Chapter 50 • Low risk: Less than 1 drink/day for women, 2 drinks/day for men; or 7 drinks/wk for women, 14 drinks/wk for men; or 3 drinks for women and 4 drinks for men on any occasion; 0 CAGE score, no dysfunction related to drinking and not using medications that interact adversely with alcohol. • Heavy and/or risky drinking: More than 7 drinks/wk, or 3 drinks/occasion for women; for men, 14 drinks/wk or 4 drinks/occasion; score greater than 1 on CAGE, evidence of drinking-related dysfunction, or use of alcohol and medications that might adversely interact with alcohol. • Abuse: More than one of the following recurring situations: drinking resulting in failure to fulfill major obligations, drinking in hazardous situations, alcohol-related legal problems, continued drinking despite persistent problems caused or worsened by alcohol. • Dependence: The “3 C’s” can identify dependence: compulsive use, continuing use despite negative consequences, and lack of control. DSM-IV criteria require three or more of the following features: tolerance, withdrawal, drinking more than intended, persistent desire to drink or unsuccessful efforts to cut down or control drinking, increased time spent in activities related to alcohol, giving up important activities because of drinking, or drinking despite knowledge of problems caused or worsened by alcohol. TABLE 50-1 Screening and Assessment Tools for Alcohol Use Disorders Scoring:
Substance Abuse
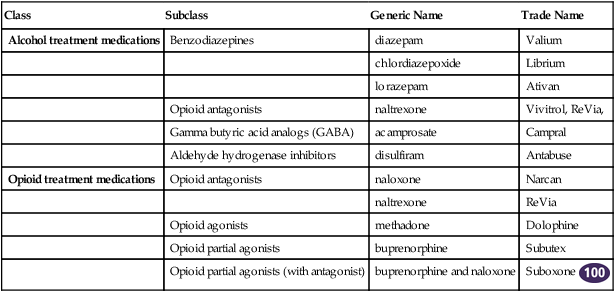
Class
Subclass
Generic Name
Trade Name
Alcohol treatment medications
Benzodiazepines
diazepam
Valium
chlordiazepoxide
Librium
lorazepam
Ativan
Opioid antagonists
naltrexone
Vivitrol, ReVia,
Gamma butyric acid analogs (GABA)
acamprosate
Campral
Aldehyde hydrogenase inhibitors
disulfiram
Antabuse
Opioid treatment medications
Opioid antagonists
naloxone
Narcan
naltrexone
ReVia
Opioid agonists
methadone
Dolophine
Opioid partial agonists
buprenorphine
Subutex
Opioid partial agonists (with antagonist)
buprenorphine and naloxone
Suboxone ![]()
![]() Top 100 drug. Also consider using phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and topiramate, which are discussed in Chapter 45.
Top 100 drug. Also consider using phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and topiramate, which are discussed in Chapter 45.
Therapeutic Overview
Assessment
Classification Levels for Alcohol Intake
Mechanism of Action and Effects of Alcohol Treatment
Alcohol Assessment Tools
Alcohol Intake Equivalents∗
Interpretation and Comments
∗Quantity-frequency question: Do you sometimes drink alcoholic beverages?
If positive, next screen with the CAGE, RAPS4-QF, or Audit questionnaire.
CAGE questions are as follows:
C = Pt felt need to Cut down on drinking?
A = People Annoyed you by criticizing your drinking?
G = Felt Guilt about drinking?
E = Need an Eye-opener in the morning?
Positive if respond positive to 2 of these questions
To distinguish those with alcoholism from those without; does not differentiate dependence from abuse
RAPS4-QF
R = Do you use alcohol/drugs at Regular times?
A = Use alcohol/drugs Alone, or with friends or family?
P = Problems due to alcohol/drugs?
S = Has alcohol/drug ever made you feel Sick?
4 = Have you had more than 4/5 drinks in one setting? More often than once a month?
Scoring:
Positive if answers yes to questions; greater sensitivity and specificity over CAGE for all gender, ethnic, and service utilization groups in ERs
Eliminates many cultural terms that do not translate to other ethnic groups, such as “eye-opener”; concept of guilt, social surroundings addressed
AUDIT: 10-question bilingual written screen that can be filled out by patient
Scoring:
Positive: 8 for men up to 60;
4 for women, adolescents, or men >60
Variable cutoff scores distinguish between harmful use, hazardous use, and dependence ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Substance Abuse
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
