Inflammation may be sparse in early disease
• Transmural fibrosis and Rokitansky-Aschoff (RA) sinuses, stigmata of chronic cholecystitis, may be present
Top Differential Diagnoses
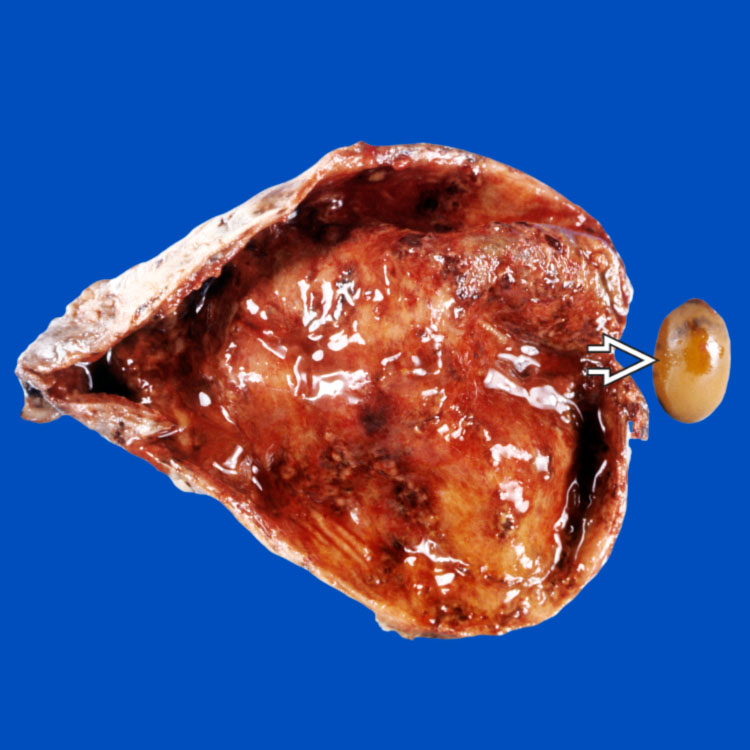
The thickened wall and congested mucosa suggest acute cholecystitis in this gallbladder. The gallstone
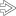 impacted in the neck of the gallbladder was the etiology of acute cholecystitis.
impacted in the neck of the gallbladder was the etiology of acute cholecystitis.
Early acute cholecystitis may show marked edema and hemorrhage but minimal inflammation. Dilation of capillaries and lymphatics can occur. Also note the reactive fibroblasts
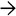 .
.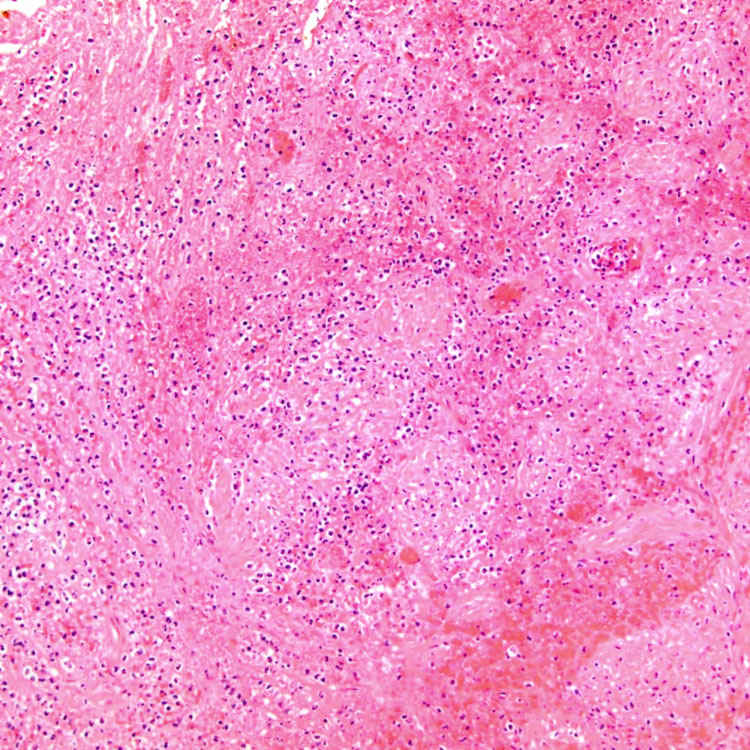
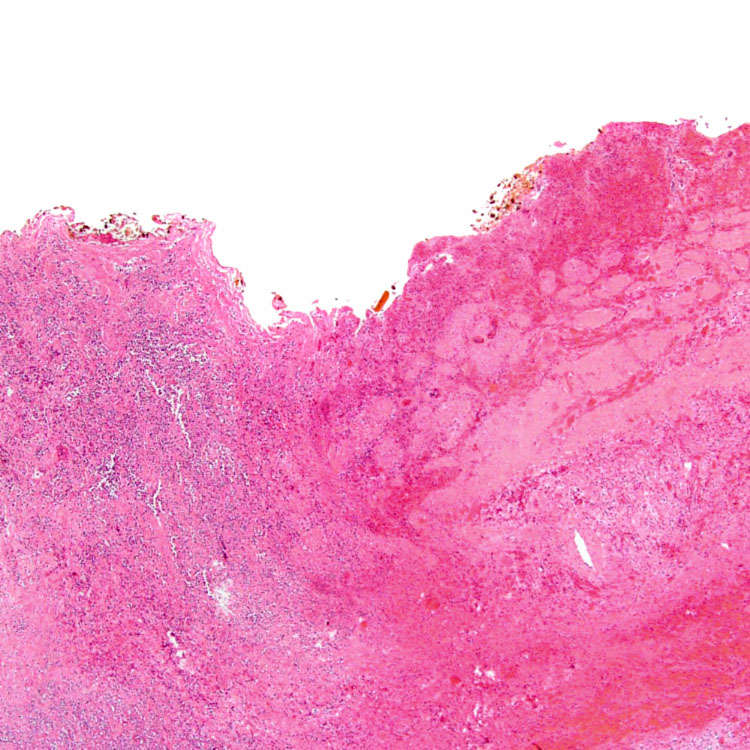
A case of severe acute cholecystitis shows mural necrosis, fresh hemorrhage, and a prominent neutrophilic exudate.
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree