Superficial Acral Fibromyxoma
Thomas Mentzel, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign fibroblastic neoplasm with predilection for hands and feet, especially nail bed region
Clinical Issues
Solitary mass involving toe, finger, or palm of hand
Significant number of cases involve nail region
Dermal subcutaneous neoplasm
Incidence: Rare
Age: Mainly adults
Treatment: Complete excision
Prognosis
Biologically benign neoplasm
Local recurrences rare
Macroscopic Features
Superficial lesions
Microscopic Pathology
Dermal neoplasms with involvement of deeper structures in some cases
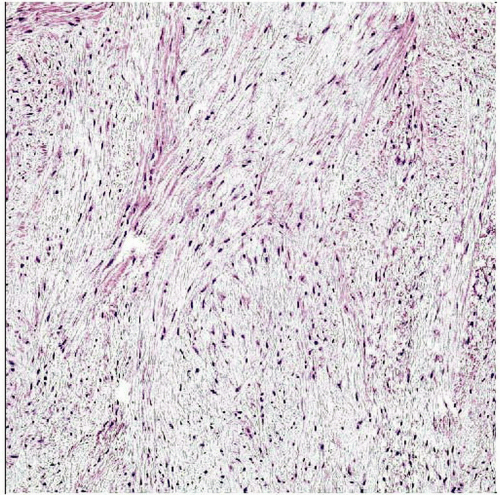
Loose storiform &/or fascicular growth pattern
Rare infiltrative growth
Spindled and stellate fibroblast-like cells
Rare multinucleated cells
Moderately cellular
Minimal cytologic atypia
Rare mitoses
Scattered inflammatory cells (mast cells)
CD34 and EMA often positive
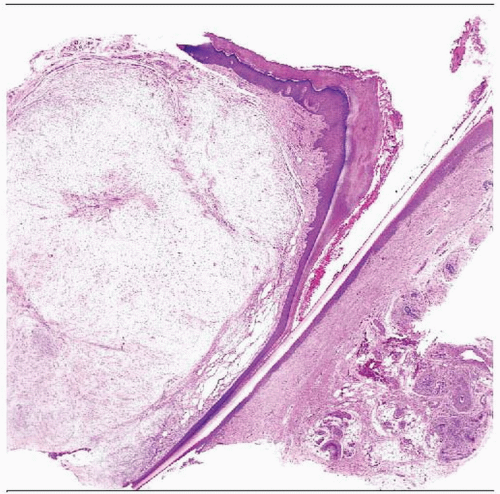 Hematoxylin & eosin shows a low-power view of a hypocellular dermal neoplasm in the nail bed region. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Superficial acral fibromyxoma (SAF)
Definitions
Benign fibroblastic neoplasm with predilection for hands and feet, especially nail bed region
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Previous trauma reported only rarely
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare
Age
Mainly adults
Gender
More frequent in males
Presentation
Solitary mass
Usually painless lesions
Longstanding lesions
Dermal subcutaneous neoplasms
Arise usually on toe, finger, or palm of hand
Majority of cases involve nail bed region
Rare on heel
Natural History
Local recurrences sometimes seen
No reported case of metastasis or progression
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete excision
Prognosis
Biologically benign neoplasm
Recurrences have been reported in up to 22%
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Superficial lesions
Lesions may appear dome-shaped, polypoid, or verrucoid
Size
Usually < 5 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Moderately cellular
Nodular, lobular, or infiltrative growth
Dermal neoplasms with involvement of deeper structures in some cases
Myxoid, myxocollagenous, or predominantly collagenous stroma
Numerous blood vessels
Rarely contains lipomatous component
May contain inflammatory cells (mast cells)
Minimal cytologic atypia
Rare mitoses
Increased cellularity and atypia
Have no prognostic influence
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Storiform
Fascicular
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree