QUESTION 53.3
A. Early proliferative phase
B. Midproliferative phase
C. Late proliferative phase
D. Interval endometrium
E. Early secretory phase (postovulatory days 2 to 5)
F. Midsecretory phase (postovulatory days 6 to 8)
G. Late secretory phase (postovulatory days 9 to 14)
4. An endometrial biopsy reveals endometrial glands lined by cells with pleomorphic large nuclei and abundant clear cytoplasm, as shown in the picture. Mitotic figures are not seen. This histologic appearance may be found in all of the following conditions, EXCEPT:
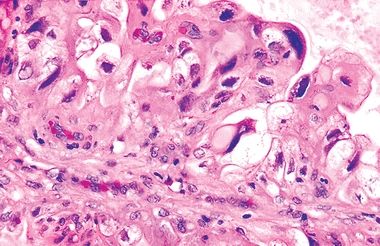
QUESTION 53.4
A. Ectopic pregnancy
B. Exogenous hormonal administration
C. Gestational trophoblastic disease
D. Postmenopause
E. Uterine pregnancy
5. An endometrial biopsy from a patient with an intrauterine device (IUD) is evaluated for assessment of possible chronic endometritis. This diagnosis would be confirmed by finding:
A. Granulomas
B. Lymphocytic infiltration
C. Neutrophilic infiltration
D. Plasmacellular infiltration
E. Viral inclusions
6. Which of the following endometrial changes represents the most typical effects of treatment with synthetic progesterone receptor antagonists such as mifepristone?
A. Atrophic noncoiled glands in a spindle cell–predecidualized stroma
B. Decidualization of endometrial stroma and marked secretory changes
C. Glandular and stromal proliferation
D. Polyps with staghorn vessels and myxoid stroma
E. Shift in gland-to-stroma ratio with prevalence of stroma
7. In which of the following forms of dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB) is endometrial hyperplasia most likely to develop?
A. Anovulatory cycle
B. Inadequate proliferative phase
C. Inadequate secretory phase
D. Irregular shedding
E. Membranous dysmenorrhea
8. A 48-year-old woman undergoes an endometrial biopsy for evaluation of abnormal uterine bleeding. The main histologic findings are illustrated in this low-power photomicrograph. There are mitoses in the glandular epithelium, but no cytologic atypia. Foci of ciliated cell metaplasia are seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
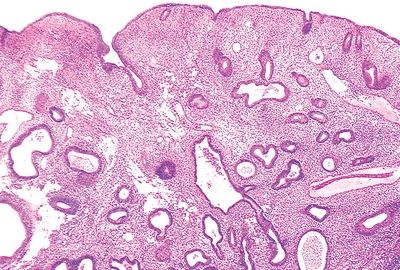
QUESTION 53.8
A. Complex hyperplasia without atypia
B. Disordered proliferative endometrium
C. Endometrial atrophy with ciliated cell metaplasia
D. Inactive (weakly proliferative) endometrium
E. Simple hyperplasia without atypia
9. Which of the following statements applies to the endometrial glandular abnormality shown in this picture?
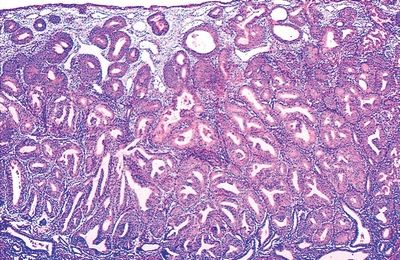
QUESTION 53.9
A. Associated with inadequate corpus luteum function
B. Cystically dilated glands are more frequent in severe hyperplasia
C. Cytologic atypia is the best predictor for subsequent cancer
D. Mild hyperplasia progresses to carcinoma in 30% of cases
E. Squamous metaplasia increases the risk of malignant degeneration
10. The type of endometrial hyperplasia shown in these low-power and high-power pictures is:
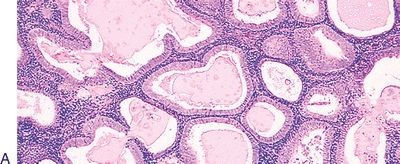
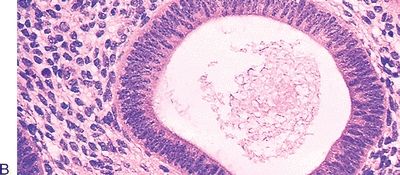
QUESTION 53.10
A. Simple without atypia
B. Simple with atypia
C. Complex without atypia
D. Complex with atypia
11. The type of endometrial hyperplasia shown in these low-power and high-power pictures is:
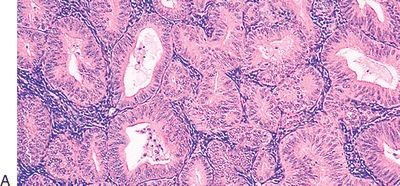
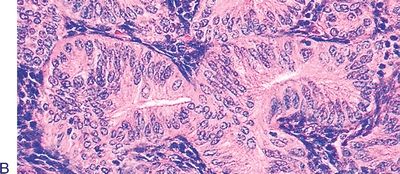
QUESTION 53.11
A. Simple without atypia
B. Simple with atypia
C. Complex without atypia
D. Complex with atypia
12. The type of endometrial hyperplasia shown in these low-power and high-power pictures is:
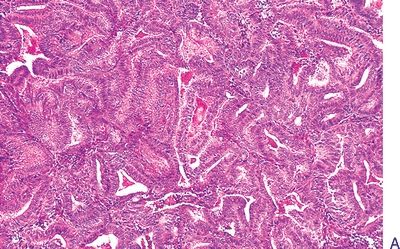
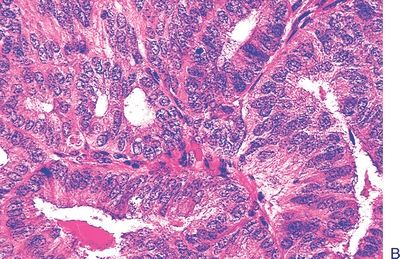
QUESTION 53.12
A. Simple without atypia
B. Simple with atypia
C. Complex without atypia
D. Complex with atypia
13. The majority of the endometrial lesion depicted in this photomicrograph most frequently contains:
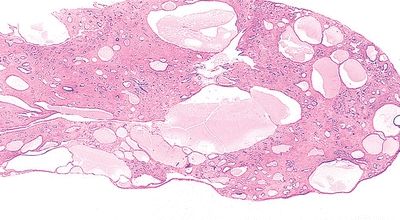
QUESTION 53.13
A. Decidual changes
B. Foci of adenocarcinoma
C. Glands lined by highly proliferative epithelium
D. Stroma composed of mitotically active cells
E. Thick-walled blood vessels
14. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) grading system of the endometrial neoplasm shown in this photomicrograph is based on:
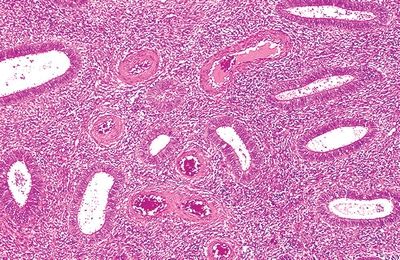
QUESTION 53.14
A. Architectural features and nuclear atypia
B. Architectural features
C. Hormone receptor status
D. Mitotic rate
E. Nuclear atypia
15. Endometrial carcinoma developing in elderly women (60 to 80 years of age) is most often characterized by:
A. Association with hyperplastic endometrium
B. ER and PR immunoreactivity
C. Low grade
D. Low Ki-67 labeling index
E. Mutations of p53
16. So-called morules are typically found in which of the following forms of endometrial metaplasia?
A. Clear cell metaplasia
B. Eosinophilic metaplasia
C. Papillary metaplasia
D. Squamous metaplasia
E. Tubal (ciliated) metaplasia
17. This high-power picture shows a type of endometrial carcinoma that does not develop in association with hyperestrinism and is characterized by extremely aggressive behavior. Which of the following is it?
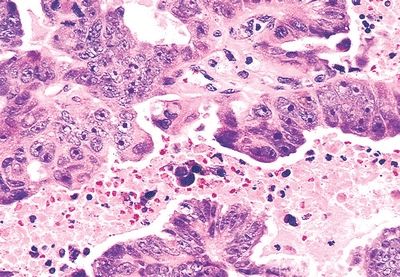
QUESTION 53.17
A. Adenosquamous
B. Clear cell
C. Mucinous
D. Secretory
E. Serous
F. Villoglandular
18. Which of the following types of endometrial carcinoma is shown in these pictures?
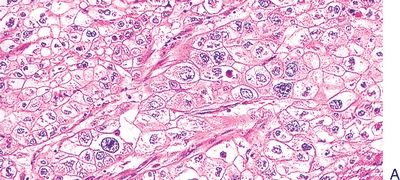
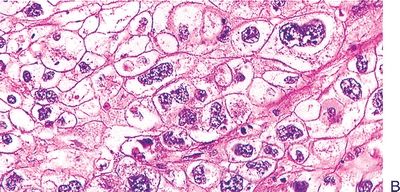
QUESTION 53.18
A. Clear cell
B. Endometrioid, secretory variant
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


