Chapter 8 The Head
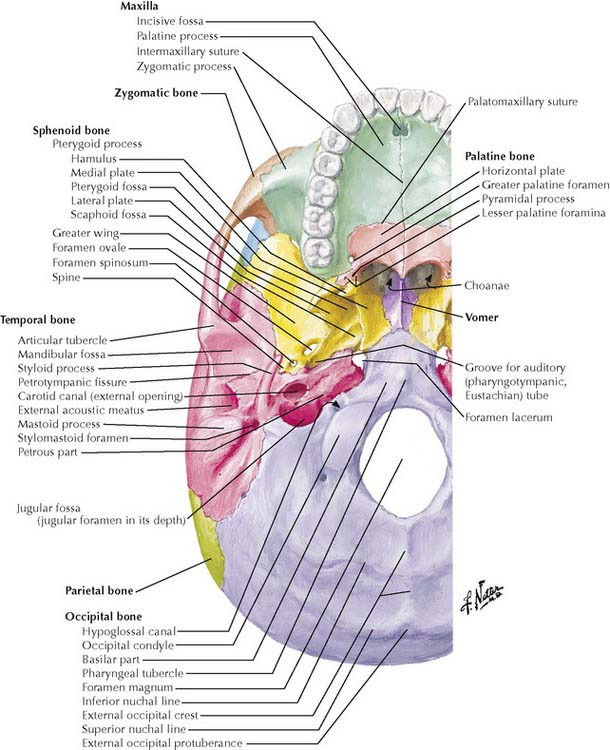
8-4 Skull base, inferior view.
(From Netter, F H: Atlas of Human Anatomy, 4th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2006, Plate 8.)
TABLE 8-1 Skull Deformities in Craniosynostosis
| Deformity | Suture(s) Involved | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Scaphocephaly | Sagittal suture | Long, narrow skull |
| Oxycephaly | Coronal suture, bilateral fusion | Short, tall, wide skull |
| Plagiocephaly | Coronal or lambdoid suture, unilateral fusion | Asymmetric skull with forehead protruding on one side and flattened on other |
| Trigonocephaly | Metopic suture | Wedge-shaped forehead |
TABLE 8-2 Major Apertures of Neurocranium
| Aperture | Communication Between | Traversed by |
|---|---|---|
| Cribriform plate | Nasal cavity and anterior cranial fossa | Olfactory nerves |
| Optic canal | Middle cranial fossa and orbit | Optic nerve, ophthalmic artery |
| Superior orbital fissure | Middle cranial fossa and orbit | Oculomotor, trochlear, ophthalmic, and abducens nerves; ophthalmic vein(s) |
| Foramen rotundum | Middle cranial fossa and pterygopalatine fossa | Maxillary nerve |
| Foramen ovale | Middle cranial fossa and infratemporal fossa | Mandibular nerve, accessory meningeal artery, lesser petrosal nerve |
| Foramen spinosum | Middle cranial fossa and infratemporal fossa | Middle meningeal artery, meningeal branch of mandibular nerve |
| Foramen lacerum | Middle cranial fossa and base of skull | Closed in life by cartilage transmitting only small vessels; sometimes defined as including opening of carotid canal |
| Carotid canal | Base of skull and middle cranial fossa | Internal carotid artery and plexus |
| Internal acoustic meatus | Posterior cranial fossa and facial canal | Facial nerve, nervus intermedius, vestibulocochlear nerve |
| Stylomastoid foramen | Facial canal and base of skull | Facial nerve |
| Jugular foramen | Posterior cranial fossa and base of skull | Glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves; internal jugular vein, inferior petrosal sinus |
| Foramen magnum | Posterior cranial fossa and base of skull | Brainstem, vertebral arteries and veins, spinal arteries, spinal portion of accessory nerve |
| Hypoglossal canal | Posterior cranial fossa and base of skull | Hypoglossal nerve |
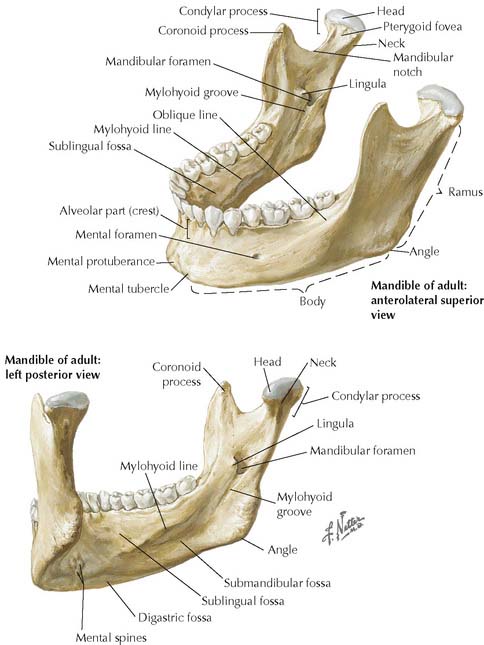
8-6 Mandible. Anterolateral superior view (upper figure). Left posteroinferior view (lower figure).
(From Norton, N S: Netter’s Head and Neck Anatomy for Dentistry. Philadelphia, Saunders 2007, p 47.)
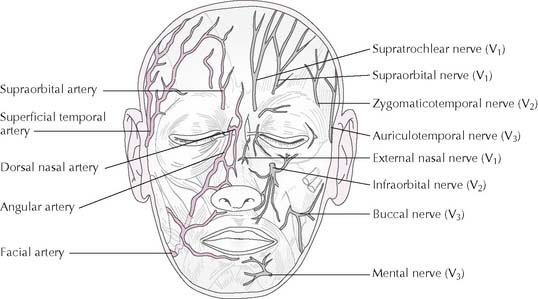
8-8 Cutaneous nerves and arteries of the face and scalp. Left, arteries (red); right, nerves (gray).
Terminal branches of CN VII may be injured by parotid cancer or by surgery to remove a parotid tumor (Figure 8-9). An infant’s facial nerve may be injured during a forceps delivery because the mastoid process has not yet developed and the stylomastoid foramen is relatively superficial. Bell palsy is idiopathic unilateral facial paralysis.
Bell palsy is unilateral paralysis of all the facial muscles from an idiopathic facial nerve lesion.
Tic douloureux is intense paroxysms of pain along the maxillary and/or mandibular divisions of CN V.
The middle third of the face is a “danger area” because infection can spread to the cavernous sinus.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree