Syphilitic Lymphadenitis
Francisco Vega, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Syphilis: Chronic systemic infection caused by T. pallidum (Gram-negative spirochete)
Clinical Issues
Course of disease divided into 3 stages: Primary, secondary, and tertiary
Penicillin G is drug of choice for all stages of syphilis
Microscopic Pathology
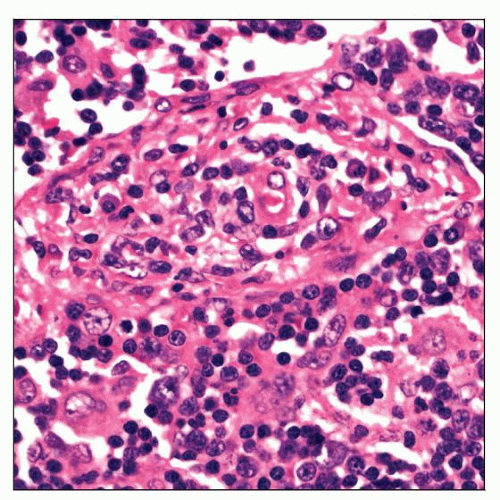
Proliferation of blood vessels with endothelial swelling, phlebitis, and endarteritis
Follicular hyperplasia
Spirochetes most frequently found in walls of blood vessels (silver stains)
Capsular and pericapsular inflammation
Diffuse plasma cell infiltration; sheets of plasma cells in medulla
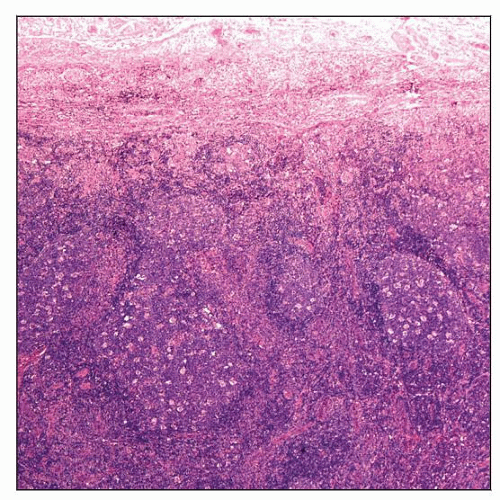 Inguinal lymph node involved by syphilis. There is pericapsular inflammation and fibrosis associated with marked follicular hyperplasia. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Luetic lymphadenitis, lues
Definitions
Lymphadenitis in course of syphilis
Syphilis: Chronic systemic infection caused by Treponema pallidum (T. pallidum)
Infection usually sexually transmitted, characterized by periods of active disease and latency
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
T. pallidum is gram-negative spirochete
At least 4 known subspecies
T. pallidum pallidum: Causes syphilis
T. pallidum pertenue: Causes yaws
T. pallidum carateum: Causes pinta
T. pallidum endemicum: Causes endemic syphilis or bejel
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree