with acute inflammation
 and pancreatic parenchymal necrosis
and pancreatic parenchymal necrosis  .
.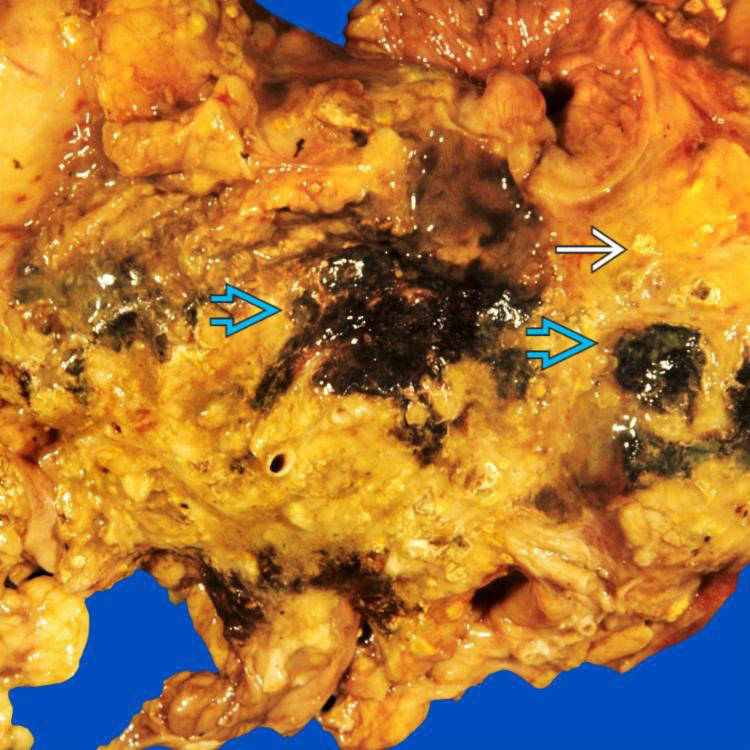
Gross examination reveals chalky white foci of fat necrosis
 and black areas of hemorrhage
and black areas of hemorrhage  .
.




 .
.




