Spermatocytic Seminoma
Steven S. Shen, MD, PhD
Mahul B. Amin, MD
Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Germ cell tumor composed of 3 cell types of variable sizes ranging from 6-100 µm
Clinical Issues
Extremely rare
Age range: 25-87 years
Macroscopic Features
Well-circumscribed, soft, friable, tan-gray mass with mucoid or gelatinous, bulging cut surface
Microscopic Pathology
Diffuse or solid sheet pattern with scant fibrous or edematous stroma is most common finding
Rare growth patterns include pseudoglandular, microcystic, trabeculae, nests, or single cells
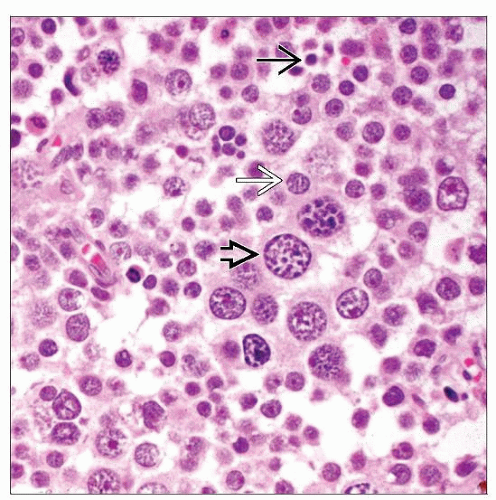
Polymorphous cell population is hallmark of spermatocytic seminoma
Small lymphocyte-like cells: 6-8 µm; densely hyperchromatic nuclei and scant amount of eosinophilic to basophilic cytoplasm
Intermediate cells: 15-20 µm; most common cell type; round nuclei, finely granular chromatin, moderate amount of cytoplasm
Giant cells: 50-100 µm; least common cell type; distinctive filamentous or “spireme-type” chromatin
Ancillary Tests
Negative for most germ cell-associated markers (Oct3/4, Podoplanin(D2-40), PLAP, α-fetoprotein, glypican-3, HCG, and CD30[BerH2])
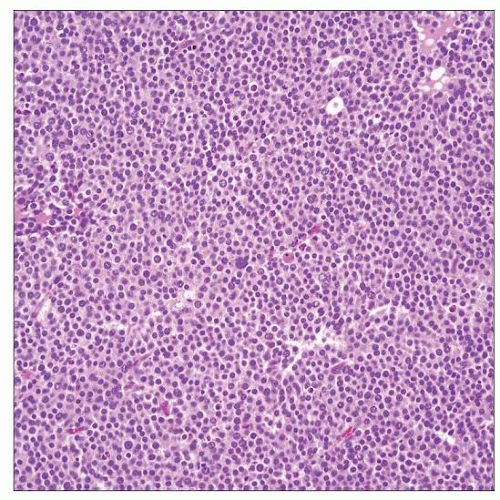 Low-power view of diffuse growth pattern of spermatocytic seminoma reveals no fibrovascular septae and no lymphocytic or granulomatous inflammation, typical features of classic seminoma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Spermatocytic seminoma (SS)
Definitions
Germ cell tumor recapitulating spermatogenic sequence composed of 3 cell types of variable sizes, ranging from 6-100 µm
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Cytogenetic Changes
Diploid or near hypodiploid, different from that of seminoma
Chromosomal numerical changes (most commonly gain of chromosome 9)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Extremely rare; only 2 major series reported
Bilaterality (up to 9%) is more common than in seminoma
Occurs only in testis; no ovarian counterpart, no extragonadal primary tumors
No race predilection as in other germ cell tumors
Not associated with cryptorchidism
Age
Range: 25-87 years (average: 53.6 years)
Rare under 30 years
Presentation
Painless testicular swelling and mass
Serum tumor markers are not elevated
Treatment
Radical inguinal orchiectomy alone is curative
Postoperative prophylactic radiation or chemotherapy do not offer additional benefit and not routinely recommended
Prognosis
Excellent prognosis with rare malignant behavior (less than 1%)
Sarcomatoid transformation is rare, but when present is associated with distant metastasis and death
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well-circumscribed, soft mass with mucoid or gelatinous bulging cut surface
Lobulation, cystic change, and focal hemorrhage or necrosis may be seen
Size
Range: 2-20 cm (average: 7.0 cm)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree