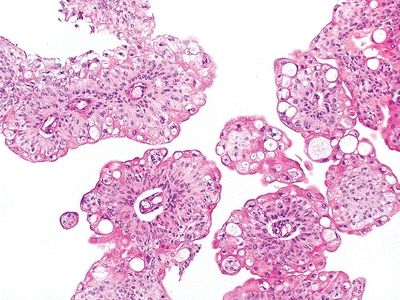
QUESTION 44.1
A. BCG treatment
B. Follicular cystitis
C. Invasive adenocarcinoma
D. Mesonephroid metaplasia
E. Reactive change
2. A middle-aged woman presents with a 3-month history of suprapubic discomfort, dysuria, and frequency. Urine cultures are negative. The finding of mucosal fissures on cystoscopy and mucosal/submucosal chronic inflammation with mast cells on biopsy is most consistent with:
A. Cystitis glandularis
B. Follicular cystitis
C. Interstitial cystitis
D. Malakoplakia
E. Ulcerative cystitis
3. A 68-year-old woman undergoes excision of an easily bleeding polypoid mass protruding through the urethral meatus. Histologically, it is composed of vascular tissue with chronic inflammatory cells and islands of squamous epithelium. The most likely diagnosis is:
A. Crohn disease
B. Fibroepithelial polyp
C. Mesonephric adenoma
D. Urethral carcinoma
E. Urethral caruncle
4. A plaque of the urinary bladder mucosa is biopsied. The biopsy shows a mixed inflammatory infiltrate predominantly located within the lamina propria, consisting of nodules of histiocytes surrounded by lymphoid aggregates. As shown by this picture, there are round laminated inclusions. Which of the following mechanisms is related to this lesion?
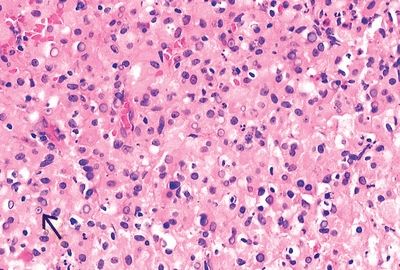
QUESTION 44.4
A. Autoimmune response
B. Defects in phagocytic function
C. Drug toxicity
D. Metaplastic change
E. Response to radiation
5. Which of the following is the most important predisposing condition for the development of bladder cancer in the United States?
A. Arylamine exposure
B. Cigarette smoking
C. Cyclophosphamide treatment
D. Human papillomavirus infection
E. Schistosoma haematobium infection
6. Pathologic staging of urothelial carcinoma (UC) of the bladder shows the poorest interobserver reliability in evaluating the depth of invasion into the:
A. Lamina propria
B. Muscularis propria
C. Pelvic wall
D. Perivesical fat
E. Prostate
7. Biopsies of a 2.0-cm exophytic tumor in the bladder trigone of a 57-year-old man show papillary structures lined by more than 10 layers of epithelial cells. Nuclear atypia is moderate, mitoses are rare, and there are foci of necrosis. The neoplasm infiltrates the underlying muscularis propria. Which of the following is the most important parameter influencing the prognosis?
A. Cell layers
B. Infiltration of the muscularis
C. Mitoses
D. Necrosis
E. Nuclear atypia
8. A 60-year-old woman without prior history of cancer presents with newly onset right hemiparesis. An MRI shows a ring-enhancing mass in the left frontal lobe. A biopsy reveals a carcinoma immunoreactive for CK7, CK20, and GATA3. Which of the following is the most likely source of this metastasis?
A. Kidney
B. Lungs
C. Prostate
D. Skin
E. Urinary bladder
A. High-grade noninvasive urothelial carcinoma
B. Inverted urothelial papilloma
C. Low-grade noninvasive urothelial carcinoma
D. Papillary hyperplasia
E. Urothelial papilloma
10. The degree of cytologic and architectural atypia present in the urothelial lesion in this picture is most compatible with:
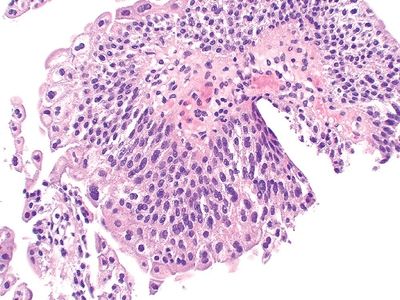
QUESTION 44.10
A. Carcinoma in situ
B. High-grade noninvasive urothelial carcinoma
C. Low-grade noninvasive urothelial carcinoma
D. Papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential
E. Urothelial papilloma
11. A papillary tumor of the bladder exhibits the cytologic and architectural features shown in this picture. This urothelial lesion is:
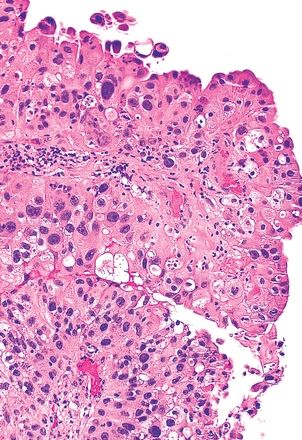
QUESTION 44.11
A. Urothelial papilloma
B. Carcinoma in situ
C. Papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential
D. Low-grade noninvasive urothelial carcinoma
E. High-grade noninvasive urothelial carcinoma
12. A 66-year-old man presents with dysuria, urgency, and microscopic hematuria. Following cytologic studies and cystoscopy, biopsies reveal the presence of the lesion shown in this picture. Which of the following is true about this lesion?
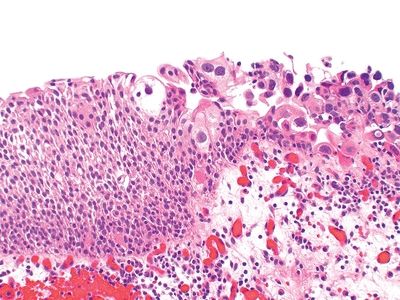
QUESTION 44.12
A. Characterized by full-thickness cellular atypia.
B. Detected usually in association with papillary or invasive tumors.
C. High nuclear–cytoplasmic ratio is always present.
D. Manifests usually with dysuria and hematuria.
E. Umbrella cells are always absent.
13. Of the following types of urothelial carcinoma (UC) with divergent differentiation, which one is the most common?
A. Sarcomatoid UC
B. UC with glandular differentiation
C. UC with squamous differentiation
D. UC with trophoblastic differentiation
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree