Chapter 7 The Neck
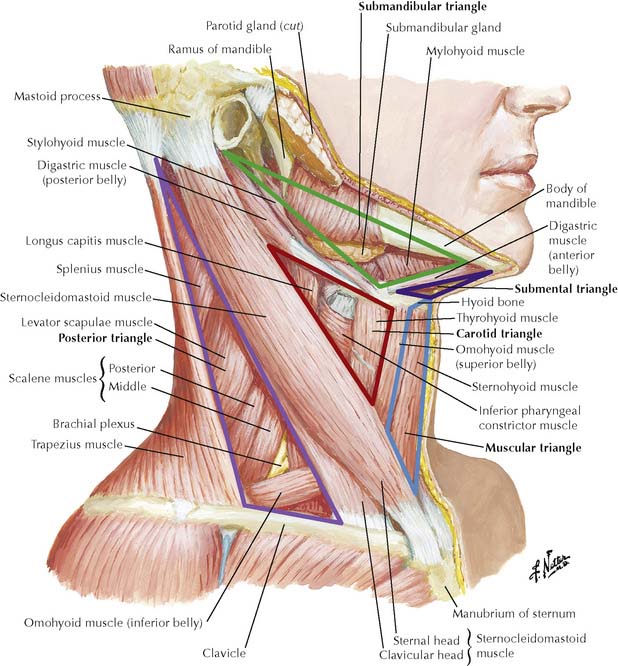
7-1 Triangles of neck viewed from right side.
(From Norton, N S: Netter’s Head and Neck Anatomy for Dentistry. Philadelphia, Saunders 2007, p 113.)
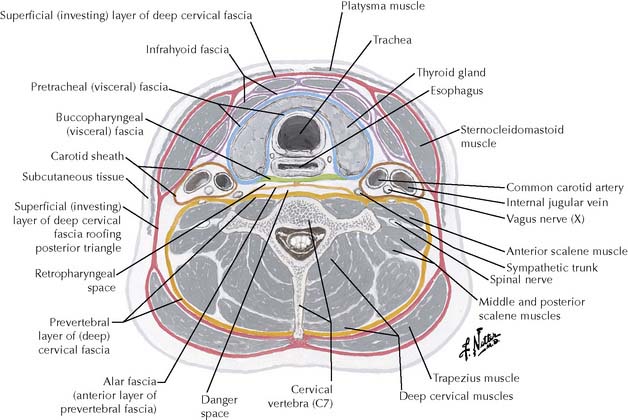
Roots of the brachial plexus and the subclavian artery pass into the posterior triangle between the anterior and middle scalenes. An elongated transverse process on vertebra C7 (cervical rib, Figure 7-3) or hypertrophy of the scalene muscles may stretch or compress the subclavian artery and/or lower trunk of the brachial plexus (C8, T1) to produce thoracic outlet syndrome. It is characterized by pain, numbness, and muscular weakness of the upper extremity, most commonly in the distribution of the ulnar nerve.
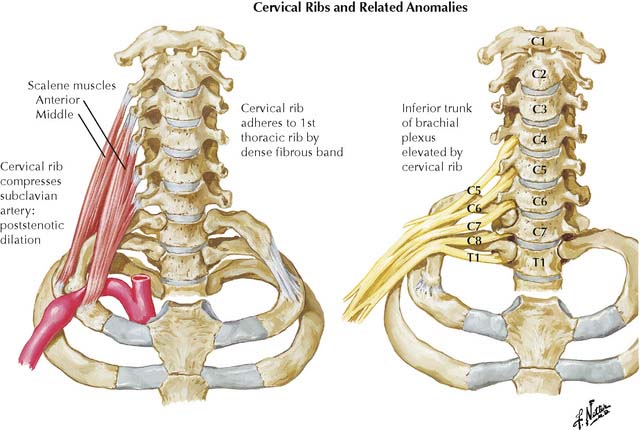
(From Netter, F H: Netter’s Atlas of Human Anatomy, 3rd ed. Icon Learning Systems, 2003, Plate 181.)
TABLE 7-1 Branches of Subclavian Artery
| Supplies | Comments | |
|---|---|---|
| First Part | Medial to anterior scalene muscle | |
| Vertebral artery | Spinal nerve roots, spinal cord, brainstem | Ascends transverse foramina of C1-C6, crosses posterior arch of atlas to enter foramen magnum; medullary branches reinforce blood flow to spinal arteries |
| Thyrocervical trunk | Three main branches | |
| Inferior thyroid | Thyroid, parathyroid gland, larynx, esophagus | Main supply to parathyroid glands; forms collateral circulation with external carotid via anastomosis with superior thyroid artery |
| Transverse cervical | Trapezius, levator scapulae, and rhomboid muscles | Superficial branch on deep surface of trapezius; deep branch deep to rhomboids |
| Suprascapular | Supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles | Crosses posterior triangle behind clavicle to pass above superior transverse scapular ligament |
| Internal thoracic | See Chapter 2 | |
| Second Part | Posterior to anterior scalene muscle | |
| Costocervical trunk | Runs posteriorly over cervical pleura dividing into deep cervical and superior intercostal branches | |
| Deep cervical | Posterior neck muscles | Forms collateral circulation between subclavian and external carotid via anastomosis with occipital artery |
| Superior intercostal | First two intercostal spaces | Gives first two posterior intercostal arteries |
| Third Part | Between lateral borders of anterior scalene and rib 1 | |
| Dorsal scapular | Levator scapulae and rhomboid muscles | Variably present; replaces deep branch of transverse cervical when present |
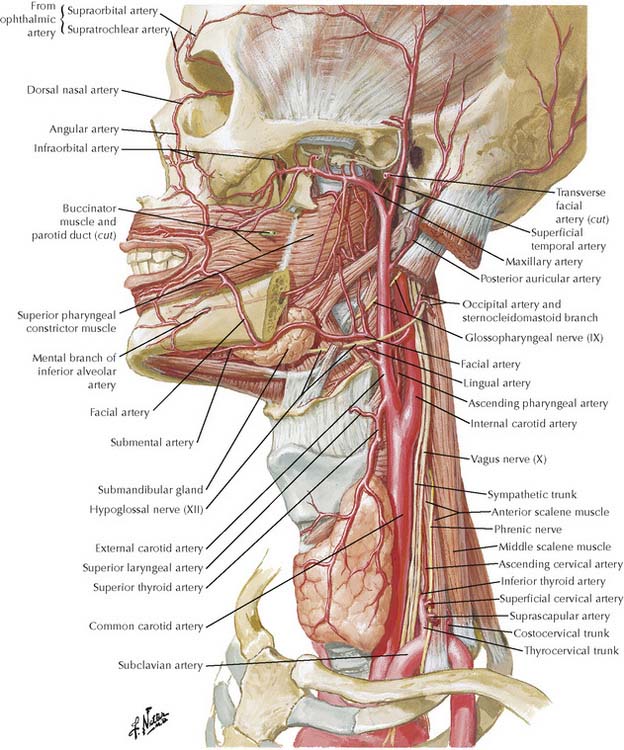
TABLE 7-2 Branches of External Carotid Artery
| Artery | Supplies | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Superior thyroid | Larynx, infrahyoid muscles, and thyroid gland | Travels with external laryngeal nerve |
| Lingual | Tongue, palatine tonsil, sublingual gland, and floor of mouth | Passes deep to hyoglossus muscle |
| Facial | Face, soft palate, palatine tonsil, and submandibular muscles | May arise in common with lingual artery |
| Ascending pharyngeal | Pharynx, palatine tonsil, and meninges | |
| Occipital | Posterior scalp, sternomastoid, and meninges | Parallels greater occipital nerve in scalp |
| Posterior auricular | Scalp, auricle, and facial nerve | |
| Maxillary | Muscles of mastication, temporomandibular joint, meninges, nasal cavity, palate, mandibular and maxillary teeth, and face | Terminal branch described with infratemporal and pterygopalatine fossae |
| Superficial temporal | Parotid gland, face, and scalp | Terminal branch described with face; ascends with auriculotemporal nerve |