Chapter 9 The Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Systems
RED BLOOD CELL DISORDERS
4 List three major groups of anemia according to their etiology and pathogenesis
 Anemia due to increased rate of RBC destruction (hemolytic anemia)
Anemia due to increased rate of RBC destruction (hemolytic anemia)5 How are anemias classified according to the red cell size and shape and their hemoglobin content?
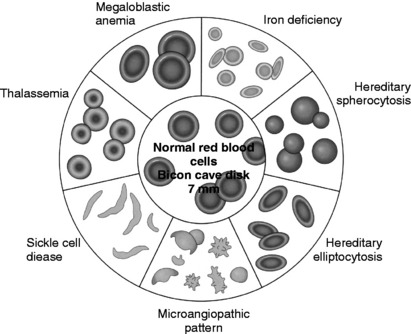
TABLE 9-1 Abnormal Red Blood Cell (RBC) Morphology
| Abnormality | Features | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Anisocytosis | Variation in RBC size | Nonspecific |
| Poikilocytosis | Variation in RBC shape | Nonspecific |
| Target cells | Targetlike appearance | Thalassemia, hemoglobinopathies |
| Sickle cells | Bipolar (sickle) or hollyleaf | Sickle cell anemia RBCs |
| Schistocytes | RBC fragments | Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia |
| Teardrops | Tennis racket RBCs | Myelofibrosis, severe anemias |
| Spherocytes | Spherical RBCs with dense hemoglobin content | Hereditary spherocytosis, alcoholism |
| Bite cells | Smooth semicircle taken from one edge | G6PD deficiency |
6 Define the main hematologic parameters
7 Discuss how reticulocyte counts are used in clinical practice
 Hypoproliferative: Patients with anemia caused by defects in erythrocyte proliferation or maturation tend to have low reticulocyte counts. Patients suffering from pernicious anemia have low reticulocyte count, which will, however, increase after vitamin B12 treatment.
Hypoproliferative: Patients with anemia caused by defects in erythrocyte proliferation or maturation tend to have low reticulocyte counts. Patients suffering from pernicious anemia have low reticulocyte count, which will, however, increase after vitamin B12 treatment. Normoproliferative or hyperproliferative: Patients with anemia caused by decreased survival of erythrocytes with a normal bone marrow proliferative response often exhibit increased peripheral blood reticulocytes. If the degree of reticulocytosis is adequate to replace the loss of erythrocytes, the anemia is said to be compensated.
Normoproliferative or hyperproliferative: Patients with anemia caused by decreased survival of erythrocytes with a normal bone marrow proliferative response often exhibit increased peripheral blood reticulocytes. If the degree of reticulocytosis is adequate to replace the loss of erythrocytes, the anemia is said to be compensated.8 List signs and symptoms common to all forms of anemia
 Koilonychia, a spoon-shaped concavity of the nails, associated with brittle nails; feature of prolonged anemia that is rarely seen today
Koilonychia, a spoon-shaped concavity of the nails, associated with brittle nails; feature of prolonged anemia that is rarely seen today13 What is the difference between intravascular and extravascular hemolysis?
 Intravascular hemolysis: Significant lysis of erythrocytes rarely occurs within the vascular spaces. In intravascular hemolysis, normal erythrocytes are damaged by:
Intravascular hemolysis: Significant lysis of erythrocytes rarely occurs within the vascular spaces. In intravascular hemolysis, normal erythrocytes are damaged by: Extravascular hemolysis: Most frequently, the premature destruction of erythrocytes occurs within the mononuclear phagocyte system of the spleen and liver. In extravascular hemolysis, erythrocytes are destroyed because:
Extravascular hemolysis: Most frequently, the premature destruction of erythrocytes occurs within the mononuclear phagocyte system of the spleen and liver. In extravascular hemolysis, erythrocytes are destroyed because:14 What are the main features of intravascular hemolysis?
 Jaundice: It is related to the excessive formation of unconjugated bilirubin from the heme portion of hemoglobin. Unconjugated bilirubin is bound to albumin and does not appear in urine.
Jaundice: It is related to the excessive formation of unconjugated bilirubin from the heme portion of hemoglobin. Unconjugated bilirubin is bound to albumin and does not appear in urine. Hemoglobinemia: It results from the release of free hemoglobin released from RBCs. Free hemoglobin binds to haptoglobin, which prevents its excretion into urine. Hemoglobin–haptoglobin complex is rapidly cleared by the mononuclear phagocyte system. Accordingly, the blood concentration of haptoglobin will be reduced. Decreased serum haptoglobin is a reliable sign of intravascular hemolysis.
Hemoglobinemia: It results from the release of free hemoglobin released from RBCs. Free hemoglobin binds to haptoglobin, which prevents its excretion into urine. Hemoglobin–haptoglobin complex is rapidly cleared by the mononuclear phagocyte system. Accordingly, the blood concentration of haptoglobin will be reduced. Decreased serum haptoglobin is a reliable sign of intravascular hemolysis. Methemalbuminemia: When the serum haptoglobin is depleted, the unbound or free hemoglobin is in part rapidly oxidized to methemoglobin, which binds to albumin forming methemalbumin.
Methemalbuminemia: When the serum haptoglobin is depleted, the unbound or free hemoglobin is in part rapidly oxidized to methemoglobin, which binds to albumin forming methemalbumin. Hemoglobinuria: Hemoglobin in urine appears after the haptoglobin binding capacity has been exceeded and the free hemoglobin is filtered through the glomeruli. Both hemoglobin and methemoglobin are excreted through the kidneys, imparting a red-brown color to the urine.
Hemoglobinuria: Hemoglobin in urine appears after the haptoglobin binding capacity has been exceeded and the free hemoglobin is filtered through the glomeruli. Both hemoglobin and methemoglobin are excreted through the kidneys, imparting a red-brown color to the urine.16 Name the common pathologic tissue findings common to all forms of chronic hemolytic anemia
 Formation of pigment gallstones (cholelithiasis) caused by elevated levels of bilirubin when it is excreted through the liver
Formation of pigment gallstones (cholelithiasis) caused by elevated levels of bilirubin when it is excreted through the liver17 What is the difference between anemia caused by extrinsic factors (extracorpuscular defects) and anemia caused by intrinsic factors (intracorpuscular defects)?
 Intracorpuscular
Intracorpuscular Hereditary disorders (i.e., red cell membrane disorders, red cell enzyme deficiencies, and disorders of hemoglobin synthesis)
Hereditary disorders (i.e., red cell membrane disorders, red cell enzyme deficiencies, and disorders of hemoglobin synthesis)Key Points: Hematology and Red Blood Cell Disorders
19 What are the exact molecular defects in HS?
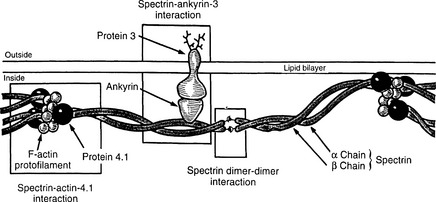
The normal membrane cytoskeleton of RBCs is composed of several proteins, the most important of which are α and β spectrin, ankyrin, actin, and proteins known as band 4.1 and band 3 (Fig. 9-2). Together these proteins maintain the normal biconcave shape of RBCs. The mutation of ankyrin gene is the most common defect in autosomal dominant HS, and the mutations of gene encoding protein band 3 account for 20% of cases. Genes encoding other cytoskeletal proteins are less often mutated.
21 Describe the pathologic findings in HS
The most prominent changes are found in the peripheral blood, the bone marrow, and the spleen:
 Blood smears: Spheroid red cells appear uniformly red in routine smears (spherocytosis). Their central pallor, corresponding to the central concavity, is lacking. Although this morphology of RBCs is distinctive, it is not pathognomonic of HS and may also be seen in autoimmune hemolytic anemias.
Blood smears: Spheroid red cells appear uniformly red in routine smears (spherocytosis). Their central pallor, corresponding to the central concavity, is lacking. Although this morphology of RBCs is distinctive, it is not pathognomonic of HS and may also be seen in autoimmune hemolytic anemias. Bone marrow: Erythroid hyperplasia with an increased number of normoblasts is seen in bone marrow biopsy.
Bone marrow: Erythroid hyperplasia with an increased number of normoblasts is seen in bone marrow biopsy. Spleen
Spleen Splenomegaly of moderate extent (500–1000 g) results from marked congestion of the red pulp cords. The sinuses appear virtually empty.
Splenomegaly of moderate extent (500–1000 g) results from marked congestion of the red pulp cords. The sinuses appear virtually empty.22 How is hereditary spherocytosis diagnosed clinically?
 Laboratory findings, including spherocytosis, increased osmotic fragility of RBCs, and hyperbilirubinemia (Osmotic lysis of RBCs can be seen in two thirds of patients and is induced in vitro by immersing patients’ RBCs into a hypotonic salt solution. Because the spherical RBCs cannot expand more, the influx of water leads to their early rupture.)
Laboratory findings, including spherocytosis, increased osmotic fragility of RBCs, and hyperbilirubinemia (Osmotic lysis of RBCs can be seen in two thirds of patients and is induced in vitro by immersing patients’ RBCs into a hypotonic salt solution. Because the spherical RBCs cannot expand more, the influx of water leads to their early rupture.)23 What is the clinical course of hereditary spherocytosis?
The severity of the disease is variable among individuals:
 In a minority of patients, hereditary spherocytosis presents at birth with marked jaundice, requiring exchange transfusion.
In a minority of patients, hereditary spherocytosis presents at birth with marked jaundice, requiring exchange transfusion. Twenty to thirty percent of patients are largely asymptomatic because of compensatory increased erythropoiesis.
Twenty to thirty percent of patients are largely asymptomatic because of compensatory increased erythropoiesis. Most patients have a chronic anemia of mild to moderate severity. This more-or-less stable clinical course may be aggravated by intercurrent infections, either by reducing erythrocyte formation (aplastic crisis) or by increasing erythrocyte destruction (hemolytic crisis). The formation of pigmented gallstones may also cause symptoms.
Most patients have a chronic anemia of mild to moderate severity. This more-or-less stable clinical course may be aggravated by intercurrent infections, either by reducing erythrocyte formation (aplastic crisis) or by increasing erythrocyte destruction (hemolytic crisis). The formation of pigmented gallstones may also cause symptoms.25 What should one know about G6PD deficiency?
 There is geographic variability. It is most prevalent in Mediterranean countries and western Africa and in Americans whose ancestors came from those regions.
There is geographic variability. It is most prevalent in Mediterranean countries and western Africa and in Americans whose ancestors came from those regions. Overall prevalence is 1 in 1000, but it is more common in some populations (e.g. African Americans, 15%).
Overall prevalence is 1 in 1000, but it is more common in some populations (e.g. African Americans, 15%). Laboratory findings include anemia, hemoglobinemia, and occasional hemoglobinuria. Peripheral blood smear shows Heinz bodies and bite cells. Heinz bodies can be seen as dark inclusions when the smears are stained with crystal violet. When the spleen pits the Heinz bodies from RBCs, it also removes a portion of the RBC cytoplasm, leading to formation of bite cells.
Laboratory findings include anemia, hemoglobinemia, and occasional hemoglobinuria. Peripheral blood smear shows Heinz bodies and bite cells. Heinz bodies can be seen as dark inclusions when the smears are stained with crystal violet. When the spleen pits the Heinz bodies from RBCs, it also removes a portion of the RBC cytoplasm, leading to formation of bite cells.28 Describe the difference between the sickle cell trait and sickle cell anemia
 When an individual is homozygous for the mutant gene, all the hemoglobin is of the abnormal HbS type. Sickling and hemolysis occur in regular living circumstances, causing the spectrum of clinical signs and symptoms known as sickle cell anemia.
When an individual is homozygous for the mutant gene, all the hemoglobin is of the abnormal HbS type. Sickling and hemolysis occur in regular living circumstances, causing the spectrum of clinical signs and symptoms known as sickle cell anemia.29 Why do dehydration and anoxia (e.g., high altitude) potentiate sickling of RBCs in sickle cell anemia?
30 Name two main causes of ischemia in sickle cell anemia
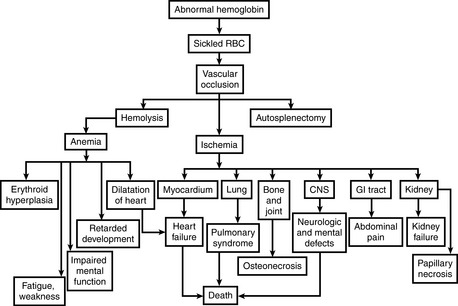
 Chronic hemolytic anemia: Anemia results from shortened life span of RBC, which survive on average only 20 days in circulation. In response to chronic hemolysis the bone marrow undergoes massive hyperplasia (Fig. 9-3).
Chronic hemolytic anemia: Anemia results from shortened life span of RBC, which survive on average only 20 days in circulation. In response to chronic hemolysis the bone marrow undergoes massive hyperplasia (Fig. 9-3). Occlusion of small blood vessels: The altered RBC membranes favor adhesion of these cells to the endothelium. The slow down of the circulation due to increased RBC adhesion promotes hypoxia, which in turn contributes to the sickling of abnormal RBCs and finally vasoocclusion. Hypoxia affects numerous organs and may even cause death.
Occlusion of small blood vessels: The altered RBC membranes favor adhesion of these cells to the endothelium. The slow down of the circulation due to increased RBC adhesion promotes hypoxia, which in turn contributes to the sickling of abnormal RBCs and finally vasoocclusion. Hypoxia affects numerous organs and may even cause death.33 Discuss the most common bacteria causing infection, death, or both in children with sickle cell anemia
34 What are three types of crisis in sickle cell anemia?
 Vasoocclusive (or painful) crises: Episodes of hypoxia and infarction are associated with severe pain in the affected area. Most commonly involved sites are bones, lungs, liver, brain, spleen, and penis.
Vasoocclusive (or painful) crises: Episodes of hypoxia and infarction are associated with severe pain in the affected area. Most commonly involved sites are bones, lungs, liver, brain, spleen, and penis. In children, painful bone crises are extremely common, causing the so-called hand–foot syndrome, which can be distinguished from acute osteomyelitis with difficulty.
In children, painful bone crises are extremely common, causing the so-called hand–foot syndrome, which can be distinguished from acute osteomyelitis with difficulty. Involvement of the lungs presents with fever, cough, chest pain, and pulmonary infiltrates. Acute chest syndrome is a major cause of death in patients older than 5 years.
Involvement of the lungs presents with fever, cough, chest pain, and pulmonary infiltrates. Acute chest syndrome is a major cause of death in patients older than 5 years. Central nervous system hypoxia may present clinically as seizures or stroke. Retarded mental development is a serious complication of these hypoxia attacks.
Central nervous system hypoxia may present clinically as seizures or stroke. Retarded mental development is a serious complication of these hypoxia attacks. The affected spleen is initially enlarged in childhood. Following multiple infarcts, it undergoes progressive shrinkage during adolescence or early adulthood and may completely vanish (autosplenectomy).
The affected spleen is initially enlarged in childhood. Following multiple infarcts, it undergoes progressive shrinkage during adolescence or early adulthood and may completely vanish (autosplenectomy). Aplastic crises: Temporary cessation of bone marrow activity is usually triggered by intercurrent infections. The most common cause is a parvovirus infection that affects the erythroid progenitor cells. Such crises are marked by sudden and rapid worsening of anemia accompanied by a disappearance of reticulocytes from the peripheral blood.
Aplastic crises: Temporary cessation of bone marrow activity is usually triggered by intercurrent infections. The most common cause is a parvovirus infection that affects the erythroid progenitor cells. Such crises are marked by sudden and rapid worsening of anemia accompanied by a disappearance of reticulocytes from the peripheral blood.38 What are the pathologic features of β-thalassemia?
 Blood smear
Blood smear Microcytic, hypochromic red cells, so MCHC is low (β-thalassemia trait is important to distinguish from iron-deficiency anemia because of opposite therapy)
Microcytic, hypochromic red cells, so MCHC is low (β-thalassemia trait is important to distinguish from iron-deficiency anemia because of opposite therapy) Abnormal cell shape: target cells (so called because of the small amount of hemoglobin that precipitates in the center), stippled red cells, and fragmented red cells
Abnormal cell shape: target cells (so called because of the small amount of hemoglobin that precipitates in the center), stippled red cells, and fragmented red cells Inclusions representing aggregates of α chains are not visible in peripheral blood (they are removed by the spleen)
Inclusions representing aggregates of α chains are not visible in peripheral blood (they are removed by the spleen) Bones
Bones Most erythroblasts die in the bone marrow (apoptosis), resulting in ineffective erythropoiesis. This, in turn, stimulates erythropoietin secretion, which leads to severe erythroid hyperplasia in the bone marrow and often at extramedullary sites.
Most erythroblasts die in the bone marrow (apoptosis), resulting in ineffective erythropoiesis. This, in turn, stimulates erythropoietin secretion, which leads to severe erythroid hyperplasia in the bone marrow and often at extramedullary sites. Massive erythropoiesis within the bones invades the cortex, impairs bone growth, and produces skeletal abnormalities (crew-cut appearance on x-rays).
Massive erythropoiesis within the bones invades the cortex, impairs bone growth, and produces skeletal abnormalities (crew-cut appearance on x-rays). Spleen
Spleen Sequestration and destruction of inclusion-bearing red cells is derived from precursors that escape intramedullary death.
Sequestration and destruction of inclusion-bearing red cells is derived from precursors that escape intramedullary death.40 What is the difference between the three clinical types of β-thalassemia (thalassemia major, intermedia, and minor)?
The clinical classification of β-thalassemias is based on:
 β-Thalassemia major
β-Thalassemia major Severe transfusion-dependent anemia that first becomes manifest 6 to 9 months after birth as hemoglobin synthesis switches from HbF to HbA
Severe transfusion-dependent anemia that first becomes manifest 6 to 9 months after birth as hemoglobin synthesis switches from HbF to HbA42 List the four main clinical types of α-thalassemia
These are classified on the basis of the number and position of the α-globin genes deleted:
 Hemoglobin H (HbH) disease
Hemoglobin H (HbH) disease Tetramers of β-globin, called HbH, are formed. These tetramers are nonfunctional in oxygen transport, so anemia is disproportionate to hemoglobin level.
Tetramers of β-globin, called HbH, are formed. These tetramers are nonfunctional in oxygen transport, so anemia is disproportionate to hemoglobin level.46 What is the difference between warm antibody and cold antibody hemolytic anemia?
 Warm antibody hemolytic anemia:
Warm antibody hemolytic anemia: In many cases, antibody binds to the Rh-antigen on erythrocytes. The coated cells then bind to Fc receptors on monocytes and splenic macrophages. They undergo spheroidal transformation (intravascular hemolysis rarely occurs) and are sequestered and removed in the spleen. There is moderate splenomegaly.
In many cases, antibody binds to the Rh-antigen on erythrocytes. The coated cells then bind to Fc receptors on monocytes and splenic macrophages. They undergo spheroidal transformation (intravascular hemolysis rarely occurs) and are sequestered and removed in the spleen. There is moderate splenomegaly. Cold antibody hemolytic anemia:
Cold antibody hemolytic anemia: IgM antibodies bind to the RBC. Two distinct forms are recognized:
IgM antibodies bind to the RBC. Two distinct forms are recognized:47 List the most common causes of anemia owing to mechanical injury of red blood cells
 Microangiopathic hemolysis (disseminated intravascular coagulation, malignant hypertension, systemic lupus erythematosus, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic–uremic syndrome, and disseminated cancer)
Microangiopathic hemolysis (disseminated intravascular coagulation, malignant hypertension, systemic lupus erythematosus, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic–uremic syndrome, and disseminated cancer)49 List the main hematologic features of megaloblastic anemia
Peripheral blood shows the following features:
 Reticulocyte count is lower than normal, and nucleated red cells occasionally appear in the circulating blood with severe anemia
Reticulocyte count is lower than normal, and nucleated red cells occasionally appear in the circulating blood with severe anemia50 What are the changes seen in bone marrow in megaloblastic anemia?
Bone marrow shows the following changes:
 As these cells differentiate, the nucleus retains its finely distributed chromatin and thus fails to undergo the chromatin clumping typical of the normoblasts.
As these cells differentiate, the nucleus retains its finely distributed chromatin and thus fails to undergo the chromatin clumping typical of the normoblasts.53 What is the pathogenesis of pernicious anemia?
 Ineffective erythropoiesis (megaloblasts are especially prone to intramedullary destruction; premature destruction of granulocytic and platelet precursors also occurs)
Ineffective erythropoiesis (megaloblasts are especially prone to intramedullary destruction; premature destruction of granulocytic and platelet precursors also occurs)Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree