Chapter 22 The Central Nervous System
REACTION OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TO INJURY
2 List the most important pathologic reactions of neurons
 Acute injury: This is most commonly caused by hypoxia/ischemia but also under the influence of toxic or infectious agents that can kill neurons. Affected neurons have pyknotic nuclei and an acidophilic cytoplasm, which stains intensely red with eosin (“red is dead”) in standard hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) slides.
Acute injury: This is most commonly caused by hypoxia/ischemia but also under the influence of toxic or infectious agents that can kill neurons. Affected neurons have pyknotic nuclei and an acidophilic cytoplasm, which stains intensely red with eosin (“red is dead”) in standard hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) slides. Axonal reaction: It occurs following transection or other severe injury of the axon and is characterized by histologic and ultrastructural changes in the cytoplasms of the neuron (perikaryon). Following axonal injury, the perikaryon swells. Ultrastructurally, the ribosomes of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) are lost. This degranulation of the RER, which in the neurons is called Nissl substance, is visible by light microscopy as a loss of basophilia and is called chromatolysis.
Axonal reaction: It occurs following transection or other severe injury of the axon and is characterized by histologic and ultrastructural changes in the cytoplasms of the neuron (perikaryon). Following axonal injury, the perikaryon swells. Ultrastructurally, the ribosomes of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) are lost. This degranulation of the RER, which in the neurons is called Nissl substance, is visible by light microscopy as a loss of basophilia and is called chromatolysis. Formation of neuronal inclusions: Neuronal inclusions can be intracytoplasmic or intranuclear. Typical examples include lipofuscin (i.e., the cytoplasmic brown “wear and tear” pigment of aging) and viral inclusions (cytoplasmic inclusions, e.g., the Negri bodies in rabies; nuclear inclusions such as those seen in herpes encephalitis and known as Cowdry type A bodies; or nuclear and cytoplasmic inclusions such as in cytomegalovirus infection).
Formation of neuronal inclusions: Neuronal inclusions can be intracytoplasmic or intranuclear. Typical examples include lipofuscin (i.e., the cytoplasmic brown “wear and tear” pigment of aging) and viral inclusions (cytoplasmic inclusions, e.g., the Negri bodies in rabies; nuclear inclusions such as those seen in herpes encephalitis and known as Cowdry type A bodies; or nuclear and cytoplasmic inclusions such as in cytomegalovirus infection). Aggregation of abnormal proteins: Cytoplasmic bodies are found in neurons in several neurodegenerative diseases, such as the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer disease or the formation of cytoplasmic Lewy bodies made out of α-synuclein in Parkinson disease.
Aggregation of abnormal proteins: Cytoplasmic bodies are found in neurons in several neurodegenerative diseases, such as the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer disease or the formation of cytoplasmic Lewy bodies made out of α-synuclein in Parkinson disease.5 What are the common forms of cerebral edema?
Three forms of cerebral edema are recognized: vasogenic, cytotoxic, and interstitial.
 Vasogenic edema: It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in between the neurons and glial cells and most prominently in the Virchow–Robin spaces around the blood vessels. It develops as a consequence of blood–brain barrier dysfunction. Fluid escapes from the vascular space into the interstitial space of the parenchyma across the cytoplasm of vascular endothelial cells or between these cells through the disrupted tight junctions. It may be localized (e.g., around a tumor or an abscess) or generalized (e.g., in encephalitis or following head trauma).
Vasogenic edema: It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in between the neurons and glial cells and most prominently in the Virchow–Robin spaces around the blood vessels. It develops as a consequence of blood–brain barrier dysfunction. Fluid escapes from the vascular space into the interstitial space of the parenchyma across the cytoplasm of vascular endothelial cells or between these cells through the disrupted tight junctions. It may be localized (e.g., around a tumor or an abscess) or generalized (e.g., in encephalitis or following head trauma). Cytotoxic edema: In this form of edema, the fluid accumulates inside the cells. It is most frequently caused by ischemia, hypoxia, or both, which lead to hydropic swelling of neurons and glial cells.
Cytotoxic edema: In this form of edema, the fluid accumulates inside the cells. It is most frequently caused by ischemia, hypoxia, or both, which lead to hydropic swelling of neurons and glial cells. Interstitial edema: It is the result of increased intracerebral influx of CSF through the ependymal lining. Fluid from the ventricles enters into the periventricular white matter, typically under conditions associated with an increased intraventricular CSF pressure. This form of edema is typically a complication of hydrocephalus.
Interstitial edema: It is the result of increased intracerebral influx of CSF through the ependymal lining. Fluid from the ventricles enters into the periventricular white matter, typically under conditions associated with an increased intraventricular CSF pressure. This form of edema is typically a complication of hydrocephalus.6 Describe the gross appearance of the brain with generalized vasogenic edema
Typical features seen at autopsy include:
 On sectioning of the unfixed brain at autopsy, the brain is heavier than normal and soft, and the fluid seeps from the cut surfaces.
On sectioning of the unfixed brain at autopsy, the brain is heavier than normal and soft, and the fluid seeps from the cut surfaces.7 Describe various forms of intracranial cerebral or cerebellar herniations
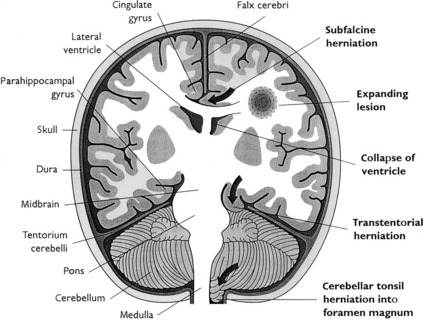
Herniations (Fig. 22-1) occur as a result of increased intracranial volume. Most often, they accompany space-occupying lesions, such as tumors, hematomas, or abscesses, but they may also be caused by trauma. The displacement of parts of the brain is morphologically most evident at three herniation sites:
 Cingulate herniation (subfalcine herniation): It results from a unilateral hemispheric mass lesion (e.g., abscess, hematoma, and tumor) that expands the volume of one hemisphere, dislocates the midline structures (midline shift), and forces the ipsilateral cingulate gyrus to be compressed (“herniate”) underneath the falx cerebri. Focal necrosis and hemorrhage may develop in the herniated tissue together with distant reduction of blood flow (i.e., compression of the anterior cerebral artery).
Cingulate herniation (subfalcine herniation): It results from a unilateral hemispheric mass lesion (e.g., abscess, hematoma, and tumor) that expands the volume of one hemisphere, dislocates the midline structures (midline shift), and forces the ipsilateral cingulate gyrus to be compressed (“herniate”) underneath the falx cerebri. Focal necrosis and hemorrhage may develop in the herniated tissue together with distant reduction of blood flow (i.e., compression of the anterior cerebral artery). Transtentorial herniation (uncinate herniation): It is caused by the expansion of one or both supratentorial tissue compartments (cerebral hemispheres). The uncus gyri hippocampi is displaced on one or both sides and is herniated underneath the free edge of the rigid cerebellar tentorium. Simultaneously, the ipsilateral third cranial nerve is compressed between the tentorium and the expanding temporal lobe, as indicated by the dilatation of the ipsilateral pupil plus abnormal eye movements on the same side.
Transtentorial herniation (uncinate herniation): It is caused by the expansion of one or both supratentorial tissue compartments (cerebral hemispheres). The uncus gyri hippocampi is displaced on one or both sides and is herniated underneath the free edge of the rigid cerebellar tentorium. Simultaneously, the ipsilateral third cranial nerve is compressed between the tentorium and the expanding temporal lobe, as indicated by the dilatation of the ipsilateral pupil plus abnormal eye movements on the same side. Tonsillar herniation: It may develop unilaterally or bilaterally and is a life-threatening condition because the herniated cerebellar tonsils that are forced into the foramen magnum compress the vital respiratory and cardiac centers within the medulla oblongata. Compression of vital centers may cause cardiac or respiratory paralysis (or both).
Tonsillar herniation: It may develop unilaterally or bilaterally and is a life-threatening condition because the herniated cerebellar tonsils that are forced into the foramen magnum compress the vital respiratory and cardiac centers within the medulla oblongata. Compression of vital centers may cause cardiac or respiratory paralysis (or both).DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS
8 Define dysraphic malformations and list the most common forms of this malformation
 Cranial dysraphism: It is associated with incomplete formation of the skull and occurs most often as anencephaly or encephalocele. This severe cerebral malformation is usually incompatible with life.
Cranial dysraphism: It is associated with incomplete formation of the skull and occurs most often as anencephaly or encephalocele. This severe cerebral malformation is usually incompatible with life. Spinal dysraphism: This group of developmental disorders includes spina bifida occulta, meningocele, meningomyelocele, and rachischisis, all of which are characterized by variably severe defective closure (most commonly) of the lumbosacral segment of the neural tube, vertebral arches, and, in the most severe cases, the skin. Severe forms of spinal dysraphism are not compatible with life. Spina bifida occulta, however, is not life threatening and is typically accompanied only by neurologic defects affecting the lower extremities.
Spinal dysraphism: This group of developmental disorders includes spina bifida occulta, meningocele, meningomyelocele, and rachischisis, all of which are characterized by variably severe defective closure (most commonly) of the lumbosacral segment of the neural tube, vertebral arches, and, in the most severe cases, the skin. Severe forms of spinal dysraphism are not compatible with life. Spina bifida occulta, however, is not life threatening and is typically accompanied only by neurologic defects affecting the lower extremities.9 List the most frequent causes of congenital CNS malformations
The cause of most congenital CNS malformations is unknown. The following are among the known causes:
 Fetal intrauterine infections such as those causing the TORCH complex, which includes toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus (CMV), herpes virus, and others such as syphilis, listeriosis, leptospirosis, and viral infection with varicella-zoster virus, Epstein–Barr and so on, etc.; human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) infection during fetal life may also cause CNS lesions.
Fetal intrauterine infections such as those causing the TORCH complex, which includes toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus (CMV), herpes virus, and others such as syphilis, listeriosis, leptospirosis, and viral infection with varicella-zoster virus, Epstein–Barr and so on, etc.; human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) infection during fetal life may also cause CNS lesions.PHYSICAL INJURY
10 What are the main forms of spinal cord or brain injury caused by physical forces?
Skull fractures are often accompanied by parenchymal injuries, which include:
 Contusions (“bruising”): This type of injury results from rapid deceleration or acceleration of the skull and the brain. Typically it involves a coup lesion at the site of the impact of force or a contrecoup contusion, diametrically opposite to it.
Contusions (“bruising”): This type of injury results from rapid deceleration or acceleration of the skull and the brain. Typically it involves a coup lesion at the site of the impact of force or a contrecoup contusion, diametrically opposite to it. Lacerations (tearing of tissue): It is a severe form of brain injury typically seen in vehicular accidents. It is associated with bleeding and high mortality.
Lacerations (tearing of tissue): It is a severe form of brain injury typically seen in vehicular accidents. It is associated with bleeding and high mortality. Diffuse axonal injury: It is usually found in the parasagittal or deep centroaxial white matter. Such injury results from the action of shearing forces in laminar planes within the brain and is frequently accompanied by focal hemorrhages.
Diffuse axonal injury: It is usually found in the parasagittal or deep centroaxial white matter. Such injury results from the action of shearing forces in laminar planes within the brain and is frequently accompanied by focal hemorrhages.11 Describe the most common spinal cord injuries
 Hyperextension injury: It typically occurs in the cervical spine and is caused by sudden posterior displacement of the head that causes rupture of the anterior spinal ligament. The so-called posterior angulation of the cervical vertebrae is accompanied by contusion of the posterior segment of the cervical spinal cord.
Hyperextension injury: It typically occurs in the cervical spine and is caused by sudden posterior displacement of the head that causes rupture of the anterior spinal ligament. The so-called posterior angulation of the cervical vertebrae is accompanied by contusion of the posterior segment of the cervical spinal cord. Hyperflexion injury: It also affects the cervical spine and results from trauma that leads to a compression of one of the cervical vertebrae. Such a “teardrop” fracture of the vertebral body is usually caused by an impact force that rapidly drives the head down and forward. This is accompanied by anterior angulation and consecutive anterior contusion of the cervical spinal cord.
Hyperflexion injury: It also affects the cervical spine and results from trauma that leads to a compression of one of the cervical vertebrae. Such a “teardrop” fracture of the vertebral body is usually caused by an impact force that rapidly drives the head down and forward. This is accompanied by anterior angulation and consecutive anterior contusion of the cervical spinal cord.VASCULAR DISORDERS
15 List the most common aneurysms found in the CNS
 Berry aneurysms: These small saccular aneurysms are typically found in and around the circle of Willis at the base of the brain. They develop at the site of arterial branching corresponding to the congenital weakest part of the vessels. The rupture of these aneurysms leads to a usually fatal subarachnoid and/or intraparenchymal/intraventricular hemorrhage.
Berry aneurysms: These small saccular aneurysms are typically found in and around the circle of Willis at the base of the brain. They develop at the site of arterial branching corresponding to the congenital weakest part of the vessels. The rupture of these aneurysms leads to a usually fatal subarachnoid and/or intraparenchymal/intraventricular hemorrhage. Atherosclerotic aneurysms: These aneurysms may involve the extraparenchymal or intracerebral arteries. Most often, they are asymptomatic and rarely rupture.
Atherosclerotic aneurysms: These aneurysms may involve the extraparenchymal or intracerebral arteries. Most often, they are asymptomatic and rarely rupture. Hypertensive microaneurysms: Long-standing hypertension leads to deposition of lipid–hyaline substances within the wall of small branches of penetrating arteries and arterioles. These deposits weaken the vessel wall and cause microscopic Charcot–Bouchard aneurysms.
Hypertensive microaneurysms: Long-standing hypertension leads to deposition of lipid–hyaline substances within the wall of small branches of penetrating arteries and arterioles. These deposits weaken the vessel wall and cause microscopic Charcot–Bouchard aneurysms.17 List the most important causes of nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage (i.e., hemorrhagic strokes)
 Hypertension: Chronic, severe (usually uncontrolled), systemic hypertension is the most common cause of hemorrhagic stroke. Hypertension accelerates arteriosclerosis of the larger arteries and also causes lipohyalinosis of the smaller branches promoting the development of rupture-prone Charcot–Bouchard aneurysms. Hypertensive hemorrhages occur most often within the basal ganglia and less commonly in the cerebellum or the medulla oblongata.
Hypertension: Chronic, severe (usually uncontrolled), systemic hypertension is the most common cause of hemorrhagic stroke. Hypertension accelerates arteriosclerosis of the larger arteries and also causes lipohyalinosis of the smaller branches promoting the development of rupture-prone Charcot–Bouchard aneurysms. Hypertensive hemorrhages occur most often within the basal ganglia and less commonly in the cerebellum or the medulla oblongata. Coagulation abnormalities: Most often, this kind of hemorrhage occurs in terminal stages of leukemia and severe thrombocytopenia.
Coagulation abnormalities: Most often, this kind of hemorrhage occurs in terminal stages of leukemia and severe thrombocytopenia. Rupture of berry aneurysms: Because the blood exits the ruptured arteries under pressure, it may penetrate into the cerebral parenchyma and even into the ventricles. Thus the blood may be found not only in the subarachnoid space but also inside the brain (mixed bleeding: subarachnoidal plus parenchymal/intraventricular).
Rupture of berry aneurysms: Because the blood exits the ruptured arteries under pressure, it may penetrate into the cerebral parenchyma and even into the ventricles. Thus the blood may be found not only in the subarachnoid space but also inside the brain (mixed bleeding: subarachnoidal plus parenchymal/intraventricular).19 What are the pathologic consequences of global cerebral ischemia?
Generalized reduction of available oxygen that affects the whole CNS may cause:
 Focal neuronal death: Typically it first affects the most vulnerable neurons (e.g., hippocampus and Purkinje cells).
Focal neuronal death: Typically it first affects the most vulnerable neurons (e.g., hippocampus and Purkinje cells). Watershed infarcts: Typically these occur in hypotensive condition (e.g., cardiogenic shock or massive bleeding) and affect the border zones between the supply area of two major arteries (e.g., area supplied by anterior and middle cerebral artery).
Watershed infarcts: Typically these occur in hypotensive condition (e.g., cardiogenic shock or massive bleeding) and affect the border zones between the supply area of two major arteries (e.g., area supplied by anterior and middle cerebral artery).INFECTIONS
21 What are the most common routes of entry of infectious agents into the intracranial space?
 Vascular spread: Most infectious agents reach the brain and the meninges through the arterial bloodstream. Venous blood may serve as a carrier of infectious agents from the infected periocular and perinasal tissues.
Vascular spread: Most infectious agents reach the brain and the meninges through the arterial bloodstream. Venous blood may serve as a carrier of infectious agents from the infected periocular and perinasal tissues. Direct extension from adjacent structures: Such infection may spread from the infected middle ear or sinuses. Herpes virus residing in the trigeminal ganglion of latently infected people can also spread into the brain.
Direct extension from adjacent structures: Such infection may spread from the infected middle ear or sinuses. Herpes virus residing in the trigeminal ganglion of latently infected people can also spread into the brain. Ascending neural route: Some viruses, such as rabies, ascend into the brain along the axons of peripheral nerves.
Ascending neural route: Some viruses, such as rabies, ascend into the brain along the axons of peripheral nerves.22 What are the most important infectious diseases of the CNS ?
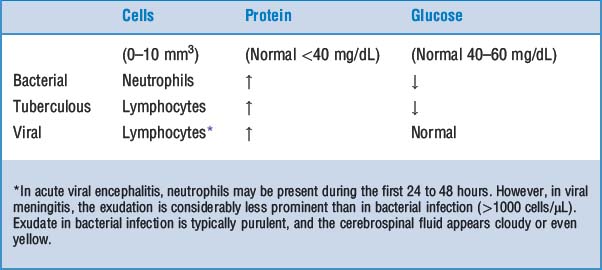
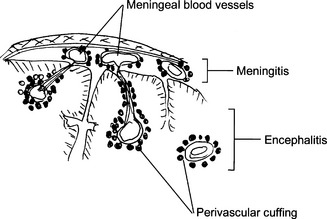
 Meningitis: Infection may be limited to the subarachnoid space (leptomeningitis) or may spread into the brain (meningoencephalitis). Such infection may be classified as acute or chronic. According to the appearance of the cerebrospinal fluid one can classify meningitis as purulent (bacterial) or serous (viral).
Meningitis: Infection may be limited to the subarachnoid space (leptomeningitis) or may spread into the brain (meningoencephalitis). Such infection may be classified as acute or chronic. According to the appearance of the cerebrospinal fluid one can classify meningitis as purulent (bacterial) or serous (viral). Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain is most often caused by viruses. It may be diffuse (i.e., involve the entire brain) or localized to a part of the brain. It may be combined with meningitis (meningoencephalitis).
Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain is most often caused by viruses. It may be diffuse (i.e., involve the entire brain) or localized to a part of the brain. It may be combined with meningitis (meningoencephalitis).24 Describe the gross and microscopic findings in acute bacterial meningitis
 The subarachnoid space is filled with a purulent exudate. The pus is most obvious in the sulci of the convexity and the subarachnoid cisterns at the base of the brain.
The subarachnoid space is filled with a purulent exudate. The pus is most obvious in the sulci of the convexity and the subarachnoid cisterns at the base of the brain.25 List the most important causes of chronic meningitis
 Fungal diseases, especially in immunosuppressed people suffering from acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)
Fungal diseases, especially in immunosuppressed people suffering from acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)28 What is tabes dorsalis?
Tabes dorsalis (Fig. 22-2) is a manifestation of tertiary syphilis involving the lumbar spinal cord. Syphilitic meningitis leads to fibrosis, compressing the posterior nerve roots. In normal circumstances, these afferent nerves, originating from the spinal ganglia, form the posterior columns in the spinal cord, and transmit proprioceptive and sensory impulses. Wallerian degeneration that results from the injury of axons entering the spinal cord results in posterior columns. Clinically, these patients experience loss of vibration and proprioception, which affects their gait. Joint degeneration resulting in deformities (Charcot joints) is commonly found.
29 What are the typical clinical features of acute and chronic meningitis?
 Brudzinski sign (upon flexion of the neck, there is spontaneous similar movement of the hips and knees)
Brudzinski sign (upon flexion of the neck, there is spontaneous similar movement of the hips and knees)31 List key facts about the pathogenesis and pathology of cerebral abscesses
 Localized suppuration of the brain is caused by pyogenic bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae or Staphylococcus aureus) presenting clinically as a destructive, space-occupying lesion.
Localized suppuration of the brain is caused by pyogenic bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae or Staphylococcus aureus) presenting clinically as a destructive, space-occupying lesion. It may be solitary (developing from local foci of infection) or multiple (in sepsis and septic embolism from endocarditis). It is also a complication of suppurative meningitis.
It may be solitary (developing from local foci of infection) or multiple (in sepsis and septic embolism from endocarditis). It is also a complication of suppurative meningitis. Solitary abscesses may evolve from suppurative infection of nasal sinuses (frontal lobe), the middle ear, and mastoid bone (temporal lobe or cerebellum).
Solitary abscesses may evolve from suppurative infection of nasal sinuses (frontal lobe), the middle ear, and mastoid bone (temporal lobe or cerebellum).32 List key facts about the clinical presentation of cerebral abscess
 General signs and symptoms of infection and increased intracranial pressure (e.g., somnolence and papilledema). Progressive intracranial hypertension may cause hemiplegia, seizures, and even coma.
General signs and symptoms of infection and increased intracranial pressure (e.g., somnolence and papilledema). Progressive intracranial hypertension may cause hemiplegia, seizures, and even coma. CSF finding is nonspecific and nondiagnostic in the majority of cases (10% bacterial culture positive).
CSF finding is nonspecific and nondiagnostic in the majority of cases (10% bacterial culture positive).Key Points: Infections and Immunologic Diseases
33 List key facts about viral encephalitis
 It may be diffuse or preferentially localized to specific areas (e.g., poliomyelitis affects the anterior horns of the spinal cord, and herpes simplex virus affects the temporal lobe).
It may be diffuse or preferentially localized to specific areas (e.g., poliomyelitis affects the anterior horns of the spinal cord, and herpes simplex virus affects the temporal lobe). Some infections occur in previously healthy people (e.g., epidemic arthropod-borne encephalitis, rabies, and poliomyelitis), but many are found more often or exclusively in immunosuppressed people (e.g., CMV encephalitis).
Some infections occur in previously healthy people (e.g., epidemic arthropod-borne encephalitis, rabies, and poliomyelitis), but many are found more often or exclusively in immunosuppressed people (e.g., CMV encephalitis).34 What are the microscopic findings in viral infection?
 Neural injury followed by phagocytosis of damaged and killed cells by microglia cells and macrophages (neuronophagia and microglial nodules)
Neural injury followed by phagocytosis of damaged and killed cells by microglia cells and macrophages (neuronophagia and microglial nodules)35 List viral infections associated with cellular inclusions visible by light microscopy
 There is CMV enlargement of cells, which contain typical bluish “owl-eyed” intranuclear inclusions. The cytoplasm also contains virions and appears bluish.
There is CMV enlargement of cells, which contain typical bluish “owl-eyed” intranuclear inclusions. The cytoplasm also contains virions and appears bluish. Herpes simplex virus is associated with “smudgy” or more distinct Cowdry type A nuclear inclusions that are surrounded by an empty delimiting space. Herpetic inclusions are found in neurons, glia cells, and endothelial cells.
Herpes simplex virus is associated with “smudgy” or more distinct Cowdry type A nuclear inclusions that are surrounded by an empty delimiting space. Herpetic inclusions are found in neurons, glia cells, and endothelial cells. Rabies infection is accompanied by the formation of cytoplasmic inclusions (Negri bodies) in neurons.
Rabies infection is accompanied by the formation of cytoplasmic inclusions (Negri bodies) in neurons. Measles virus causing subacute sclerosing panencephalitis forms intranuclear inclusions in neurons. The inclusions have a clear halo around them.
Measles virus causing subacute sclerosing panencephalitis forms intranuclear inclusions in neurons. The inclusions have a clear halo around them.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree