QUESTION 51.2
A. Herpes simplex type 1
B. Herpes simplex type 2
C. Herpes zoster
D. Human papillomavirus
E. Poxvirus
3. The lesion known as condyloma latum is caused by:
A. Calymmatobacterium granulomatis
B. Chlamydia trachomatis
C. Haemophilus ducreyi
D. Human papillomavirus
E. Treponema pallidum
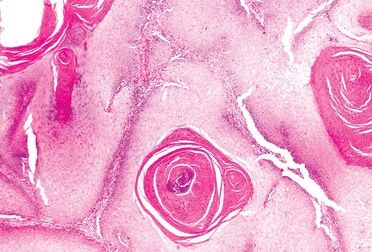
4. A 28-year-old woman presents with a large polypoid vulvar mass, which is excised. At low magnification, the lesion appears as in this photomicrograph. There is no nuclear atypia or mitotic activity. The most probable diagnosis is:
QUESTION 51.4
A. Aggressive angiomyxoma
B. Angiomyofibroblastoma
C. Fibroepithelial polyp
D. Hemangioma
E. Leiomyoma with myxoid features
5. The major difference between angiomyofibroblastoma and aggressive angiomyxoma of the vulva is related to:
A. Age of patients
B. Immunohistochemical phenotype
C. Macroscopic appearance
D. Likelihood of recurrence
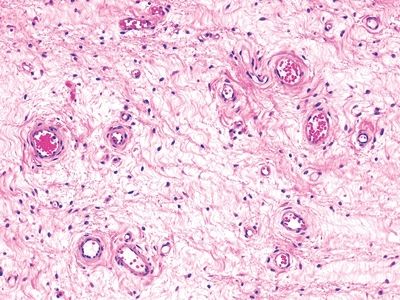
6. A biopsy of a dry, itchy plaque on the vulva of a 55-year-old woman shows the histologic changes seen in this picture. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
QUESTION 51.6
A. Differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
B. Lichen sclerosus
C. High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL)
D. Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
E. Squamous hyperplasia
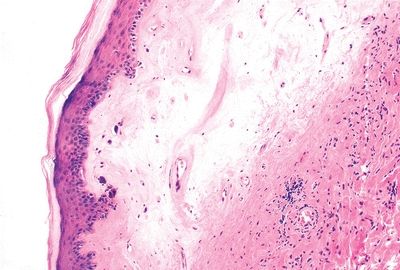
7. These pictures show three squamous lesions associated with increased risk of vulvar SCC. Which one of them is most often associated with HPV infection?
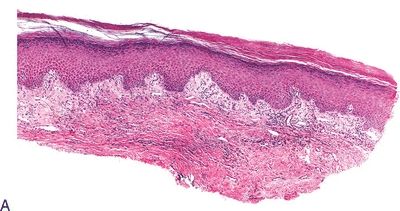
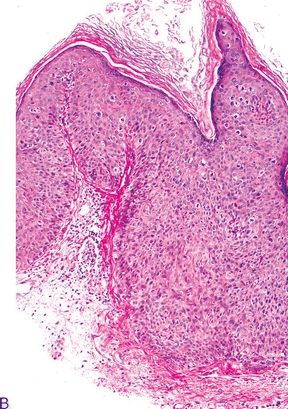
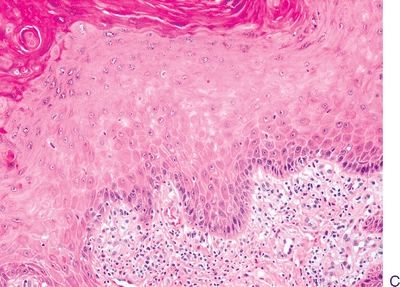
QUESTION 51.7
A. Lesion A
B. Lesion B
C. Lesion C
8. A vulvar mass shows a keratinizing neoplasm, as seen in this picture. Which of the following is true about this neoplasm?
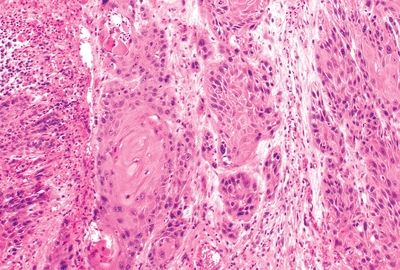
QUESTION 51.8
A. Characterized by a condylomatous appearance
B. Frequently found in association with squamous hyperplasia
C. Most commonly occurs in young women
D. Often associated with bowenoid-type VIN
E. Usually associated with HPV type 16 or 33
A. Adenoid squamous
B. Basaloid
C. Sarcomatoid
D. Verrucous
E. Warty
10. Which of the following features distinguishes Paget disease of the vulva from Paget disease of the breast?
A. Immunoreactivity for apocrine marker (GCDFP-15)
B. Immunoreactivity for epithelial markers
C. Immunoreactivity for HMB-45
D. Presence of pruritic crusted erythema
E. Underlying type of carcinoma
11. A 35-year-old Caucasian woman undergoes excision of a small, well-circumscribed, ulcerated nodule located in the interlabial sulcus. Its histologic appearance is demonstrated in this picture. Which of the following breast lesions is morphologically similar to this tumor?
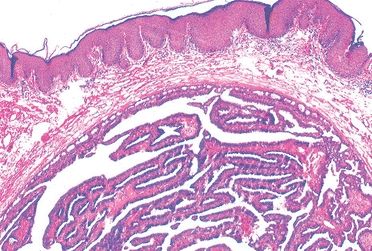
QUESTION 51.11
A. Adenomyoepithelioma
B. Fibroadenoma
C. Hidradenoma papilliferum
D. Myoepithelioma
E. Paget disease
12. A true statement concerning vaginal adenosis is:
A. Inapparent on gross inspection
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree