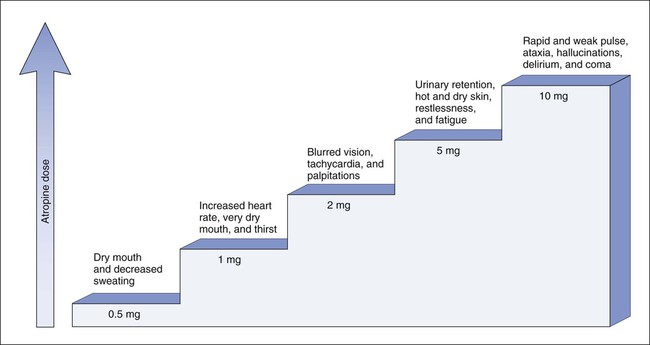
Atropine, scopolamine, and hyoscyamine are examples of belladonna alkaloids. The belladonna alkaloids can be highly toxic and are sometimes the cause of accidental or intentional poisonings (Box 7-1). In fact, atropine was named after Atropos, one of the Fates in Greek mythology, who was known for cutting the thread of life. The muscarinic blockers inhibit the effects of parasympathetic nerve stimulation and thereby relax smooth muscle, increase heart rate and cardiac conduction, and inhibit exocrine gland secretion. As shown in Figure 7-1, as the dose of atropine increases, the severity of its effects increases. The signs of atropine toxicity are expressed by the mnemonic “dry as a bone, blind as a bat, red as a beet, and mad as a hatter.”
Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonists
Muscarinic Receptor Antagonists
Belladonna Alkaloids
Atropine and Scopolamine
Pharmacologic Effects
Indications
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonists
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue