Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
1 What are the most important diseases of the respiratory system?
 Circulatory disturbances, such as pulmonary edema and chronic passive congestion, and adult respiratory distress syndrome
Circulatory disturbances, such as pulmonary edema and chronic passive congestion, and adult respiratory distress syndrome2 Define atelectasis
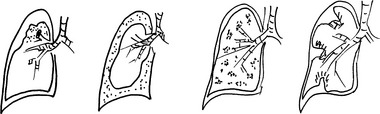
Atelectasis refers to incomplete expansion of the lungs or the collapse of previously inflated lung substance (Fig. 10-1). It is a pathologic condition that produces areas of relatively airless pulmonary parenchyma. Severe atelectasis significantly reduces oxygenation and predisposes to infection. Acquired atelectasis is generally encountered in adults and may be divided into the following categories:
Atelectasis is a reversible disorder (except that caused by contraction).
3 What are the main characteristics of obstruction atelectasis?
The mediastinum may shift toward the atelectatic lung.
4 What are the main characteristics of compression, patchy, and contraction atelectasis?
 Compression atelectasis ensues whenever the pleural cavity is partially (or completely) filled by fluid exudate, tumor, blood, or air (pneumothorax) or, in the case of tension pneumothorax, when the entry of air into the pleural cavity causes pulmonary collapse. It is most commonly found in patients with cardiac failure who develop pleural effusions as well as in patients experiencing malignant effusions within the pleural cavities; abnormal elevation of the diaphragm (peritonitis and subdiaphragmatic abscesses) induces basal atelectasis. With compression atelectasis, the mediastinum shifts away from the affected lung.
Compression atelectasis ensues whenever the pleural cavity is partially (or completely) filled by fluid exudate, tumor, blood, or air (pneumothorax) or, in the case of tension pneumothorax, when the entry of air into the pleural cavity causes pulmonary collapse. It is most commonly found in patients with cardiac failure who develop pleural effusions as well as in patients experiencing malignant effusions within the pleural cavities; abnormal elevation of the diaphragm (peritonitis and subdiaphragmatic abscesses) induces basal atelectasis. With compression atelectasis, the mediastinum shifts away from the affected lung. Patchy atelectasis develops when there is loss of pulmonary surfactant, as in neonatal and adult respiratory distress syndrome.
Patchy atelectasis develops when there is loss of pulmonary surfactant, as in neonatal and adult respiratory distress syndrome.5 What are the main causes of pulmonary edema?
 Hemodynamic disturbances
Hemodynamic disturbances The most common mechanism is the one attributable to increased hydrostatic pressure, as occurs in left-sided congestive heart failure.
The most common mechanism is the one attributable to increased hydrostatic pressure, as occurs in left-sided congestive heart failure.6 What are the pathologic features of pulmonary congestion and edema?
7 What is adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
 ARDS has many synonyms, such as diffuse alveolar damage, adult respiratory failure, shock lungs, acute alveolar injury, and traumatic wet lungs.
ARDS has many synonyms, such as diffuse alveolar damage, adult respiratory failure, shock lungs, acute alveolar injury, and traumatic wet lungs. Its clinical features are the rapid onset of life-threatening respiratory insufficiency, cyanosis, and severe arterial hypoxemia that is refractory to oxygen therapy and sometimes progresses to extrapulmonary multisystem organ failure.
Its clinical features are the rapid onset of life-threatening respiratory insufficiency, cyanosis, and severe arterial hypoxemia that is refractory to oxygen therapy and sometimes progresses to extrapulmonary multisystem organ failure.9 What are the pathologic features of ARDS?
 Microscopic findings in acute stage: There is congestion, interstitial and intraalveolar edema, inflammation, and fibrin deposition along the inside of alveoli in form of hyaline membranes.
Microscopic findings in acute stage: There is congestion, interstitial and intraalveolar edema, inflammation, and fibrin deposition along the inside of alveoli in form of hyaline membranes. Healing stage: It is characterized by the organization of fibrin exudate, with resultant intraalveolar fibrosis and marked thickening of the alveolar septa.
Healing stage: It is characterized by the organization of fibrin exudate, with resultant intraalveolar fibrosis and marked thickening of the alveolar septa.10 Describe the pathogenesis of ARDS
 ARDS is the end result of acute alveolar injury caused by a variety of insults, whereas the respiratory distress syndrome of newborns is caused by deficiency in pulmonary surfactant.
ARDS is the end result of acute alveolar injury caused by a variety of insults, whereas the respiratory distress syndrome of newborns is caused by deficiency in pulmonary surfactant. In ARDS, the initial injury affects capillary endothelium (most frequently) or alveolar epithelium (occasionally), but in the end both are clearly affected.
In ARDS, the initial injury affects capillary endothelium (most frequently) or alveolar epithelium (occasionally), but in the end both are clearly affected. Increased capillary permeability is followed by interstitial and then intraalveolar edema, fibrin exudation, and formation of hyaline membranes.
Increased capillary permeability is followed by interstitial and then intraalveolar edema, fibrin exudation, and formation of hyaline membranes.CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE AND RESTRICTIVE LUNG DISEASES
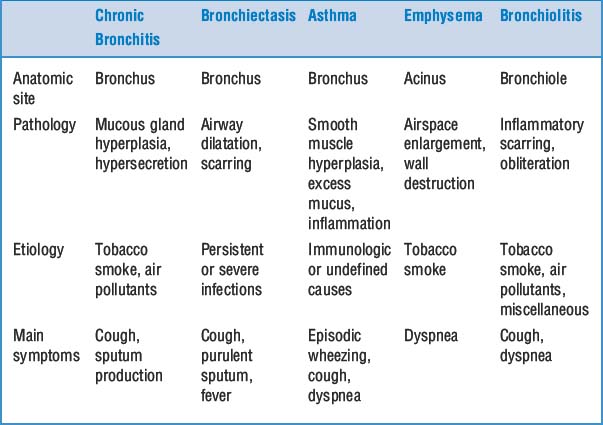
16 What are the main characteristics of different types of emphysema?
 Centriacinar (centrilobular)
Centriacinar (centrilobular) The central or proximal parts of acini, formed by respiratory bronchioles, are affected, whereas distal alveoli are spared.
The central or proximal parts of acini, formed by respiratory bronchioles, are affected, whereas distal alveoli are spared. The lesions are often localized and usually more severe in the upper lobes, particularly in the apical segments.
The lesions are often localized and usually more severe in the upper lobes, particularly in the apical segments. Panacinar (panlobular)
Panacinar (panlobular) The acini are uniformly enlarged because the process affects all of the structures, from the respiratory bronchiole to the alveoli (the prefix pan refers to the entire acinus but not to the entire lung).
The acini are uniformly enlarged because the process affects all of the structures, from the respiratory bronchiole to the alveoli (the prefix pan refers to the entire acinus but not to the entire lung).18 What is the difference in clinical presentation between patients with emphysema and those with chronic bronchitis?
20 What is chronic bronchitis?
 Simple chronic bronchitis: Patients experience a productive cough but have no evidence of airflow obstruction.
Simple chronic bronchitis: Patients experience a productive cough but have no evidence of airflow obstruction. Chronic asthmatic bronchitis: Some patients may demonstrate severe dyspnea and wheezing in association with inhaled irritants or during respiratory infections due to hyperreactive airways.
Chronic asthmatic bronchitis: Some patients may demonstrate severe dyspnea and wheezing in association with inhaled irritants or during respiratory infections due to hyperreactive airways.23 What are the clinical features of chronic bronchitis?
 In time, and usually with continued smoking, hypercapnia, hypoxemia, and mild cyanosis with other elements of COPD may appear.
In time, and usually with continued smoking, hypercapnia, hypoxemia, and mild cyanosis with other elements of COPD may appear.25 What are the main differences between extrinsic and intrinsic asthma?
The intrinsic (idiosyncratic) type is initiated by diverse, nonimmune mechanisms, including:
26 What is the pathogenesis of atopic asthma?
Key Points: Chronic Obstructive and Restrictive Diseases
1. Dyspnea (i.e., difficulty in breathing) can be caused by several pathologic conditions, such as atelectasis, edema, diffuse alveolar damage (adult respiratory distress syndrome), pneumonia, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
2. Clinically and pathologically, the lung diseases can be classified as obstructive or restrictive.
3. Asthma, a disease that has an immunologic basis, is the most common childhood respiratory disease encountered in the emergency room setting.
27 Describe the main differences between acute and late-phase reactions in patients with bronchial asthma
28 What are the major mediators responsible for bronchospasm in patients with bronchial asthma?
 Leukotrienes C4, D4, and E4 cause prolonged bronchoconstriction, increased vascular permeability, and increased mucus secretion.
Leukotrienes C4, D4, and E4 cause prolonged bronchoconstriction, increased vascular permeability, and increased mucus secretion.< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree